Difference between revisions of "Rhus copallinum"
Lsandstrum (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonym: ''Rhus copallina'' L.; '' | + | Synonym: ''Rhus copallina'' L.; ''Rhus leucantha'' Jacquin; ''Rhus obtusifolia'' (Small) Small.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | Varieties: | + | Varieties: ''R. copallinum'' Linnaeus var. ''latifolia'' Engler.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | "Upright shrubs or small trees, not poisonous. Leaves once-pinnately compound. Inflorescence a terminal panicle. Drupes red, ripening in the autumn. Seeds smooth. Flowers produced after the leaves." <ref name=rad> Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 678. Print.</ref> | + | "Upright shrubs or small trees, not poisonous. Leaves once-pinnately compound. Inflorescence a terminal panicle. Drupes red, ripening in the autumn. Seeds smooth. Flowers produced after the leaves."<ref name=rad> Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 678. Print.</ref> |
| − | "Rhizomatous shrub or small tree to 7 m tall; stems densely short-pubescent. Leaflets 9-23 (mostly 9-11), sessile, oblong to elliptic, 3-8 cm long, 1-4 cm wide, acute to acuminate, entire or less frequently crenate to serrate, base cuneate to rarely rounded, glabrous or densely pubescent beneath; rachis winged. Panicle 0.5-3 dm long and usually as broad. Drupe densely short-pubescent, 3-4 mm broad. Seeds 2.5-3 mm long." <ref name=rad/> | + | "Rhizomatous shrub or small tree to 7 m tall; stems densely short-pubescent. Leaflets 9-23 (mostly 9-11), sessile, oblong to elliptic, 3-8 cm long, 1-4 cm wide, acute to acuminate, entire or less frequently crenate to serrate, base cuneate to rarely rounded, glabrous or densely pubescent beneath; rachis winged. Panicle 0.5-3 dm long and usually as broad. Drupe densely short-pubescent, 3-4 mm broad. Seeds 2.5-3 mm long."<ref name=rad/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''R. copallinum'' habitats include old fields, oak-hickory woods, oak scrubs, marsh banks, roadsides, and sand ridges. <ref name="fsu">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: March 2016. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Tom Barnes, Kathy Craddock Burks, G. Fleming, P. Genelle, Robert K. Godfrey, Gary R. Knight. States and Counties: Florida: Florida: Citrus, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, St. Johns, Wakulla.</ref> | + | ''R. copallinum'' habitats include old fields, oak-hickory woods, oak scrubs, marsh banks, roadsides, and sand ridges.<ref name="fsu">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: March 2016. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Tom Barnes, Kathy Craddock Burks, G. Fleming, P. Genelle, Robert K. Godfrey, Gary R. Knight. States and Counties: Florida: Florida: Citrus, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, St. Johns, Wakulla.</ref> |
| − | ''R. copallinum'' | + | |
| + | ''R. copallinum'' has shown regrowth in reestablished longleaf pine woodlands that were disturbed by agriculture in South Carolina coastal plain communities, making it a possible indicator species for post-agricultural woodlands.<ref>Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.</ref> It increased its cover in response to clearcutting and chopping in north Florida flatwoods.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> This species also increased its frequency in response to roller chopping in east Texas hardwood forests.<ref name=stransky>Stransky, J.J., J.C. Huntley, and Wanda J. Risner. (1986). Net Community Production Dynamics in the Herb-Shrub Stratum of a Loblolly Pine-Hardwood Forest: Effects of Clearcutting and Site Preparation. Gen. Tech. Rep. SO-61. New Orleans, LA: U.S. Dept of Agriculture, Forest Service, Southern Forest Experiment Station. 11 p.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It was unaffected by agriculture in South Carolina pine woodlands.