Difference between revisions of "Quercus minima"
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | + | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | |
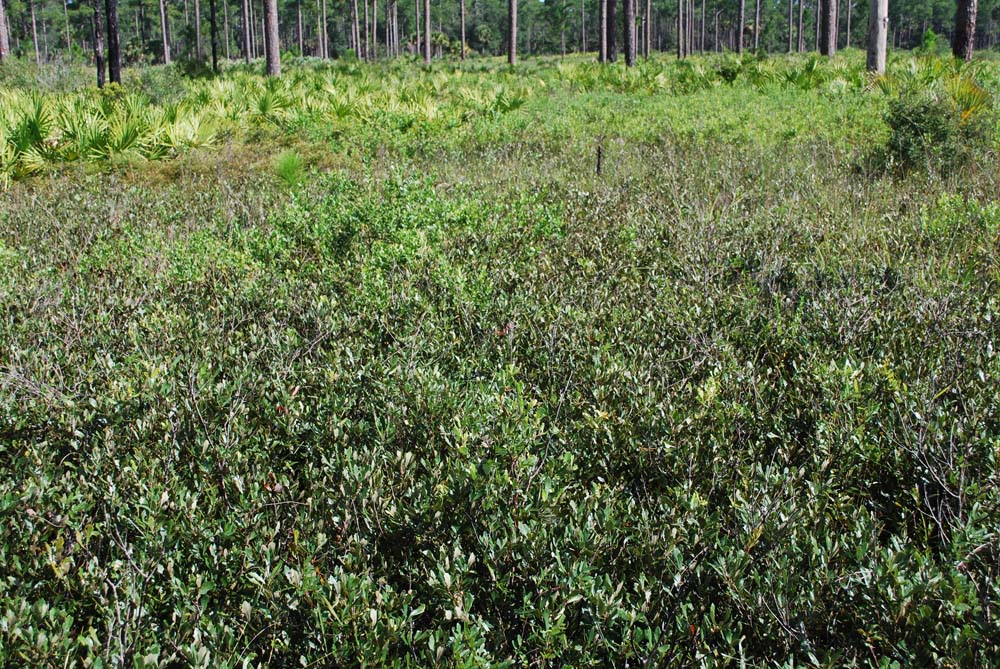
| + | ''Q. minima'' has been found in pine flatwoods, turkey oak-longleaf pine sand ridges, open rocky areas, longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, slash pine flatwoods, scrub oak stands, oak woodlands, sand pine scrub, along wetland shores, and sandstone outcroppings.<ref name="FSU"> Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert Kral, and Sidney McDaniel. States and counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Highlands, Leon, Liberty, Osceola, and Washington.</ref> It is also found in disturbed areas like burned fields.<ref name="FSU"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species: ''Q. pumila, Q. geminata, Q. laevis, Q. margaretta, Q. incana, Q. myrtifolia'', and ''Q. chapmanii''.<ref name="FSU"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Q. minima'' reduced its frequency and density in response to soil disturbance by roller chopping in northwest Florida sandhills.<ref>Hebb, E.A. (1971). Site Preparation Decreases Game Food Plants in Florida Sandhills. The Journal of Wildlife Management 35(1):155-162.</ref> It decreased its cover and stems per acre in response to chopping in south Florida saw palmetto-pineland communities.<ref>Moore, W.H. (1974). Effects of Chopping Saw-Plametto-Pineland Threeawn Range in South Florida. Journal of Range Management 27(2):101-104.</ref> Additionally, this species decreased its occurrence in response to soil disturbance by disking, bedding, and planting slash pines in north Florida flatwoods.<ref>Schultz, R.P. and L.P. Wilhite. (1974). Changes in a Flatwoods Site Following Intensive Preparation. Forest Science 20(3):230-237.</ref> ''Q. minima'' has shown resistance to regrowth in these reestablished habitats that were disturbed by these practices. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Quercus minima'' is frequent and abundant in the Xeric Flatwoods community type and is an indicator species for the North Florida Mesic Flatwoods community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | ''Q. minima'' has been observed to flower from March to May and in September with peak inflorescence in April.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 13 DEC 2016</ref> | |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| + | ===Herbivory and toxicology===<!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> | ||
| + | ''Quercus minima'' has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host species such as ''Apis mellifera'' (family Apidae) and ''Colletes brimleyi'' (family Colletidae).<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Cultural use== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
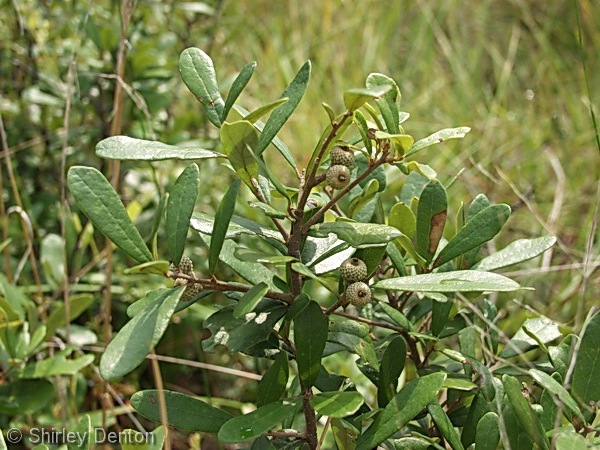
