Difference between revisions of "Persea borbonia"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: Red bay | + | Common name: Red bay<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Tamala borbonia'' (Linnaeus) Rafinesque | + | Synonyms: ''Tamala borbonia'' (Linnaeus) Rafinesque.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | |
| − | Redbay is in the order Ranales (formally called Magnoliids). This order includes magnolias, yellow poplars, pawpaws, anise tree, wild cinnamon, and laurels.<ref name="warnell"/> | + | This species has had many scientific names since its discovery. The genus name ''Persea'' is derived from a Greek term for a Persian tree with fruits growing from the stem.<ref name="warnell">[[https://www.warnell.uga.edu/outreach/pubs/pdf/forestry/Redbay%20pub%2012-9.pdf]]Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources. Accessed: February 20, 2016</ref> Redbay is in the order Ranales (formally called Magnoliids). This order includes magnolias, yellow poplars, pawpaws, anise tree, wild cinnamon, and laurels.<ref name="warnell"/> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | + | There are five different varieties of redbay in the southeastern U.S., they can be easily differentiated by the flower/fruit stem lengths, and trichomes on the abaxial leaf side.<ref name="warnell"/> ''P. borbonia'' is an evergreen, aromatic tree/shrub. Its leaves have an entire margin, an elliptic shape, and glabrous to pubescent underside. They are 5-15 cm long and 2-6 cm wide. The flowers are perfect with axillary cymes on tomentose peduncles that are 2-16 cm long. The drupe is dark blue or black, subglobose, and 7-10 mm in diameter. | |
| − | |||
| − | There are five different varieties of redbay in the southeastern U.S., they can be easily differentiated by the flower/fruit stem lengths, and trichomes on the abaxial leaf side.<ref name="warnell"/> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | The native distribution of redbay includes the Coastal Plain from | + | The native distribution of redbay includes the Coastal Plain from southern Delaware to Florida, west to southeast Texas, with isolated populations in central Texas.<ref name="wildflower">[[http://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=PEBO]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: February 19, 2016</ref> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''P. borbonia'' has been observed in cabbage palm-live oak hammocks, pine/scrub oak communities, mixed hardwood forests, vegetated shell mounds, tropical evergreen hardwood forests, dune thickets, oak-hickory-magnolia coastal hammocks, and wet pine flatwoods. It has been found in disturbed areas such as bulldozed turkey oak/longleaf pine communities and roadsides. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Delzie Demaree, R.J. Eaton, J.P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, R. Komarek, Robert Kral, H. Kurz, O. Lakela, Elbert L. Little Jr., Sidney McDaniel, K.M. Meyer, Richard S. Mitchell, T. Myint, Jackie Patman, Elmer C. Prichard, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray Jr., G. Robertson, Cecil R. Slaughter, Annie Schmidt, C.E. Smith, R.R. Smith, R.F. Thorne, A. Townesmith, Rodie White, C.E. Wood, Jean W. Wooten, Richard P. Wunderlin. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Brevard, Calhoun, Citrus, Columbia, Dade, Dixie, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Marion, Martin, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, Pasco, Pinellas, Suwannee, St. Johns, St. Lucie, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Redbay requires partial to fun sun, plenty of water supply, and root oxygen.<ref name="warnell"/> It does not tolerate long periods of inundation.<ref name="Conner and George 1993">Conner, W. H. and R. A. George (1993). "Impact of Saltwater Flooding on Red Maple, Redbay, and Chinese Tallow Seedlings." Castanea 58(3): 214-219.</ref> Soils are mostly Histosols.