<ref>Brudvig, L.A., J.L. Orrock, E.I. Damschen, C.D. Collins, P.G. Hahn, W.B. Mattingly, J.W. Veldman, and J.L. Walker. (2014). Land-Use History and Contemporary Management Inform an Ecological Reference Model for Longleaf Pine Woodland Understory Plant Communities. PLoS ONE 9(1): e86604.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''R. copallinum'' had variable changes in frequency in response to soil disturbance by a KG blade in east Texas. It either showed regrowth or resistance to regrowth in reestablished hardwood forests that were disturbed by this practice.<ref name=stransky/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Rhus copallinum'' is frequent and abundant in the Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands and Upper Panhandle Savannas community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | This species has been observed to flower from July to August.<ref name="missouri">[[http://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=g850]]Missouri Botanical Gardens. Accessed: March 7, 2016</ref><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> | |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates. <ref name="KK"> Kay Kirkman, Jones Ecological Research Center, unpublished data, 2015. </ref> | + | This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates.<ref name="KK"> Kay Kirkman, Jones Ecological Research Center, unpublished data, 2015.</ref> |
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | The rhizomes, flowers, fruits, senescent leaves and leaf litter contain toxins that significantly inhibit both seed germination and seedling growth of climax prairie and weedy species. <ref name="petranka">Petranka, J. W. and J. K. McPherson (1979). "The Role of Rhus Copallina in the Dynamics of the Forest-Prairie Ecotone in North-Central Oklahoma." Ecology 60(5): 956-965.</ref> Seed germination responds positively to heat shock with highest germination rates at 90 C.<ref>Bolin, J. F. 2009. Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species. Castanea, v. 74, no. 2, p. 160-167.</ref> | + | The rhizomes, flowers, fruits, senescent leaves and leaf litter contain toxins that significantly inhibit both seed germination and seedling growth of climax prairie and weedy species.<ref name="petranka">Petranka, J. W. and J. K. McPherson (1979). "The Role of Rhus Copallina in the Dynamics of the Forest-Prairie Ecotone in North-Central Oklahoma." Ecology 60(5): 956-965.</ref> Seed germination responds positively to heat shock with highest germination rates at 90 C.<ref>Bolin, J. F. 2009. Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species. Castanea, v. 74, no. 2, p. 160-167.</ref> |
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | Fire stimulates root and root collar sprouting along with enhancing germination, making this a fire-climax species. Density declines 3 to 4 years following a fire, with fire exclusion reducing density and cover. <ref name="fs"/> Seeds respond positively to heat shock, suggesting that its germination is dependent on or facilitated by fire.<ref>Bolin, J. F. 2009. Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species. Castanea, v. 74, no. 2, p. 160-167.</ref> | + | Fire stimulates root and root collar sprouting along with enhancing germination, making this a fire-climax species. Density declines 3 to 4 years following a fire, with fire exclusion reducing density and cover.<ref name="fs"/> Seeds respond positively to heat shock, suggesting that its germination is dependent on or facilitated by fire.<ref>Bolin, J. F. 2009. Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species. Castanea, v. 74, no. 2, p. 160-167.</ref> Populations of ''Rhus copallinum'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.<ref>Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref><ref>Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.</ref><ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> |
| + | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | === | + | ===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> |
| − | + | ''Rhus copallinum'' has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host a variety of bee species such as ''Colletes mandibularis'' (family Colletidae), members of the the Halictidae family such as ''Augochlora pura'', ''Augochlorella aurata'', ''Augochloropsis sumptuosa'', ''Lasioglossum pectoralis'' and ''L. placidensis'', members of the Megachilidae family such as ''Coelioxys sayi'' and ''Megachile xylocopoides'', as well as wasps from the Pompilidae family such as ''Episyron conterminus posterus'', ''Poecilopompilus interruptus'' and ''Tachypompilus f. ferrugineus'', members of the Sphecidae family such as ''Cerceris flavofasciata floridensis'', ''C. tolteca'', ''Ectemnius rufipes ais'', ''Isodontia apicalis'', ''Oxybelus decorosum'', ''Palmodes dimidiatus'', ''Philanthus ventilabris'', ''Sphex ichneumoneus'' and ''Tachysphex similis'', as well as ''Leucospis robertsoni'' (family Leucospididae) and members of the Vespidae family such as ''Eumenes fraternus'', ''Monobia quadridens'', ''Pachodynerus erynnis'', ''Parancistrocerus fulvipes rufovestris'', ''Parancistrocerus perennis anacardivora'', ''Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus'', ''Polistes dorsalis hunteri'', ''Stenodynerus beameri'', ''Stenodynerus pulvinatus surrufus'', ''Vespula maculifrons'', ''Vespula squamosa'' and ''Zethus spinipes''.<ref>Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowering plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> Additionaly, ''R. copallinum'' has been observed to host members of the Andrenidae family such as ''Andrena brevipalpis, A. crataegi, A. miserabilis'' and ''A. robertsonii,'' ''Bombus griseocollis'' (family Apidae), ''Tibicen tibicen'' (family Cicadidae), ''Oecleus borealis'' (family Cixiidae), ''Harmonia axyridis'' (family Coccinellidae), members of the Colletidae family such as ''Colletes speculiferus'' and ''Hylaeus modestus'', ''Agapostemon virescens'' (family Halictidae), and members of the Megachilidae family such as ''Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis, M. petulans'', and ''M. texana.''<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> The foliage is a food source for the caterpillar ''Pyrrhia umbra''.<ref name="illinois">[[http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/trees/plants/winged_sumac.htm]]Accessed: March 10, 2016</ref> The berries are eaten by wild turkeys and songbirds.<ref name="fs"/> Birds have been observed to choose fruits of ''R. copallina'' rather than fruits of ''R. glabra'' when they were both available as winter foods. This could be due to the higher caloric value and larger fruits of ''R. copallinum''.<ref name="graber">Graber, J. W. and P. M. Powers (1981). "Dwarf Sumac as Winter Bird Food." The American Midland Naturalist 105(2): 410-412.</ref> | |
| − | + | ===Diseases and parasites=== | |
| + | Fusarium wilt infects the roots, causing the leaves to droop and wilt.<ref name="uf">[[https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/st568]]University of Florida Extension Accessed: March 10, 2016</ref> | ||
| − | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
| + | The fruits are used to make a sweet drink by the Cherokee Indians.<ref>Deuerling D., Lantz P. 1991 Native Wild Foods: Indian Lemonade. Palmetto 11(3):7</Ref> The drink was similar to what we think of as pink lemonade. Additionally, boiling the berries can create a cure for sore throats.<ref> Fernald, et al. 1958. Edible Plants of Eastern North America. Harper and Row Publishers, New York.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:08, 15 July 2022
| Rhus copallinum | |
|---|---|
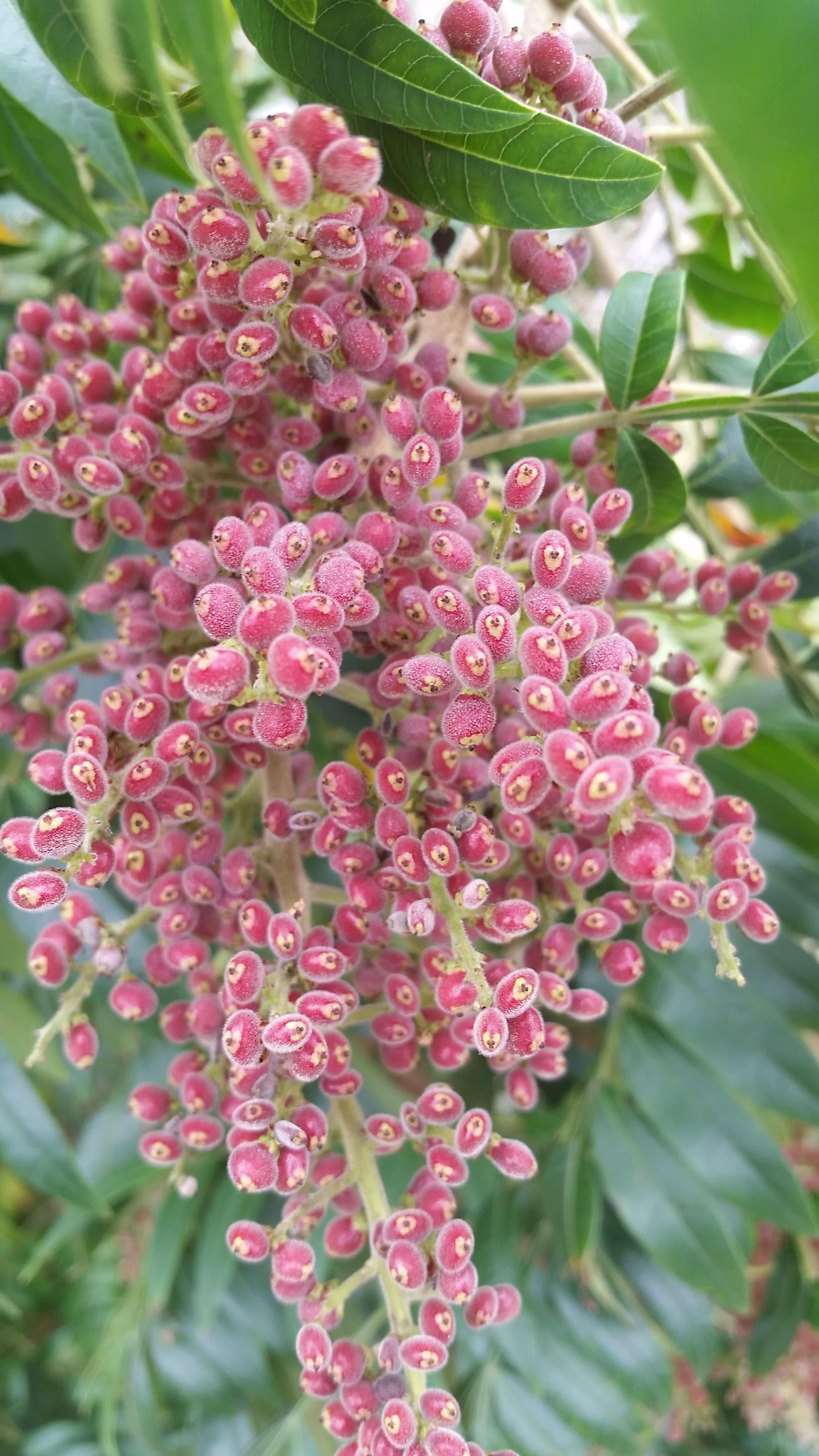

| |
| Photo taken by Michelle Smith | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Tracheophyta- Vascular plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Anacardiaceae |
| Genus: | Rhus |
