Difference between revisions of "Centrosema arenicola"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
Associated species include ''Quercus, Myrica, Sabal palmetto, Eupatorium, Galactia'', and ''Clematis.''<ref name="FSU"></ref> | Associated species include ''Quercus, Myrica, Sabal palmetto, Eupatorium, Galactia'', and ''Clematis.''<ref name="FSU"></ref> | ||
| − | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting | + | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> |
''Centrosema arenicola'' flowers in August and September.<ref name="FSU"></ref><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> | ''Centrosema arenicola'' flowers in August and September.<ref name="FSU"></ref><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--><!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--><!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ===Pollination | + | ===Pollination=== |
''Centrosema arenicola'' was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees such as ''Bombus pennsylvanicus'' (family Apidae) and leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as ''Megachile integra'' and ''M. mendica''<ref>Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ''Centrosema arenicola'' was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees such as ''Bombus pennsylvanicus'' (family Apidae) and leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as ''Megachile integra'' and ''M. mendica''<ref>Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
Latest revision as of 20:17, 21 June 2022
| Centrosema arenicola | |
|---|---|
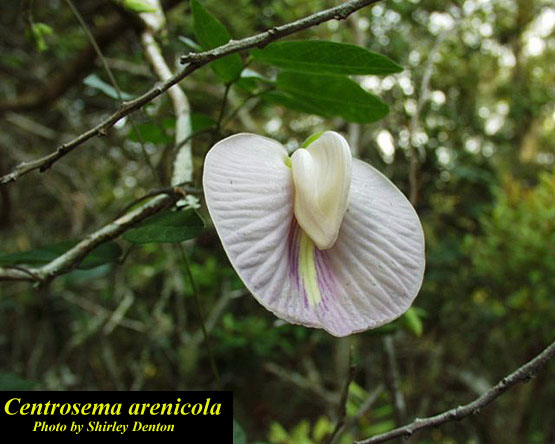

| |
| Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Centrosema |
| Species: | C. arenicola |
| Binomial name | |
| Centrosema arenicola (Small) F.J. Herm. | |
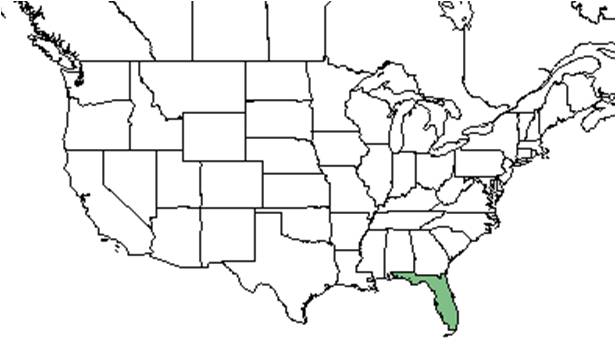
| |
| Natural range of Centrosema arenicola from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Pineland butterfly pea; sand butterfly pea
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Centrosema arenicolum (Small) F.J.Herm.; Bradburya arenicola Small; Bradburya floridana Britton.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
Distribution
Centrosema arenicola is endemic to central peninsular Florida to the Lake Wales Ridge area.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, C. arenicola has been found to occur in upland hardwood associations of Quercus and Sabal palmetto.[3]
Centrosema arenicola is an indicator species for the North Florida Longleaf Woodlands community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[4]
Associated species include Quercus, Myrica, Sabal palmetto, Eupatorium, Galactia, and Clematis.[3]
Phenology
Centrosema arenicola flowers in August and September.[3][5]
Pollination
Centrosema arenicola was observed at the Archbold Biological Station to host bees such as Bombus pennsylvanicus (family Apidae) and leafcutting bees from the Megachilidae family such as Megachile integra and M. mendica[6]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Sorrie, B. A. and A. S. Weakley 2001. Coastal Plain valcular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66: 50-82.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Olga Lakela. States and Counties: Florida: Citrus, Hernando, Hillsborough. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.