<ref name="fs">[[http://www.na.fs.fed.us/pubs/silvics_manual/volume_2/persea/borbonia.htm]]Accessed: February 19, 2016</ref> It grows in loamy sand, sandy loam, and limestone substrate. ''P. borbonia'' does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''P. borbonia'' has been observed in cabbage palm-live oak hammocks, pine/scrub oak communities, mixed hardwood forests, vegetated shell mounds, tropical evergreen hardwood forests, dune thickets, oak-hickory-magnolia coastal hammocks, and wet pine flatwoods. It has been found in disturbed areas such as bulldozed turkey oak/longleaf pine communities and roadsides.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Delzie Demaree, R.J. Eaton, J.P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, R. Komarek, Robert Kral, H. Kurz, O. Lakela, Elbert L. Little Jr., Sidney McDaniel, K.M. Meyer, Richard S. Mitchell, T. Myint, Jackie Patman, Elmer C. Prichard, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray Jr., G. Robertson, Cecil R. Slaughter, Annie Schmidt, C.E. Smith, R.R. Smith, R.F. Thorne, A. Townesmith, Rodie White, C.E. Wood, Jean W. Wooten, Richard P. Wunderlin. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Brevard, Calhoun, Citrus, Columbia, Dade, Dixie, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Marion, Martin, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, Pasco, Pinellas, Suwannee, St. Johns, St. Lucie, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Redbay requires partial to fun sun, plenty of water supply, and root oxygen.<ref name="warnell"/> It does not tolerate long periods of inundation.<ref name="Conner and George 1993">Conner, W. H. and R. A. George (1993). "Impact of Saltwater Flooding on Red Maple, Redbay, and Chinese Tallow Seedlings." Castanea 58(3): 214-219.</ref> Soils are mostly Histosols.<ref name="fs">[[http://www.na.fs.fed.us/pubs/silvics_manual/volume_2/persea/borbonia.htm]]Accessed: February 19, 2016</ref> It grows in loamy sand, sandy loam, and limestone substrate. ''P. borbonia'' does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.<ref>Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.</ref> |
| − | Associated species include ''Gordonia lasianthus, Quercus geminata, Celtis, Exothea paniculata, Xanthoxylum, Fagara, Persea littoralis, Rapanea guianensis, Parthenocissus quinquefolia, Plumbago scandens, Bumelia, Forestiera, Rhizophora, Baccharis halimifolia'', black cherry and hackberry. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | Associated species include ''Gordonia lasianthus, Quercus geminata, Celtis, Exothea paniculata, Xanthoxylum, Fagara, Persea littoralis, Rapanea guianensis, Parthenocissus quinquefolia, Plumbago scandens, Bumelia, Forestiera, Rhizophora, Baccharis halimifolia'', black cherry and hackberry.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowers are perfect and monecious.<ref name="warnell"/> ''P. borbonia'' | + | Flowers are perfect and monecious.<ref name="warnell"/> ''P. borbonia'' flowers from April through June and fruits from January through July.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> Cross-pollination is required for viable seeds.<ref name="warnell"/> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | Seeds are dispersed by songbirds, white tailed deer, bobwhite, wild turkeys, and black bears.<ref name="fs"/> | + | Seeds are dispersed by songbirds, white-tailed deer, bobwhite, wild turkeys, and black bears.<ref name="fs"/> |
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | Germination is hypogeal.<ref name="fs"/> Seeds germinate well in mucky, swampy, and poorly drained areas; however, these conditions may be stressful to an adult tree. Adults require water and plenty of root oxygen which makes | + | Germination is hypogeal.<ref name="fs"/> Seeds germinate well in mucky, swampy, and poorly drained areas; however, these conditions may be stressful to an adult tree. Adults require water and plenty of root oxygen which makes permanently inundated conditions damaging.<ref name="warnell"/> |