File: Quercus_minima_ShirleyDenton_NatPhotography_lvs4.jpg | <center> Fruit of ''Quercus minima'' <p> Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), [http://www.shirleydenton.com/welcome Nature Photography by Shirley Denton] </gallery> | File: Quercus_minima_ShirleyDenton_NatPhotography_lvs4.jpg | <center> Fruit of ''Quercus minima'' <p> Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), [http://www.shirleydenton.com/welcome Nature Photography by Shirley Denton] </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 14:53, 15 July 2022
| Quercus minima | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Fagaceae |
| Genus: | Quercus |
| Species: | Q. minima |
| Binomial name | |
| Quercus minima (Sarg.) Small | |
| |
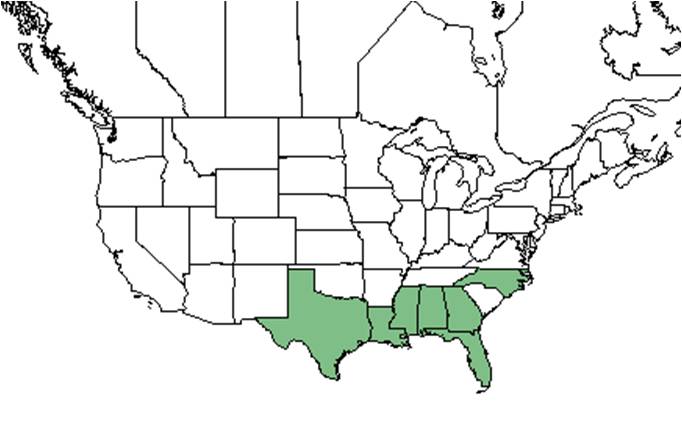
| Natural range of Quercus minima from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Dwarf live oak, Minimal oak
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Quercus minima is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Q. minima has been found in pine flatwoods, turkey oak-longleaf pine sand ridges, open rocky areas, longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, slash pine flatwoods, scrub oak stands, oak woodlands, sand pine scrub, along wetland shores, and sandstone outcroppings.[1] It is also found in disturbed areas like burned fields.[1]
Associated species: Q. pumila, Q. geminata, Q. laevis, Q. margaretta, Q. incana, Q. myrtifolia, and Q. chapmanii.[1]
Q. minima reduced its frequency and density in response to soil disturbance by roller chopping in northwest Florida sandhills.[2] It decreased its cover and stems per acre in response to chopping in south Florida saw palmetto-pineland communities.[3] Additionally, this species decreased its occurrence in response to soil disturbance by disking, bedding, and planting slash pines in north Florida flatwoods.[4] Q. minima has shown resistance to regrowth in these reestablished habitats that were disturbed by these practices.
Quercus minima is frequent and abundant in the Xeric Flatwoods community type and is an indicator species for the North Florida Mesic Flatwoods community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[5]
Phenology
Q. minima has been observed to flower from March to May and in September with peak inflorescence in April.[6]
Herbivory and toxicology
Quercus minima has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host species such as Apis mellifera (family Apidae) and Colletes brimleyi (family Colletidae).[7]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Fruit of Quercus minima Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Nature Photography by Shirley Denton
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert Kral, and Sidney McDaniel. States and counties: Florida: Calhoun, Franklin, Highlands, Leon, Liberty, Osceola, and Washington.
- ↑ Hebb, E.A. (1971). Site Preparation Decreases Game Food Plants in Florida Sandhills. The Journal of Wildlife Management 35(1):155-162.
- ↑ Moore, W.H. (1974). Effects of Chopping Saw-Plametto-Pineland Threeawn Range in South Florida. Journal of Range Management 27(2):101-104.
- ↑ Schultz, R.P. and L.P. Wilhite. (1974). Changes in a Flatwoods Site Following Intensive Preparation. Forest Science 20(3):230-237.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 13 DEC 2016
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
