Difference between revisions of "Dyschoriste oblongifolia"
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
</ref> <ref name="Gilliam et al 2006">Gilliam, F. S., W. J. Platt, et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.</ref><ref>Wade, K. A. and E. S. Menges (1987). "Effects of fire on invasion and community structure of a southern Indiana cedar barrens." Indiana Academy of Science 96: 273-286.</ref> It is abundant in longleaf pine communities.<ref name="Simkin et al 2001"/> Resides in upland, midslope, and lowland areas old growth longleaf pine/wiregrass sandhill habitat.<ref name="Gilliam et al 2006"/> In deep sand soils it can grow in human disturbed areas such as recently cleared pine forests, ruderal edges of sandhills, roadsides, plowed areas, bulldozed areas, and open fields.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> This suggests that its absence from Ultisols influenced by past agriculture may be in part due to changes in the soil structure associated with erosion of the sandy A horizon,<ref name="KMR"/> and it may also relate to loss of native ants that act as seed dispersers.<ref name="Creech et al 2012">Creech, M. N., L. K. Kirkman, et al. (2012). "Alteration and Recovery of Slash Pile Burn Sites in the Restoration of a Fire-Maintained Ecosystem." Restoration Ecology 20(4): 505-516.</ref> ''D. oblongifolia'' can grow in both full light and semi shaded environments in deep, loose, and/or loamy sands along ridges and generally flat areas.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> It is also a characteristic species of the shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands habitat in the Red Hills Region of north Florida and south Georgia.<ref>Clewell, A. F. (2013). "Prior prevalence of shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands in the Tallahassee red hills." Castanea 78(4): 266-276.</ref> | </ref> <ref name="Gilliam et al 2006">Gilliam, F. S., W. J. Platt, et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.</ref><ref>Wade, K. A. and E. S. Menges (1987). "Effects of fire on invasion and community structure of a southern Indiana cedar barrens." Indiana Academy of Science 96: 273-286.</ref> It is abundant in longleaf pine communities.<ref name="Simkin et al 2001"/> Resides in upland, midslope, and lowland areas old growth longleaf pine/wiregrass sandhill habitat.<ref name="Gilliam et al 2006"/> In deep sand soils it can grow in human disturbed areas such as recently cleared pine forests, ruderal edges of sandhills, roadsides, plowed areas, bulldozed areas, and open fields.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> This suggests that its absence from Ultisols influenced by past agriculture may be in part due to changes in the soil structure associated with erosion of the sandy A horizon,<ref name="KMR"/> and it may also relate to loss of native ants that act as seed dispersers.<ref name="Creech et al 2012">Creech, M. N., L. K. Kirkman, et al. (2012). "Alteration and Recovery of Slash Pile Burn Sites in the Restoration of a Fire-Maintained Ecosystem." Restoration Ecology 20(4): 505-516.</ref> ''D. oblongifolia'' can grow in both full light and semi shaded environments in deep, loose, and/or loamy sands along ridges and generally flat areas.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> It is also a characteristic species of the shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands habitat in the Red Hills Region of north Florida and south Georgia.<ref>Clewell, A. F. (2013). "Prior prevalence of shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands in the Tallahassee red hills." Castanea 78(4): 266-276.</ref> | ||
