Difference between revisions of "Tephrosia spicata"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Common name: Spiked hoarypea | Common name: Spiked hoarypea | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Tephrosia spicata'' var. ''semitonsa'' Fernald | + | Synonyms: ''Tephrosia spicata'' var. ''semitonsa'' Fernald.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Variations: ''Cracca spicata'' (Walter) Kuntze.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | "Perennial herbs and shrubs with either monopodial or sympodial branching. Leaves odd-pinnate; leaflets 7-29 or rarely 1-41, entire, glabrous or pubescent above and always pubescent beneath, usually with prominent, parallel, secondary veins, estipellate, inflorescences terminal, axillary or apparently opposite a leaf, more or less racemose, with 2-10, papilionaceous, pedicellate flowers at each node with the cluster subtended by a bract and each pedicels subtended, 5-lobed, the lowers the long longest; petals clawed; stamens monadelphous or diadelphous. Legume sessile, linear, straight or slightly curved, usually compressed, nonseptate, dehiscing into 2 separate valves." <ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 626. Print.</ref> | + | "Perennial herbs and shrubs with either monopodial or sympodial branching. Leaves odd-pinnate; leaflets 7-29 or rarely 1-41, entire, glabrous or pubescent above and always pubescent beneath, usually with prominent, parallel, secondary veins, estipellate, inflorescences terminal, axillary or apparently opposite a leaf, more or less racemose, with 2-10, papilionaceous, pedicellate flowers at each node with the cluster subtended by a bract and each pedicels subtended, 5-lobed, the lowers the long longest; petals clawed; stamens monadelphous or diadelphous. Legume sessile, linear, straight or slightly curved, usually compressed, nonseptate, dehiscing into 2 separate valves."<ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 626. Print.</ref> |
| − | "Perennial herb from a cylindric taproot; stems decumbent to erect, mostly 3-6 dm long, densely pilose or occasionally sparsely appressed pubescent. Leaves 4-12 cm long; leaflets 9-17, oblong-obovate to obovate or elliptic, 1-2.7 (3.7) cm long, 6-14 mm wide, glabrous to finely pilose above, somewhat appressed to spreading short-pubescent to pilose below. Principal inflorescences appearing opposite the leaf or terminal, 4-60 cm long, usually longer than nearest leaf, erect or upwardly curving with a terete or angled peduncle and rachis with persistent, lanceolate to linear bracts; pedicels 1-8 mm long. Calyx 6-7 mm long, sparsely to more typically densely pilose or villous; petals at first white, turning pink then carmine (drying purplish), 1.2-1.7 cm long; stamens diadelphous. Legume 3-5 cm long, 4-6 mm broad, sparsely to moderately pubescent, trichomes more than 0.6 mm long." <ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> | + | "Perennial herb from a cylindric taproot; stems decumbent to erect, mostly 3-6 dm long, densely pilose or occasionally sparsely appressed pubescent. Leaves 4-12 cm long; leaflets 9-17, oblong-obovate to obovate or elliptic, 1-2.7 (3.7) cm long, 6-14 mm wide, glabrous to finely pilose above, somewhat appressed to spreading short-pubescent to pilose below. Principal inflorescences appearing opposite the leaf or terminal, 4-60 cm long, usually longer than nearest leaf, erect or upwardly curving with a terete or angled peduncle and rachis with persistent, lanceolate to linear bracts; pedicels 1-8 mm long. Calyx 6-7 mm long, sparsely to more typically densely pilose or villous; petals at first white, turning pink then carmine (drying purplish), 1.2-1.7 cm long; stamens diadelphous. Legume 3-5 cm long, 4-6 mm broad, sparsely to moderately pubescent, trichomes more than 0.6 mm long."