Difference between revisions of "Oldenlandia boscii"
Rwagner914 (talk | contribs) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: ''Hedyotis boscii'' A.P. de Candolle.<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | ''O. boscii'' has been found in pine flatwoods, floodplain forest clearings, and small ponds.<ref name="FSU"/> It is also found in disturbed areas including borrow pits, powerline corridors, and roadsides.<ref name="FSU"> Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: L.C. Anderson and R.K. Godfrey. States and counties: Florida: Calhoun, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, and Santa Rosa.</ref> Associated species: ''Polypremum procumbens, Juncus repens, Eremochloa ophiuroides, Rotala ramosior, Lindernia dubia, Diodia teres'', and ''Diodia virginiana''.<ref name="FSU"/> | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | < | + | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> |
| − | + | Populations of ''Oldenlandia boscii'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.<ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> | |
| + | |||
| + | ===Pollination and use by animals=== | ||
| + | This species has been observed to flower from June to November.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:33, 26 July 2021
| Oldenlandia boscii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Larry Allain USGS, hosted by the USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Rubiales |
| Family: | Rubiaceae |
| Genus: | Oldenlandia |
| Species: | L. boscii |
| Binomial name | |
| Oldenlandia boscii DC. | |
| |
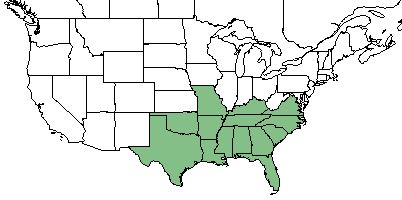
| Natural range of Oldenlandia boscii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Hedyotis boscii A.P. de Candolle.[1]
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
O. boscii has been found in pine flatwoods, floodplain forest clearings, and small ponds.[2] It is also found in disturbed areas including borrow pits, powerline corridors, and roadsides.[2] Associated species: Polypremum procumbens, Juncus repens, Eremochloa ophiuroides, Rotala ramosior, Lindernia dubia, Diodia teres, and Diodia virginiana.[2]
Fire ecology
Populations of Oldenlandia boscii have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[3]
Pollination and use by animals
This species has been observed to flower from June to November.[4]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: L.C. Anderson and R.K. Godfrey. States and counties: Florida: Calhoun, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, and Santa Rosa.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021