| Species: | R. copallinum |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhus copallinum L. | |
| |
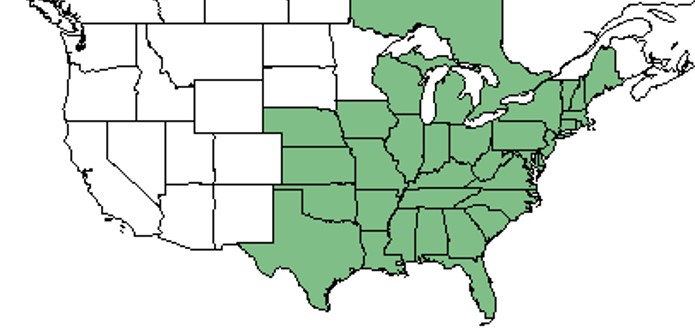
| Natural range of Rhus copallinum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Winged sumac, Flameleaf sumac, Shining sumac
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Rhus copallina L.; Rhus leucantha Jacquin; Rhus obtusifolia (Small) Small.[1]
Varieties: R. copallinum Linnaeus var. latifolia Engler.[2]
Description
"Upright shrubs or small trees, not poisonous. Leaves once-pinnately compound. Inflorescence a terminal panicle. Drupes red, ripening in the autumn. Seeds smooth. Flowers produced after the leaves."[3] "Rhizomatous shrub or small tree to 7 m tall; stems densely short-pubescent. Leaflets 9-23 (mostly 9-11), sessile, oblong to elliptic, 3-8 cm long, 1-4 cm wide, acute to acuminate, entire or less frequently crenate to serrate, base cuneate to rarely rounded, glabrous or densely pubescent beneath; rachis winged. Panicle 0.5-3 dm long and usually as broad. Drupe densely short-pubescent, 3-4 mm broad. Seeds 2.5-3 mm long."[3]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
R. copallinum habitats include old fields, oak-hickory woods, oak scrubs, marsh banks, roadsides, and sand ridges.[4]
R. copallinum has shown regrowth in reestablished longleaf pine woodlands that were disturbed by agriculture in South Carolina coastal plain communities, making it a possible indicator species for post-agricultural woodlands.[5] It increased its cover in response to clearcutting and chopping in north Florida flatwoods.[6] This species also increased its frequency in response to roller chopping in east Texas hardwood forests.[7]
It was unaffected by agriculture in South Carolina pine woodlands.[8]
R. copallinum had variable changes in frequency in response to soil disturbance by a KG blade in east Texas. It either showed regrowth or resistance to regrowth in reestablished hardwood forests that were disturbed by this practice.[7]
Rhus copallinum is frequent and abundant in the Clayhill Longleaf Woodlands and Upper Panhandle Savannas community types as described in Carr et al. (2010).[9]
Phenology
This species has been observed to flower from July to August.[10][11]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates.[12]
Seed bank and germination
The rhizomes, flowers, fruits, senescent leaves and leaf litter contain toxins that significantly inhibit both seed germination and seedling growth of climax prairie and weedy species.[13] Seed germination responds positively to heat shock with highest germination rates at 90 C.[14]
Fire ecology
Fire stimulates root and root collar sprouting along with enhancing germination, making this a fire-climax species. Density declines 3 to 4 years following a fire, with fire exclusion reducing density and cover.[15] Seeds respond positively to heat shock, suggesting that its germination is dependent on or facilitated by fire.[16] Populations of Rhus copallinum have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.[17][18][19]
Herbivory and toxicology
Rhus copallinum has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host a variety of bee species such as Colletes mandibularis (family Colletidae), members of the the Halictidae family such as Augochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis sumptuosa, Lasioglossum pectoralis and L. placidensis, members of the Megachilidae family such as Coelioxys sayi and Megachile xylocopoides, as well as wasps from the Pompilidae family such as Episyron conterminus posterus, Poecilopompilus interruptus and Tachypompilus f. ferrugineus, members of the Sphecidae family such as Cerceris flavofasciata floridensis, C. tolteca, Ectemnius rufipes ais, Isodontia apicalis, Oxybelus decorosum, Palmodes dimidiatus, Philanthus ventilabris, Sphex ichneumoneus and Tachysphex similis, as well as Leucospis robertsoni (family Leucospididae) and members of the Vespidae family such as Eumenes fraternus, Monobia quadridens, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus fulvipes rufovestris, Parancistrocerus perennis anacardivora, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Polistes dorsalis hunteri, Stenodynerus beameri, Stenodynerus pulvinatus surrufus, Vespula maculifrons, Vespula squamosa and Zethus spinipes.