| − | ''D. oblongifolia'' was found to have reduced occurrence or it became absent in response to soil disturbance by agriculture in the South Carolina coastal plains and southwest Georgia.<ref name=brudvig11>Brudvig, L.A. and E.I. Damchen. (2011). Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.</ref><ref name=hedman>Hedman, C.W., S.L. Grace, and S.E. King. (2000). Vegetation composition and structure of southern coastal plain pine forests: an ecological comparison. Forest Ecology and Management 134:233-247.</ref><ref name=kirkman>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref | + | ''D. oblongifolia'' was found to have reduced occurrence or it became absent in response to soil disturbance by agriculture in the South Carolina coastal plains and southwest Georgia.<ref name="Ostertag and Robertson 2007"/><ref name=brudvig11>Brudvig, L.A. and E.I. Damchen. (2011). Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.</ref><ref name=hedman>Hedman, C.W., S.L. Grace, and S.E. King. (2000). Vegetation composition and structure of southern coastal plain pine forests: an ecological comparison. Forest Ecology and Management 134:233-247.</ref><ref name=kirkman>Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.</ref> It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished habitats that were disturbed by agricultural practices, making it a remnant woodland indicator species.<ref name=brudvig13>Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.</ref><ref name=brudvig14>Brudvig, L.A., J.L. Orrock, E.I. Damschen, C.D. Collins, P.G. Hahn, W.B. Mattingly, J.W. Veldman, and J.L. Walker. (2014). Land-Use History and Contemporary Management Inform an Ecological Reference Model for Longleaf Pine Woodland Understory Plant Communities. PLoS ONE 9(1): e86604.</ref> |
Although it spreads by runners, it does not compete well with larger and denser species.<ref name="Huegel"/> | Although it spreads by runners, it does not compete well with larger and denser species.<ref name="Huegel"/> | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 7 July 2021
| Dyschoriste oblongifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
| photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Acanthaceae |
| Genus: | Dyschoriste |
| Species: | D. oblongifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Dyschoriste oblongifolia (Michx.) Kunz | |
| |
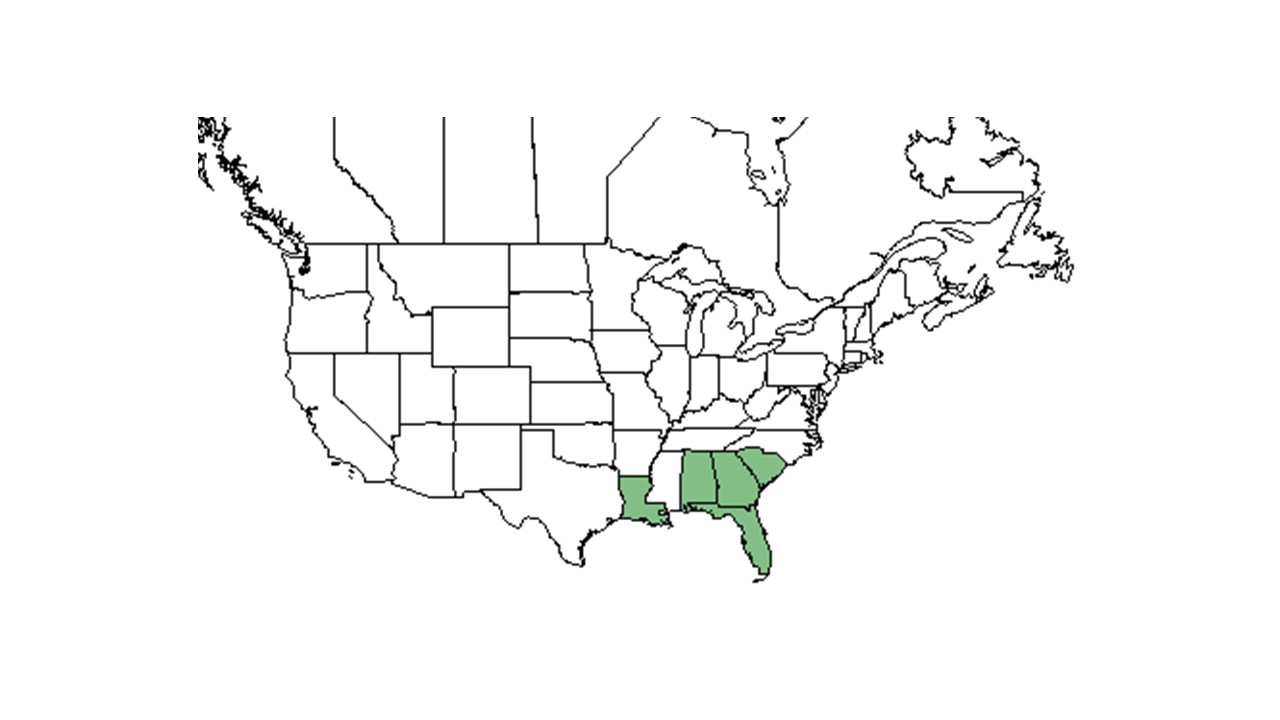
| Natural range of Dyschoriste oblongifolia. Image from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: oblongleaf snakeherb; oblongleaf twinflower; blue twinflower; pineland Dyschoriste
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: none.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
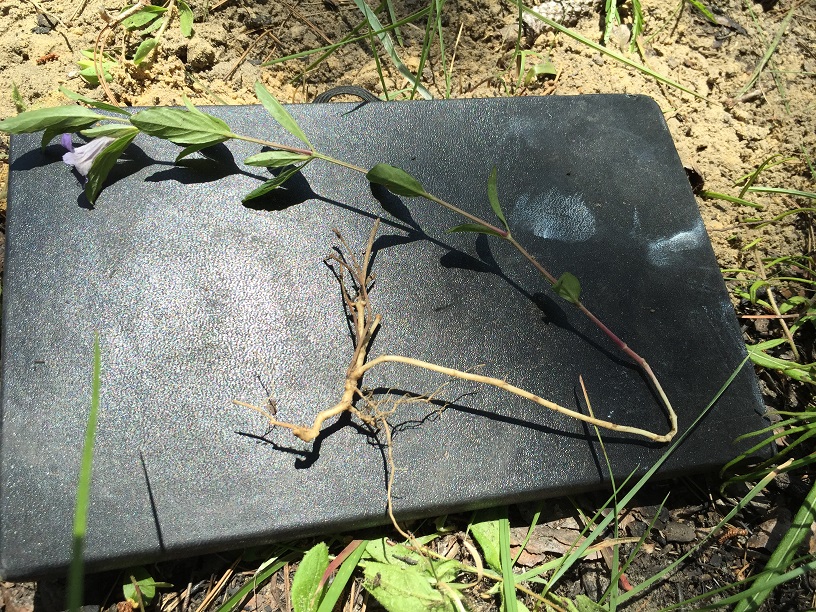
Dyschoriste oblongifolia is a perennial herb with opposite branches from elongate, slender rhizomes. Plant 1-5 dm tall; stems pilose. Leaves glabrate, oblanceolate to eliptic, to 4.5 cm long and 1.5 cm wide, entire or undulate, ciliate, sesslie or subsessile. Flowers subsessile, solitary or clustered in the leaf axils; bracts foliaceous, opposite, 15-18 mm long. Calyx pubescent, 15-20 cm long, tube short, lobes 5, linear-aristate; corolla 1.5-3 cm long, blue, funnelform, somewhat 2-lipped, lobes 5, 5-10 cm long; stamens 4, anther locules parallel; style to 1.5 cm long, 1-2 ovlues per locule, seeds 1 per locule, gray, ca. 2.5 mm broad. Capsules, brown, oblong, 12-14 mm long, ca. 3 mm in diameter. [2]
D. oblongifolia is a low-growing groundcover that spreads by underground runners.[3]
Distribution
The Florida distribution is provided by the Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants.
Ecology
Habitat
General habitats include pine flatwoods, savannas, and sandhills.[4] Indicator of native (unplowed) longleaf pine woodlands in upland Ultisol soils, and conversely rarely found on pasture or cultivated lands in that soil type[5][6][7]. Appears to be restricted to soils with a sandy A horizon, whether in Entisols (sandhills) or Ultisols (clayhills).[8] Where present in native longleaf pine-wiregrass habitats it is common and abundant.[9][6]