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ''P. borbonia'' has been described as a late successional species that does not thrive in areas of disturbance such as fire.<ref name="warnell"/> Menges et al. (1993) found that ''P. borbonia'' densities and basal areas had increased in flatwoods and bayhead communitites that were fire suppressed for over 20 years. Fire may cause substantial damage to redbay; fire scarring and deterioration of the lower trunk portion of the tree is common.<ref name="fs"/> However, a study on Long Pine Key in the Everglades found ''P. borbonia'' to resprout, flower, and fruit within about one year following a fire in April. The degree and timing of flowering and fruiting did not vary substantially among plots burned one, two, six, and seven years prior.<ref>Gunderson, L., D. Taylor and J. Craig 1983. Report SFRC-83/04 Fire effects on flowering and fruiting patterns of understory plants in pinelands of EVER. Everglades National Park, South Florida Research Center, Homestead, Florida, 36 pg.</ref> | + | ''P. borbonia'' has been described as a late-successional species that does not thrive in areas of disturbance such as fire.<ref name="warnell"/> Menges et al. (1993) found that ''P. borbonia'' densities and basal areas had increased in flatwoods and bayhead communitites that were fire suppressed for over 20 years. Fire may cause substantial damage to redbay; fire scarring and deterioration of the lower trunk portion of the tree is common.<ref name="fs"/> However, a study on Long Pine Key in the Everglades found ''P. borbonia'' to resprout, flower, and fruit within about one year following a fire in April. The degree and timing of flowering and fruiting did not vary substantially among plots burned one, two, six, and seven years prior.<ref>Gunderson, L., D. Taylor and J. Craig 1983. Report SFRC-83/04 Fire effects on flowering and fruiting patterns of understory plants in pinelands of EVER. Everglades National Park, South Florida Research Center, Homestead, Florida, 36 pg.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Colletidae | + | ===Pollination === |
| + | ''Persea borbonia'' has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees from the Apidae family such as ''Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens'' and ''Epeolus zonatus'', plasterer bees from the Colletidae family such as ''Colletes banksi, C. brimleyi'' and ''C. nudus'', sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as ''Augochlora pura, Augochloropsis metallica'' and ''Lasioglossum pectoralis'', thread-waisted wasps from the Sphecidae family such as ''Cerceris fumipennis'' and ''Tachytes auricomans'', and wasps from the Vespidae family such as ''Mischocyttarus cubensis, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Polistes metricus'' and ''Zethus spinipes''.<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ||
| − | + | ===Herbivory and toxicology=== <!--Common herbivores, granivory, insect hosting, poisonous chemicals, allelopathy, etc--> | |
| − | + | The fruits of ''P. borbonia'' are a sizable portion of the bobwhite quail diet during fall and winter months.<ref name="fs"/> | |
| − | + | Redbay rupes are eaten by songbirds, wild turkeys, quail, rodents, deer, and black bear. The leaves are also the primary larval food source for the palamedes swallowtail butterfly. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | ||
| − | |||
| − | Redbay rupes are eaten by songbirds, wild turkeys, quail, rodents, deer, and black bear. The leaves are also the primary larval food source for the palamedes swallowtail butterfly. | ||
===Diseases and parasites=== | ===Diseases and parasites=== | ||
