Difference between revisions of "Eustachys floridana"
(→Ecology) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: ''Chloris floridana'' (Chapman) Wood | + | Synonyms: ''Chloris floridana'' (Chapman) Wood.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| − | Varieties: none | + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''E. floridana'' is a perennial graminoid of the ''Poaceae'' family native to North America. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=EUFL3 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=EUFL3] </ref> | + | ''E. floridana'' is a perennial graminoid of the ''Poaceae'' family native to North America.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"> USDA Plant Database [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=EUFL3 https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=EUFL3] </ref> It generally reaches heights of between 4 and 10 dm tall with slender stems.<ref name= "nature">[[http://explorer.natureserve.org]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 13, 2019</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | ''E. floridana'' is found in Alabama, Georgia, and Florida. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | + | ''E. floridana'' is found in Alabama, Georgia, and Florida.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> Within this range, it is found from eastern Georgia south to central peninsular Florida and west to the western panhandle of Florida and southern Alabama.<ref name= "Weakley 2015"/> |
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''E. floridana'' proliferates in sandhills and pine flatwoods <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref>, as well as pine rocklands and marl prairies <ref name= "Coile 2000"/> Specimens have been collected from open oak woods, open longleaf sandhill, flatwoods, and wiregrass sandhill communities. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. Kral, Loran C. Anderson, H. Kurz, R.K. Godfrey, J. P. Gillespie, R.E. Perdue, Richard Carter, W.W. Baker. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Madison, Leon, Suwannee) Georgia (Thomas, Baker)</ref> | + | ''E. floridana'' proliferates in sandhills and pine flatwoods<ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref>, as well as pine rocklands and marl prairies.<ref name= "Coile 2000"/> Specimens have been collected from open oak woods, open longleaf sandhill, flatwoods, and wiregrass sandhill communities.<ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. Kral, Loran C. Anderson, H. Kurz, R.K. Godfrey, J. P. Gillespie, R.E. Perdue, Richard Carter, W.W. Baker. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Madison, Leon, Suwannee) Georgia (Thomas, Baker)</ref> It is considered an indicator species of the north Florida longleaf woodlands habitat.<ref name= "Carr">Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.</ref> Thinning the overstory has a negative effect on the abundance of ''E. floridana'' but this species was found to persist with clearcutting disturbance.<ref>Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Pinus palustris'', ''Pinus taeda'', ''Aristida'' sp., ''Croptilion'' sp., ''Liatris'' sp., ''Eupatorium'' sp., and ''Tridens'' sp.<ref name= "FSU herbarium"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Eustachys floridana'' is an indicator species for the North Florida Longleaf Woodlands community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 44: | ||
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. <ref> Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. <ref> Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | |
| − | <!--===Pollination===--> | + | This species occurs in habitats that are fire-dependent.<ref name= "Carr"/> |
| − | <!--=== | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 19:46, 30 June 2022
Common name: twospike fingergrass [1], Florida fingergrass [2]
| Eustachys floridana | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Eustachys |
| Species: | E. floridana |
| Binomial name | |
| Eustachys floridana Chapm. | |
| |
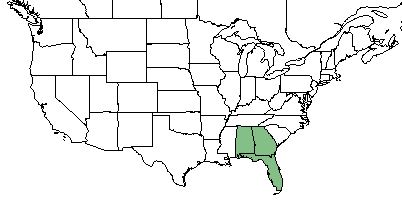
| Natural range of Eustachys floridana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Chloris floridana (Chapman) Wood.[3]
Varieties: none.[3]
Description
E. floridana is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America.[1] It generally reaches heights of between 4 and 10 dm tall with slender stems.[4]
Distribution
E. floridana is found in Alabama, Georgia, and Florida.[1] Within this range, it is found from eastern Georgia south to central peninsular Florida and west to the western panhandle of Florida and southern Alabama.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
E. floridana proliferates in sandhills and pine flatwoods[2], as well as pine rocklands and marl prairies.[5] Specimens have been collected from open oak woods, open longleaf sandhill, flatwoods, and wiregrass sandhill communities.[6] It is considered an indicator species of the north Florida longleaf woodlands habitat.[7] Thinning the overstory has a negative effect on the abundance of E. floridana but this species was found to persist with clearcutting disturbance.[8]
Associated species include Pinus palustris, Pinus taeda, Aristida sp., Croptilion sp., Liatris sp., Eupatorium sp., and Tridens sp.[6]
Eustachys floridana is an indicator species for the North Florida Longleaf Woodlands community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[9]
Phenology
E. floridana is a perennial herb to 1 m tall; raceme rachis wingless, triangular, fertile lemma pale or gray. [5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by wind. [10]
Fire ecology
This species occurs in habitats that are fire-dependent.[7]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=EUFL3
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ [[1]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 13, 2019
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Coile, N. C. (2000). Notes on Florida �s Regulated Plant Index (Rule 5B-40), Botany Contribution No. 38, 3nd edition. Gainesville, Florida, Florida Deaprtment of Agriculture and Consumer Services, Division of Plant Industry.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. Kral, Loran C. Anderson, H. Kurz, R.K. Godfrey, J. P. Gillespie, R.E. Perdue, Richard Carter, W.W. Baker. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Madison, Leon, Suwannee) Georgia (Thomas, Baker)
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (2003). "Influence of deer, cattle grazing and timber harvest on plant species diversity in a longleaf pine bluestem ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 175: 49-69.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.