<ref name="Radford et al 1964"/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''Tephrosia spicata'' can be found in coastal hammocks; wiregrass/pine communities; pine savannas; mixed hardwood forests; longleaf pine-turkey oak hills; turkey oak barrens; and longleaf pine scrub oak sand ridges. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: W.P. Adams, Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, C. Ritchie Bell, WM. M. CanbyA.F. Clewell, K. Craddock Burks, H.S. Daoud, ,R.A. Davidson, J.A. Duke, J. Kevin England, R.K. Godfrey, J.B. Hilmon, S.C. Hood, Clarke Hudson, C. Jackson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Mabel Kral, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Richard S. Mitchell, R.A. Norris, Kevin Oakes, R.C. Phillips, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray Jr., H.R. Reed, A.B. Seymour, Cecil Slaughter, R.F. Thorne, Rodie White, Mary Margaret Williams. States and Counties: Alabama: Geneva, Marengo. Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Charlotte, Citrus, Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hernando, Hillsborough, Jackson, Jefferson, Liberty, Leon, Madison, Marion, Pasco, Polk,Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Maryland: Salisbury. Mississippi: Forrest, Jackson, Marion, Newton, Ocean Springs, Pike, Poplarville. North Carolina: Rutherford, Wayne. South Carolina: Marion. Virginia: Greensville. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref | + | ''Tephrosia spicata'' can be found in coastal hammocks; wiregrass/pine communities; pine savannas; mixed hardwood forests; longleaf pine-turkey oak hills; turkey oak barrens; and longleaf pine scrub oak sand ridges.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: W.P. Adams, Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, C. Ritchie Bell, WM. M. CanbyA.F. Clewell, K. Craddock Burks, H.S. Daoud, ,R.A. Davidson, J.A. Duke, J. Kevin England, R.K. Godfrey, J.B. Hilmon, S.C. Hood, Clarke Hudson, C. Jackson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Mabel Kral, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Richard S. Mitchell, R.A. Norris, Kevin Oakes, R.C. Phillips, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray Jr., H.R. Reed, A.B. Seymour, Cecil Slaughter, R.F. Thorne, Rodie White, Mary Margaret Williams. States and Counties: Alabama: Geneva, Marengo. Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Charlotte, Citrus, Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hernando, Hillsborough, Jackson, Jefferson, Liberty, Leon, Madison, Marion, Pasco, Polk,Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Maryland: Salisbury. Mississippi: Forrest, Jackson, Marion, Newton, Ocean Springs, Pike, Poplarville. North Carolina: Rutherford, Wayne. South Carolina: Marion. Virginia: Greensville. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> It has been found in human disturbed areas such as railroad beds, cut over pine flatwoods, and roadsides. Soil types include loamy sand, sandy loam, clay soil, sand, sandy peat, and sandy clay.