Dyschoriste oblongifolia has been found to be strongly associated with native groundcover as opposed to old-field groundcover upland pinelands of southern Georgia.[6] This species also has been observed in scrub environments, turkey oak barrens, wiregrass-palmetto flatwoods, mixed hardwood forests, mixed pine-hardwoods, and slopes and ridges of longleaf pine forests. [10] [11][12] It is abundant in longleaf pine communities.[13] Resides in upland, midslope, and lowland areas old growth longleaf pine/wiregrass sandhill habitat.[11] In deep sand soils it can grow in human disturbed areas such as recently cleared pine forests, ruderal edges of sandhills, roadsides, plowed areas, bulldozed areas, and open fields.[10] This suggests that its absence from Ultisols influenced by past agriculture may be in part due to changes in the soil structure associated with erosion of the sandy A horizon,[8] and it may also relate to loss of native ants that act as seed dispersers.[7] D. oblongifolia can grow in both full light and semi shaded environments in deep, loose, and/or loamy sands along ridges and generally flat areas.[10] It is also a characteristic species of the shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands habitat in the Red Hills Region of north Florida and south Georgia.[14]
D. oblongifolia was found to have reduced occurrence or it became absent in response to soil disturbance by agriculture in the South Carolina coastal plains and southwest Georgia.[6][15][16][17] It has shown resistance to regrowth in reestablished habitats that were disturbed by agricultural practices, making it a remnant woodland indicator species.[18][19]
Although it spreads by runners, it does not compete well with larger and denser species.[3]
Associated species include Serenoa repens, Ilex glabra, Myrica, Aristida, Quercus laevis, Scutellaria multiglandulosa, Tephrosia virginiana.[10]
Dyschoriste oblongifolia is an indicator species for the North Florida Subxeric Sandhills community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[20]
Phenology
D. oblongifolia generally flowers from April until May.[4] It germinates and flowers within a few weeks following fire at a wide range of burn dates, at least from March to July.[8] It has been observed to flower from March to November with peak inflorescence in April and May.[21][10] Kevin Robertson has observed this species flower within three months of burning. KMR
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by ants.[7] Although it spreads primiarily by underground runners, it does produce many seeds when its seed capsules split open.[3] This species is thought to be dispersed by ants and/or explosive dehiscence. [22]
Fire ecology
It has been found in both burned and unburned areas.[10] It resprouts rapidly after fire[13] and flowers predictably within one or two months following burning in the spring and summer.[8][23] Conversely, flowering is rather sparse and inconsistent in years without fire.[24] On Long Pine Key in Everglades National Park, D. oblongifolia was found to flower and fruit from May to September one year following an April fire and to a lesser degree in April to June two years following the fire, but it did not flower or fruit at all in plots burned six years prior.[25]
Pollination and use by animals
Dyschoriste oblongifolia attracts many pollinators, especially bees.[3] D. oblongifolia is a larval food sources for the common buckeye butterfly (Junonia coenia).[3] D. oblongifolia has been observed to be eaten by adult and juvenile gopher tortoises (Gohperus polyphemus).[26]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
D. oblongifolia is critically imperiled in the state of Alabama.[27]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Radford, A.E., H.E. Ahles, and C.R. Bell. 1968. Manual of the vascular flora of the Carolinas. The University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1183 pp.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Huegel, Craig. [Florida Native Wildflowers] Accessed November 13, 2015
