Difference between revisions of "Crataegus lassa"
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| + | Common names: Bluffton Hawthorn; Sandhill Hawthorn | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
| ordo = Rosales | | ordo = Rosales | ||
| familia = Rosaceae | | familia = Rosaceae | ||
| − | | genus = '' | + | | genus = ''Crataegus'' |
| species = '''''C. lassa''''' | | species = '''''C. lassa''''' | ||
| binomial = ''Crataegus lassa'' | | binomial = ''Crataegus lassa'' | ||
| Line 18: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | + | Synonyms: ''Crataegus colonica'' Beadle; ''C. constans'' Beadle; ''C. dolosa'' Beadle; ''C. flava''; ''C. integra'' Beadle; ''C. sodalis'' Beadle.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | |
| − | + | Varieties: ''Crataegus lassa'' Beadle var. ''colonica'' (Beadle) R.W. Lance, ''C. lassa'' Beadle var. ''integra'' (Beadle) R.W. Lance, ''C. lassa'' Beadle var. ''lanata'' (Beadle) R.W. Lance, ''C. lassa'' Beadle var. ''lassa'', ''C. lassa'' Beadle var. ''recurva'' (Beadle) R.W. Lance.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | ''C. lassa'' is a perennial shrub/tree that belongs to the Rosaceae family.<ref>USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 22 April 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> It is typically small and of arborescent habit <ref name="Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Helen Roth, Sidney McDaniel, Charles T Bryson, Nancy B. Bryson, John Gwaltney, and Laurie Gwaltney. | ||
| + | States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden and Walton. </ref>. | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The distribution of ''C. lassa'' ranges from Alabama to central North Carolina <ref name= "Weakley"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | < | + | ''C. lassa'' is found in oak-pine scrub, xeric woodlands, upland scrublands, sandy uplands, and most commonly in soils of rapid drainage and deep sand.<ref name="Weakley">Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref>. It has been observed in dry loamy sand bordering a pond, on a ridge, and other disturbed areas. <ref name= "Herbarium"/> |
| + | |||
| + | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | ''C. lassa'' typically flowers during late March and April as well as between August and September.<ref name="Weakley"/> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | <!--===Pollination | + | <!--===Pollination and use by animals===--> |
| − | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | |
| − | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:19, 22 June 2022
Common names: Bluffton Hawthorn; Sandhill Hawthorn
| Crataegus lassa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Southeastern Flora Plant Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Rosaceae |
| Genus: | Crataegus |
| Species: | C. lassa |
| Binomial name | |
| Crataegus lassa Beadle | |
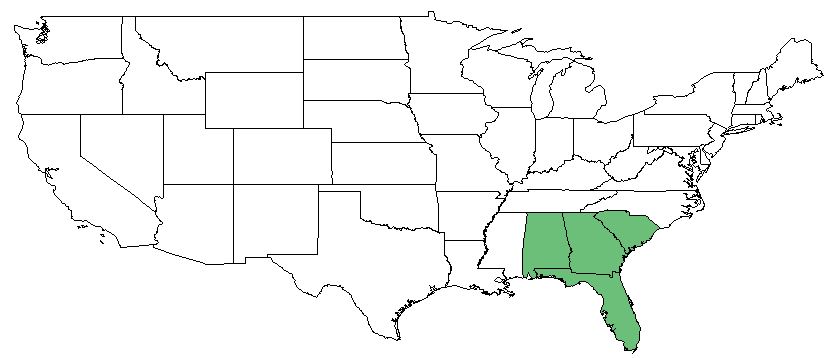
| |
| Natural range of Crataegus lassa from Weakley [1] | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Crataegus colonica Beadle; C. constans Beadle; C. dolosa Beadle; C. flava; C. integra Beadle; C. sodalis Beadle.[2]
Varieties: Crataegus lassa Beadle var. colonica (Beadle) R.W. Lance, C. lassa Beadle var. integra (Beadle) R.W. Lance, C. lassa Beadle var. lanata (Beadle) R.W. Lance, C. lassa Beadle var. lassa, C. lassa Beadle var. recurva (Beadle) R.W. Lance.[2]
Description
C. lassa is a perennial shrub/tree that belongs to the Rosaceae family.[3] It is typically small and of arborescent habit [4].
Distribution
The distribution of C. lassa ranges from Alabama to central North Carolina [5]
Ecology
Habitat
C. lassa is found in oak-pine scrub, xeric woodlands, upland scrublands, sandy uplands, and most commonly in soils of rapid drainage and deep sand.[5]. It has been observed in dry loamy sand bordering a pond, on a ridge, and other disturbed areas. [4]
Phenology
C. lassa typically flowers during late March and April as well as between August and September.[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1320 pp.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 22 April 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Helen Roth, Sidney McDaniel, Charles T Bryson, Nancy B. Bryson, John Gwaltney, and Laurie Gwaltney. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden and Walton.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.