Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum cordifolium"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Common names: Common blue wood aster, Heart-leaved aster | Common names: Common blue wood aster, Heart-leaved aster | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Aster cordifolius'' Linnaeus | + | Synonyms: ''Aster cordifolius'' Linnaeus; ''A. cordifolius'' var. ''polycephalus'' Porter ; ''A. cordifolius'' var. ''racemiflorus'' Fernald.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Variations: ''S. cordifolium'' (Linnaeus) Nesom var. ''polycephalum'' (Porter) Nesom; ''S. cordifolium'' (Linnaeus) Nesom var. ''racemiflorum'' (Fernald) Nesom.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 30: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | + | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | |
| + | |||
| + | ''S. cordifolium'' has been found in alluvial thickets, rich woodlands, meadows, marshes, and wooden ravines.<ref name="PH"> Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: F. S. Fender, John M. Fogg Jr., Bayard H. Long, Francis W. Pennell, A. MacElwee, and Robert L. Schaeffer Jr. States and Counties: Pennsylvania: Delaware, Montgomery, Northampton, Philadelphia, and Tioga.</ref> It is also found in disturbed areas including along roadsides and abandoned dumps.<ref name="PH"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species: ''Carya tomentosa, C. ovata, Quercus velutina, Q. alba, Acer rubrum, Betula lenta, Clethra alnifolia, Viburnum acerifolia, Athyrium angustum, Dryopteris carthusiana, Actaea pachypoda, Eurybia divaricata, Pinus strobus, Acer saccharum, Fraxinus americana, Quercus rubra, Fagus grandifolia, Acer pensylvanicum, Caulophyllum thalictroides, Tiarella cordifolia, Polygonatum biflorum'', and ''Carex pensylvanica''.<ref name="BRU"> Brown University Herbarium accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Sophie Duncan, Andrew Pisaturo, and Timothy J. S. Whitfeld. States and Counties: Rhode Island: Berkshire and Providence.</ref> | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| Line 33: | Line 40: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:22, 15 July 2022
| Symphyotrichum cordifolium | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. cordifolium |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum cordifolium (L.) G.L. Nesom | |
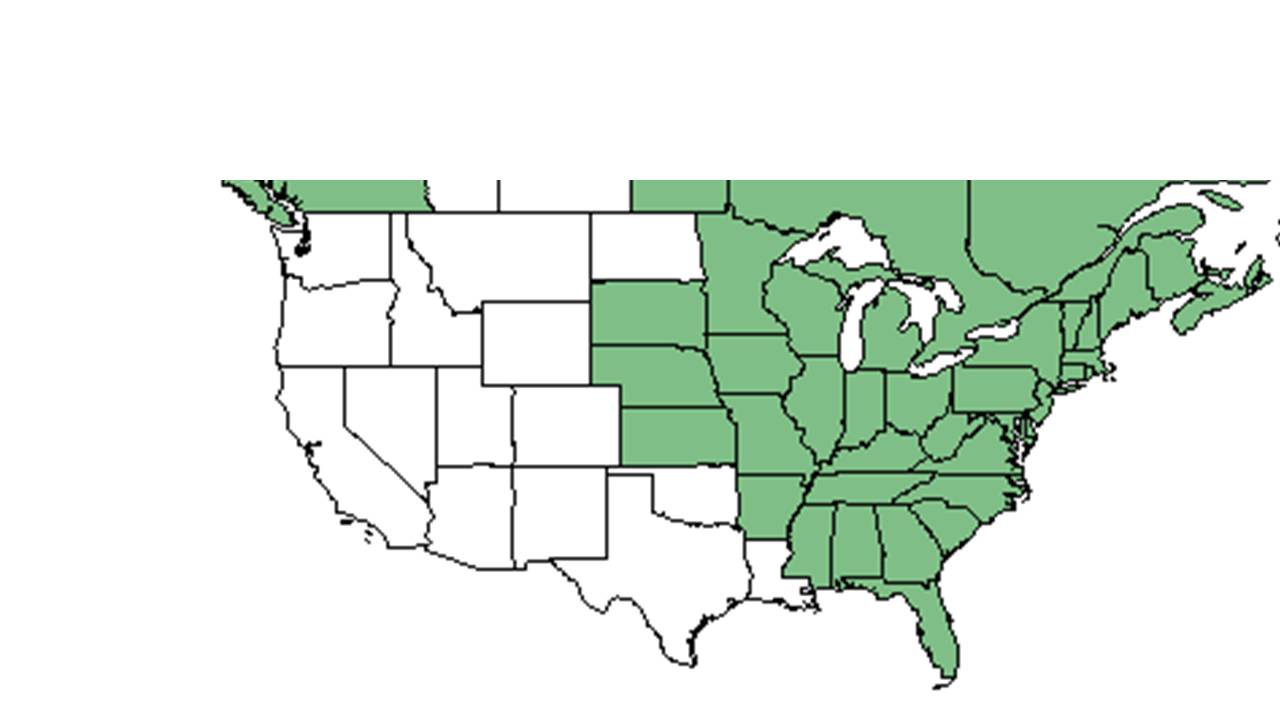
| |
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum cordifolium from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Common blue wood aster, Heart-leaved aster
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Aster cordifolius Linnaeus; A. cordifolius var. polycephalus Porter ; A. cordifolius var. racemiflorus Fernald.[1]
Variations: S. cordifolium (Linnaeus) Nesom var. polycephalum (Porter) Nesom; S. cordifolium (Linnaeus) Nesom var. racemiflorum (Fernald) Nesom.[2]
Description
A description of Symphyotrichum cordifolium is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
S. cordifolium has been found in alluvial thickets, rich woodlands, meadows, marshes, and wooden ravines.[3] It is also found in disturbed areas including along roadsides and abandoned dumps.[3]
Associated species: Carya tomentosa, C. ovata, Quercus velutina, Q. alba, Acer rubrum, Betula lenta, Clethra alnifolia, Viburnum acerifolia, Athyrium angustum, Dryopteris carthusiana, Actaea pachypoda, Eurybia divaricata, Pinus strobus, Acer saccharum, Fraxinus americana, Quercus rubra, Fagus grandifolia, Acer pensylvanicum, Caulophyllum thalictroides, Tiarella cordifolia, Polygonatum biflorum, and Carex pensylvanica.[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: F. S. Fender, John M. Fogg Jr., Bayard H. Long, Francis W. Pennell, A. MacElwee, and Robert L. Schaeffer Jr. States and Counties: Pennsylvania: Delaware, Montgomery, Northampton, Philadelphia, and Tioga.
- ↑ Brown University Herbarium accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Sophie Duncan, Andrew Pisaturo, and Timothy J. S. Whitfeld. States and Counties: Rhode Island: Berkshire and Providence.