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Brudvig, L. A. and E. I. Damschen (2010). "Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition." Ecography 34: 257-266.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Ostertag, T.E. and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference Proceedings 23:109-120.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Creech, M. N., L. K. Kirkman, et al. (2012). "Alteration and Recovery of Slash Pile Burn Sites in the Restoration of a Fire-Maintained Ecosystem." Restoration Ecology 20(4): 505-516.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 Robertson, Kevin M. personal observation.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K., M. B. Drew, et al. (1998). "Effects of experimental fire regimes on the population dynamics of Schwalbea americana L." Plant Ecology 137: 115-137.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 Mast, A. R., A. Stuy, G. Nelson, A. Bugher, N. Weddington, J. Vega, K. Weismantel, D. S. Feller, and D. Paul. 2004 onward (continuously updated). Database of Florida State University's Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium. Website http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu/ [accessed 13 November 2015]. Collectors: Andre Clewell, Robert Godfrey, Robert Kral, P.L. Redfearn, Jr., William P. Adams, Loran Anderson, Richard Carter, H. Larry Stripling, S.W. Leonard, Gwynn W. Ramsey, R.S. Mitchell, George Cooley, James D. Ray, Jr., C.E. Wood, C.E. Smith, R.J. Eaton, Roy Komarek, Gary R. Knight, Mark A. Garland, C. Jackson, Mary Margaret Williams, T. Myint, Grady W. Reinert, Bill & Pam Anderson, John B. Nelson, R. L. Wilbur, C. R. Bell, Rodie White, R. A. Norris, D. C. Hunt, and Wilson Baker. States and Counties: Alabama: Heny. Florida: Charlotte, Citrus, Clay, Columbia, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Marion, Orange, Pasco, Polk, Seminole, Suwannee, Taylor, Volusia, and Wakulla. Georgia: Bryan, Grady, McIntosh, Seminole, Sumter, and Thomas. South Carolina: Hampton and Jasper.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Gilliam, F. S., W. J. Platt, et al. (2006). "Natural disturbances and the physiognomy of pine savannas: A phenomenological model." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 83-96.
- ↑ Wade, K. A. and E. S. Menges (1987). "Effects of fire on invasion and community structure of a southern Indiana cedar barrens." Indiana Academy of Science 96: 273-286.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Simkin, S. M., W. K. Michener, et al. (2001). "Plant response following soil disturbance in a longleaf pine ecosystem." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 128: 208-218.
- ↑ Clewell, A. F. (2013). "Prior prevalence of shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands in the Tallahassee red hills." Castanea 78(4): 266-276.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A. and E.I. Damchen. (2011). Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.
- ↑ Hedman, C.W., S.L. Grace, and S.E. King. (2000). Vegetation composition and structure of southern coastal plain pine forests: an ecological comparison. Forest Ecology and Management 134:233-247.
- ↑ Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., J.L. Orrock, E.I. Damschen, C.D. Collins, P.G. Hahn, W.B. Mattingly, J.W. Veldman, and J.L. Walker. (2014). Land-Use History and Contemporary Management Inform an Ecological Reference Model for Longleaf Pine Woodland Understory Plant Communities. PLoS ONE 9(1): e86604.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 8 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Pavon, M. L. (1995). Diversity and response of ground cover arthropod communities to different seasonal burns in longleaf pine forests. Tallahassee, Florida A&M University.
- ↑ Robertson, Kevin M. observations at Pebble Hill Fire Plots on Pebble Hill Plantation near Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Gunderson, L., D. Taylor and J. Craig 1983. Report SFRC-83/04 Fire effects on flowering and fruiting patterns of understory plants in pinelands of EVER. Everglades National Park, South Florida Research Center, Homestead, Florida, 36 pg. URL https://ufdcimages.uflib.ufl.edu/FI/83/25/63/47/00001/FI83256347.pdf
- ↑ Mushinsky, H. R., Terri A. Stilson and Earl D. McCoy (2003). "Diet and Dietary Preference of the Juvenile Gopher Tortoise " Herpetologists' League 59(4): 475-486.
- ↑ [[1]] NatureServe Explorer. Accessed: May 3, 2019