[20] Additionaly, R. copallinum has been observed to host members of the Andrenidae family such as Andrena brevipalpis, A. crataegi, A. miserabilis and A. robertsonii, Bombus griseocollis (family Apidae), Tibicen tibicen (family Cicadidae), Oecleus borealis (family Cixiidae), Harmonia axyridis (family Coccinellidae), members of the Colletidae family such as Colletes speculiferus and Hylaeus modestus, Agapostemon virescens (family Halictidae), and members of the Megachilidae family such as Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis, M. petulans, and M. texana.[21] The foliage is a food source for the caterpillar Pyrrhia umbra.[22] The berries are eaten by wild turkeys and songbirds.[15] Birds have been observed to choose fruits of R. copallina rather than fruits of R. glabra when they were both available as winter foods. This could be due to the higher caloric value and larger fruits of R. copallinum.[23]
Diseases and parasites
Fusarium wilt infects the roots, causing the leaves to droop and wilt.[24]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
The fruits are used to make a sweet drink by the Cherokee Indians.[25] The drink was similar to what we think of as pink lemonade. Additionally, boiling the berries can create a cure for sore throats.[26]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 678. Print.
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2016. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Tom Barnes, Kathy Craddock Burks, G. Fleming, P. Genelle, Robert K. Godfrey, Gary R. Knight. States and Counties: Florida: Florida: Citrus, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, St. Johns, Wakulla.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Stransky, J.J., J.C. Huntley, and Wanda J. Risner. (1986). Net Community Production Dynamics in the Herb-Shrub Stratum of a Loblolly Pine-Hardwood Forest: Effects of Clearcutting and Site Preparation. Gen. Tech. Rep. SO-61. New Orleans, LA: U.S. Dept of Agriculture, Forest Service, Southern Forest Experiment Station. 11 p.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., J.L. Orrock, E.I. Damschen, C.D. Collins, P.G. Hahn, W.B. Mattingly, J.W. Veldman, and J.L. Walker. (2014). Land-Use History and Contemporary Management Inform an Ecological Reference Model for Longleaf Pine Woodland Understory Plant Communities. PLoS ONE 9(1): e86604.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ [[1]]Missouri Botanical Gardens. Accessed: March 7, 2016
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, Jones Ecological Research Center, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Petranka, J. W. and J. K. McPherson (1979). "The Role of Rhus Copallina in the Dynamics of the Forest-Prairie Ecotone in North-Central Oklahoma." Ecology 60(5): 956-965.
- ↑ Bolin, J. F. 2009. Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species. Castanea, v. 74, no. 2, p. 160-167.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedfs - ↑ Bolin, J. F. 2009. Heat shock germination responses of three eastern North American temperate species. Castanea, v. 74, no. 2, p. 160-167.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowering plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [2]
- ↑ [[3]]Accessed: March 10, 2016
- ↑ Graber, J. W. and P. M. Powers (1981). "Dwarf Sumac as Winter Bird Food." The American Midland Naturalist 105(2): 410-412.
- ↑ [[4]]University of Florida Extension Accessed: March 10, 2016
- ↑ Deuerling D., Lantz P. 1991 Native Wild Foods: Indian Lemonade. Palmetto 11(3):7
- ↑ Fernald, et al. 1958. Edible Plants of Eastern North America. Harper and Row Publishers, New York.