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: W.P. Adams, Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, C. Ritchie Bell, WM. M. CanbyA.F. Clewell, K. Craddock Burks, H.S. Daoud, ,R.A. Davidson, J.A. Duke, J. Kevin England, R.K. Godfrey, J.B. Hilmon, S.C. Hood, Clarke Hudson, C. Jackson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Mabel Kral, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Richard S. Mitchell, R.A. Norris, Kevin Oakes, R.C. Phillips, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray Jr., H.R. Reed, A.B. Seymour, Cecil Slaughter, R.F. Thorne, Rodie White, Mary Margaret Williams. States and Counties: Alabama: Geneva, Marengo. Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Charlotte, Citrus, Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hernando, Hillsborough, Jackson, Jefferson, Liberty, Leon, Madison, Marion, Pasco, Polk,Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Maryland: Salisbury. Mississippi: Forrest, Jackson, Marion, Newton, Ocean Springs, Pike, Poplarville. North Carolina: Rutherford, Wayne. South Carolina: Marion. Virginia: Greensville. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | ''T. spicata'' decreased its occurrence in response to soil disturbance by agriculture in southwest Georgia.<ref>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref> However, it increased its frequency and biomass in response to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in north Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Phlox floridana, Calamintha dentata, Canna, Sambucus, Aristida stricta, Rhynchospora, Tephrosia floridana'' and ''T. chrysophylla.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Tephrosia spicata'' is an indicator species for the Upper Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 45: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | + | This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.<ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> |
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | + | Populations of ''Tephrosia spicata'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burns,<ref>Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref><ref>Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.</ref><ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> and has been found in recently burned longleaf pine communities.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | |
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc.--> |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:13, 18 July 2022
| Tephrosia spicata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Tephrosia |
| Species: | T. spicata |
| Binomial name | |
| Tephrosia spicata (Walter) Torr. & A. Gray | |
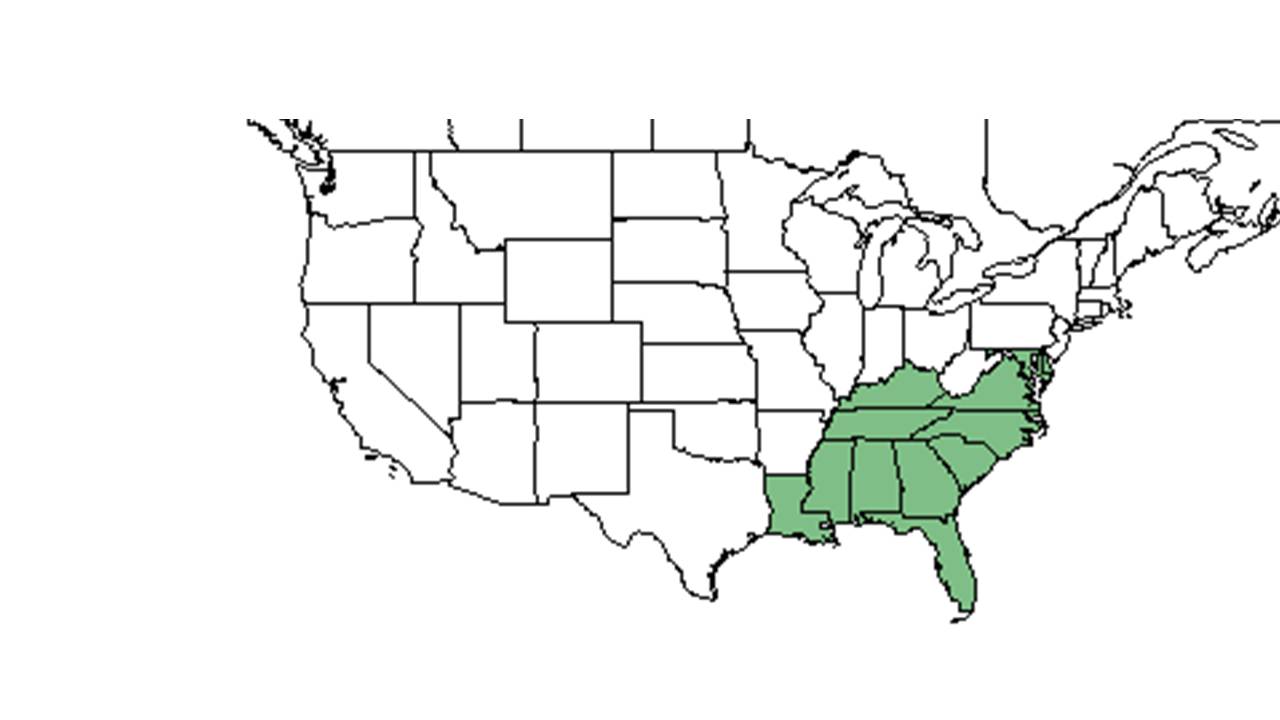
| |
| Natural range of Tephrosia spicata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Spiked hoarypea
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Tephrosia spicata var. semitonsa Fernald.[1]
Variations: Cracca spicata (Walter) Kuntze.[2]
Description
"Perennial herbs and shrubs with either monopodial or sympodial branching. Leaves odd-pinnate; leaflets 7-29 or rarely 1-41, entire, glabrous or pubescent above and always pubescent beneath, usually with prominent, parallel, secondary veins, estipellate, inflorescences terminal, axillary or apparently opposite a leaf, more or less racemose, with 2-10, papilionaceous, pedicellate flowers at each node with the cluster subtended by a bract and each pedicels subtended, 5-lobed, the lowers the long longest; petals clawed; stamens monadelphous or diadelphous. Legume sessile, linear, straight or slightly curved, usually compressed, nonseptate, dehiscing into 2 separate valves."[3]