| − | ''P. borbonia'' is susceptible to laurel wilt disease (LWD) which is a lethal vascular infection in trees of the laurel family cause by the fungus ''Raffaelea lauricola'' that is transported by the non-native ambrosia beetle ''Xyleborus glabratus''. Laurel wilt disease is characterized by mortality of redbay stems in the infected sites. Distribution of LWD includes South Carolina, Georgia, Florida and parts of North Carolina. <ref name="Shearman et al. 2015">Shearman, T. M., G. Geoff Wang, et al. (2015). "Population dynamics of redbay (Persea borbonia) after laurel wilt disease: an assessment based on forest inventory and analysis data." Biology Invasions 17: 1371-1382.</ref> The greatest decline in redbay populations is in Georgia (Fraedrich et al. 2008). | + | ''P. borbonia'' is susceptible to laurel wilt disease (LWD) which is a lethal vascular infection in trees of the laurel family cause by the fungus ''Raffaelea lauricola'' that is transported by the non-native ambrosia beetle ''Xyleborus glabratus''. Laurel wilt disease is characterized by mortality of redbay stems in the infected sites. Distribution of LWD includes South Carolina, Georgia, Florida and parts of North Carolina.<ref name="Shearman et al. 2015">Shearman, T. M., G. Geoff Wang, et al. (2015). "Population dynamics of redbay (Persea borbonia) after laurel wilt disease: an assessment based on forest inventory and analysis data." Biology Invasions 17: 1371-1382.</ref> The greatest decline in redbay populations is in Georgia (Fraedrich et al. 2008). |
''P. borbonia'' is also the primary host of a psyllid leaf-galler ''Trioza magnoliae'', which produce galls on leaves. Galls use up resources that would otherwise be used for plant growth, therefore directly affecting plant fitness. <ref name="Leege 2006">Leege, L. M. (2006). "The Relationship between Psyllid Leaf Galls and Redbay (Persea borbonia) Fitness Traits in Sun and Shade." Plant Ecology 184(2): 203-212.</ref> | ''P. borbonia'' is also the primary host of a psyllid leaf-galler ''Trioza magnoliae'', which produce galls on leaves. Galls use up resources that would otherwise be used for plant growth, therefore directly affecting plant fitness. <ref name="Leege 2006">Leege, L. M. (2006). "The Relationship between Psyllid Leaf Galls and Redbay (Persea borbonia) Fitness Traits in Sun and Shade." Plant Ecology 184(2): 203-212.</ref> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 65: | ||
It is resistant to the fungus ''Phytophthora cinnamomi'' which affects the roots of many other laurel species. This resistance is due to borbonol found in the roots and stems that is an antifungal substance.<ref name="fs"/> | It is resistant to the fungus ''Phytophthora cinnamomi'' which affects the roots of many other laurel species. This resistance is due to borbonol found in the roots and stems that is an antifungal substance.<ref name="fs"/> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | |
| − | The wood is often used for cabinetwork and lumber, while the leaves can be used to add spice and flavor to food.<ref name="wildflower"/> | + | ==Cultural use== |
| + | The wood is often used for cabinetwork and lumber, while the leaves can be used to add spice and flavor to food.<ref name="wildflower"/> Humans use redbay for carpentry trim, flavoring tea and gumbos, and medicinal purposes by Native Americans.<ref>Mayfield A.E. III 2007. Laurel Wilt: A serious threat to redbay and other related native plants. Palmetto 24(3):8-11.</ref> | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Latest revision as of 12:24, 15 July 2022
| Persea borbonia | |
|---|---|
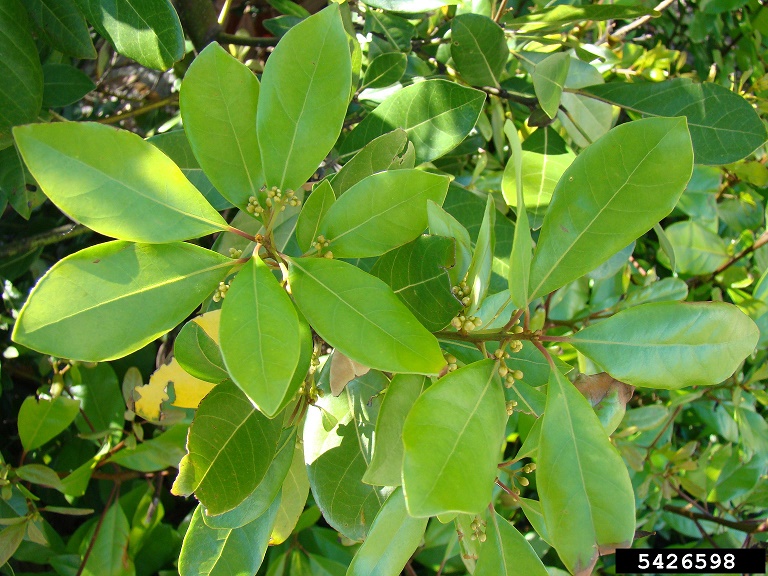

| |
| Photo by Rebekah D. Wallace, University of Georgia Bugwood.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Laurales |
| Family: | Lauraceae |
| Genus: | Persea |
| Species: | P. borbonia |
| Binomial name | |
| Persea borbonia (L.) Spreng. | |
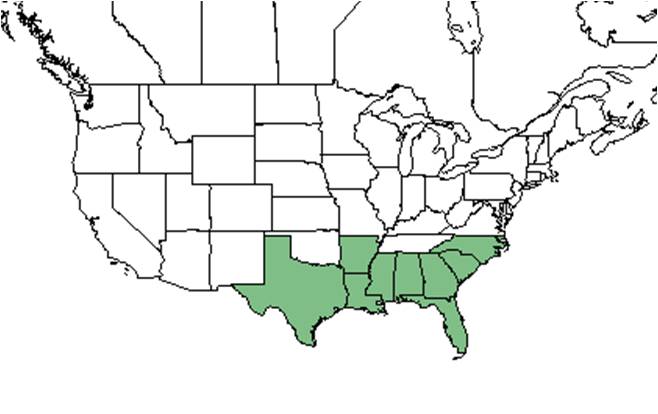
| |
| Natural range of Persea borbonia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Red bay[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Tamala borbonia (Linnaeus) Rafinesque.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
This species has had many scientific names since its discovery. The genus name Persea is derived from a Greek term for a Persian tree with fruits growing from the stem.[2] Redbay is in the order Ranales (formally called Magnoliids). This order includes magnolias, yellow poplars, pawpaws, anise tree, wild cinnamon, and laurels.[2]
