Difference between revisions of "Juncus polycephalos"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | + | ===Pollination and use by animals=== | |
| − | < | + | The ''Juncus'' genus has been observed to host planthoppers from the family Delphacidae such as ''Nothodelphax consimilis'' and ''Nothodelphax occlusa''.<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> |
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 15:57, 23 June 2021
Common names: Many-headed rush [1]
| Juncus polycephalos | |
|---|---|
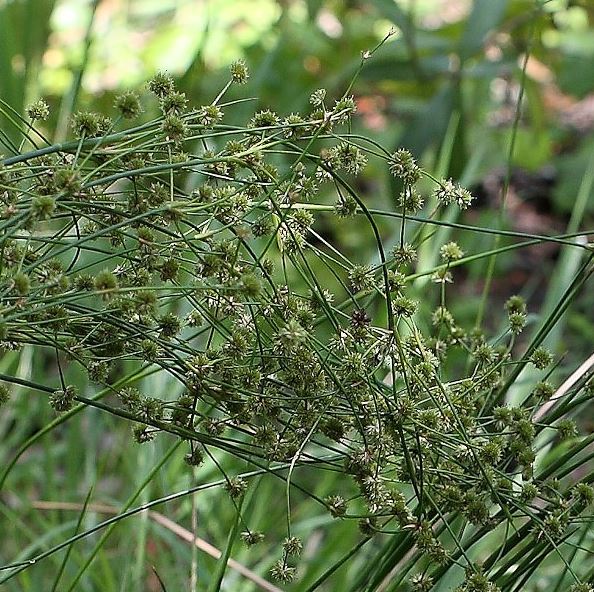

| |
| Photo by John B | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Juncales |
| Family: | Juncaceae |
| Genus: | Juncus |
| Species: | J. polycephalos |
| Binomial name | |
| Juncus polycephalos Michx. | |
| |
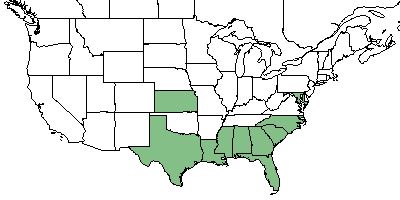
| Natural range of Juncus polycephalos from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none.[2]
Varieties: none.[2]
Description
J. polycephalos is a perennial graminoid of the Juncaceae family that is native to North America.[1]
Distribution
J. polycephalos is found in Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Texas, Kansas, and Maryland.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
J. polycephalos is found in sandy pond margins, ditches, and savannas.[3]
Phenology
J. polycephalos flowers July through September.[4]
Pollination and use by animals
The Juncus genus has been observed to host planthoppers from the family Delphacidae such as Nothodelphax consimilis and Nothodelphax occlusa.[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]