"Perennial herb from a cylindric taproot; stems decumbent to erect, mostly 3-6 dm long, densely pilose or occasionally sparsely appressed pubescent. Leaves 4-12 cm long; leaflets 9-17, oblong-obovate to obovate or elliptic, 1-2.7 (3.7) cm long, 6-14 mm wide, glabrous to finely pilose above, somewhat appressed to spreading short-pubescent to pilose below. Principal inflorescences appearing opposite the leaf or terminal, 4-60 cm long, usually longer than nearest leaf, erect or upwardly curving with a terete or angled peduncle and rachis with persistent, lanceolate to linear bracts; pedicels 1-8 mm long. Calyx 6-7 mm long, sparsely to more typically densely pilose or villous; petals at first white, turning pink then carmine (drying purplish), 1.2-1.7 cm long; stamens diadelphous. Legume 3-5 cm long, 4-6 mm broad, sparsely to moderately pubescent, trichomes more than 0.6 mm long."[3]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Tephrosia spicata can be found in coastal hammocks; wiregrass/pine communities; pine savannas; mixed hardwood forests; longleaf pine-turkey oak hills; turkey oak barrens; and longleaf pine scrub oak sand ridges.[4] It has been found in human disturbed areas such as railroad beds, cut over pine flatwoods, and roadsides. Soil types include loamy sand, sandy loam, clay soil, sand, sandy peat, and sandy clay.[4]
T. spicata decreased its occurrence in response to soil disturbance by agriculture in southwest Georgia.[5] However, it increased its frequency and biomass in response to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in north Florida flatwoods forests.[6]
Associated species include Phlox floridana, Calamintha dentata, Canna, Sambucus, Aristida stricta, Rhynchospora, Tephrosia floridana and T. chrysophylla.[4]
Tephrosia spicata is an indicator species for the Upper Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[7]
Phenology
T. spicata has been observed flowering April through October with peak inflorescence in June and fruiting May through October.[4][8]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[9]
Fire ecology
Populations of Tephrosia spicata have been known to persist through repeated annual burns,[10][11][12] and has been found in recently burned longleaf pine communities.[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 626. Print.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: W.P. Adams, Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, C. Ritchie Bell, WM. M. CanbyA.F. Clewell, K. Craddock Burks, H.S. Daoud, ,R.A. Davidson, J.A. Duke, J. Kevin England, R.K. Godfrey, J.B. Hilmon, S.C. Hood, Clarke Hudson, C. Jackson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, Mabel Kral, R. Kral, O. Lakela, Richard S. Mitchell, R.A. Norris, Kevin Oakes, R.C. Phillips, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray Jr., H.R. Reed, A.B. Seymour, Cecil Slaughter, R.F. Thorne, Rodie White, Mary Margaret Williams. States and Counties: Alabama: Geneva, Marengo. Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Charlotte, Citrus, Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hernando, Hillsborough, Jackson, Jefferson, Liberty, Leon, Madison, Marion, Pasco, Polk,Wakulla. Georgia: Grady, Thomas. Maryland: Salisbury. Mississippi: Forrest, Jackson, Marion, Newton, Ocean Springs, Pike, Poplarville. North Carolina: Rutherford, Wayne. South Carolina: Marion. Virginia: Greensville. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.