Description
There are five different varieties of redbay in the southeastern U.S., they can be easily differentiated by the flower/fruit stem lengths, and trichomes on the abaxial leaf side.[2] P. borbonia is an evergreen, aromatic tree/shrub. Its leaves have an entire margin, an elliptic shape, and glabrous to pubescent underside. They are 5-15 cm long and 2-6 cm wide. The flowers are perfect with axillary cymes on tomentose peduncles that are 2-16 cm long. The drupe is dark blue or black, subglobose, and 7-10 mm in diameter.
Distribution
The native distribution of redbay includes the Coastal Plain from southern Delaware to Florida, west to southeast Texas, with isolated populations in central Texas.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, P. borbonia has been observed in cabbage palm-live oak hammocks, pine/scrub oak communities, mixed hardwood forests, vegetated shell mounds, tropical evergreen hardwood forests, dune thickets, oak-hickory-magnolia coastal hammocks, and wet pine flatwoods. It has been found in disturbed areas such as bulldozed turkey oak/longleaf pine communities and roadsides.[4] Redbay requires partial to fun sun, plenty of water supply, and root oxygen.[2] It does not tolerate long periods of inundation.[5] Soils are mostly Histosols.[6] It grows in loamy sand, sandy loam, and limestone substrate. P. borbonia does not respond to soil disturbance by clearcutting and chopping in North Florida flatwoods forests.[7]
Associated species include Gordonia lasianthus, Quercus geminata, Celtis, Exothea paniculata, Xanthoxylum, Fagara, Persea littoralis, Rapanea guianensis, Parthenocissus quinquefolia, Plumbago scandens, Bumelia, Forestiera, Rhizophora, Baccharis halimifolia, black cherry and hackberry.[4]
Phenology
Flowers are perfect and monecious.[2] P. borbonia flowers from April through June and fruits from January through July.[4][8] Cross-pollination is required for viable seeds.[2]
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by songbirds, white-tailed deer, bobwhite, wild turkeys, and black bears.[6]
Seed bank and germination
Germination is hypogeal.[6] Seeds germinate well in mucky, swampy, and poorly drained areas; however, these conditions may be stressful to an adult tree. Adults require water and plenty of root oxygen which makes permanently inundated conditions damaging.[2]
Fire ecology
P. borbonia has been described as a late-successional species that does not thrive in areas of disturbance such as fire.[2] Menges et al. (1993) found that P. borbonia densities and basal areas had increased in flatwoods and bayhead communitites that were fire suppressed for over 20 years. Fire may cause substantial damage to redbay; fire scarring and deterioration of the lower trunk portion of the tree is common.[6] However, a study on Long Pine Key in the Everglades found P. borbonia to resprout, flower, and fruit within about one year following a fire in April. The degree and timing of flowering and fruiting did not vary substantially among plots burned one, two, six, and seven years prior.[9]
Pollination
Persea borbonia has been observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees from the Apidae family such as Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens and Epeolus zonatus, plasterer bees from the Colletidae family such as Colletes banksi, C. brimleyi and C. nudus, sweat bees from the Halictidae family such as Augochlora pura, Augochloropsis metallica and Lasioglossum pectoralis, thread-waisted wasps from the Sphecidae family such as Cerceris fumipennis and Tachytes auricomans, and wasps from the Vespidae family such as Mischocyttarus cubensis, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Polistes metricus and Zethus spinipes.[10]
Herbivory and toxicology
The fruits of P. borbonia are a sizable portion of the bobwhite quail diet during fall and winter months.[6] Redbay rupes are eaten by songbirds, wild turkeys, quail, rodents, deer, and black bear. The leaves are also the primary larval food source for the palamedes swallowtail butterfly.
Diseases and parasites
P. borbonia is susceptible to laurel wilt disease (LWD) which is a lethal vascular infection in trees of the laurel family cause by the fungus Raffaelea lauricola that is transported by the non-native ambrosia beetle Xyleborus glabratus. Laurel wilt disease is characterized by mortality of redbay stems in the infected sites. Distribution of LWD includes South Carolina, Georgia, Florida and parts of North Carolina.[11] The greatest decline in redbay populations is in Georgia (Fraedrich et al. 2008).
P. borbonia is also the primary host of a psyllid leaf-galler Trioza magnoliae, which produce galls on leaves. Galls use up resources that would otherwise be used for plant growth, therefore directly affecting plant fitness. [12]
It is resistant to the fungus Phytophthora cinnamomi which affects the roots of many other laurel species. This resistance is due to borbonol found in the roots and stems that is an antifungal substance.[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
The wood is often used for cabinetwork and lumber, while the leaves can be used to add spice and flavor to food.[3] Humans use redbay for carpentry trim, flavoring tea and gumbos, and medicinal purposes by Native Americans.[13]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Menges, E. S., W. G. Abrahamson, et al. (1993). "Twenty Years of Vegetation Change in Five Long-Unburned Florida Plant Communities." Journal of Vegetation Science 4(3): 375-386.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 [[1]]Warnell School of Forestry and Natural Resources. Accessed: February 20, 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [[2]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: February 19, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Delzie Demaree, R.J. Eaton, J.P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, R. Komarek, Robert Kral, H. Kurz, O. Lakela, Elbert L. Little Jr., Sidney McDaniel, K.M. Meyer, Richard S. Mitchell, T. Myint, Jackie Patman, Elmer C. Prichard, Gwynn W. Ramsey, James D. Ray Jr., G. Robertson, Cecil R. Slaughter, Annie Schmidt, C.E. Smith, R.R. Smith, R.F. Thorne, A. Townesmith, Rodie White, C.E. Wood, Jean W. Wooten, Richard P. Wunderlin. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Brevard, Calhoun, Citrus, Columbia, Dade, Dixie, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Marion, Martin, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, Pasco, Pinellas, Suwannee, St. Johns, St. Lucie, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Conner, W. H. and R. A. George (1993). "Impact of Saltwater Flooding on Red Maple, Redbay, and Chinese Tallow Seedlings." Castanea 58(3): 214-219.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 [[3]]Accessed: February 19, 2016
- ↑ Moore, W.H., B.F. Swindel, and W.S. Terry. (1982). Vegetative Response to Clearcutting and Chopping in a North Florida Flatwoods Forest. Journal of Range Management 35(2):214-218.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Gunderson, L., D. Taylor and J. Craig 1983. Report SFRC-83/04 Fire effects on flowering and fruiting patterns of understory plants in pinelands of EVER. Everglades National Park, South Florida Research Center, Homestead, Florida, 36 pg.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Shearman, T. M., G. Geoff Wang, et al. (2015). "Population dynamics of redbay (Persea borbonia) after laurel wilt disease: an assessment based on forest inventory and analysis data." Biology Invasions 17: 1371-1382.
- ↑ Leege, L. M. (2006). "The Relationship between Psyllid Leaf Galls and Redbay (Persea borbonia) Fitness Traits in Sun and Shade." Plant Ecology 184(2): 203-212.
- ↑ Mayfield A.E. III 2007. Laurel Wilt: A serious threat to redbay and other related native plants. Palmetto 24(3):8-11.