Difference between revisions of "Ilex ambigua"
(→Pollination) |
(→Pollination and use by animals) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
===Pollination and use by animals=== | ===Pollination and use by animals=== | ||
| − | The drupes are eaten by animals such as birds, white-tailed deer, and squirrels.<ref name="fs"/> The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Ilex ambigua'' at the Archbold Biological Station:<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | + | The drupes are eaten by animals such as birds, white-tailed deer, and squirrels.<ref name="fs"/> |
| + | |||
| + | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Ilex ambigua'' at the Archbold Biological Station:<ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> | ||
Bees from the family Apidae: ''Apis mellifera'' | Bees from the family Apidae: ''Apis mellifera'' | ||
Revision as of 13:51, 22 June 2021
| Ilex ambigua | |
|---|---|

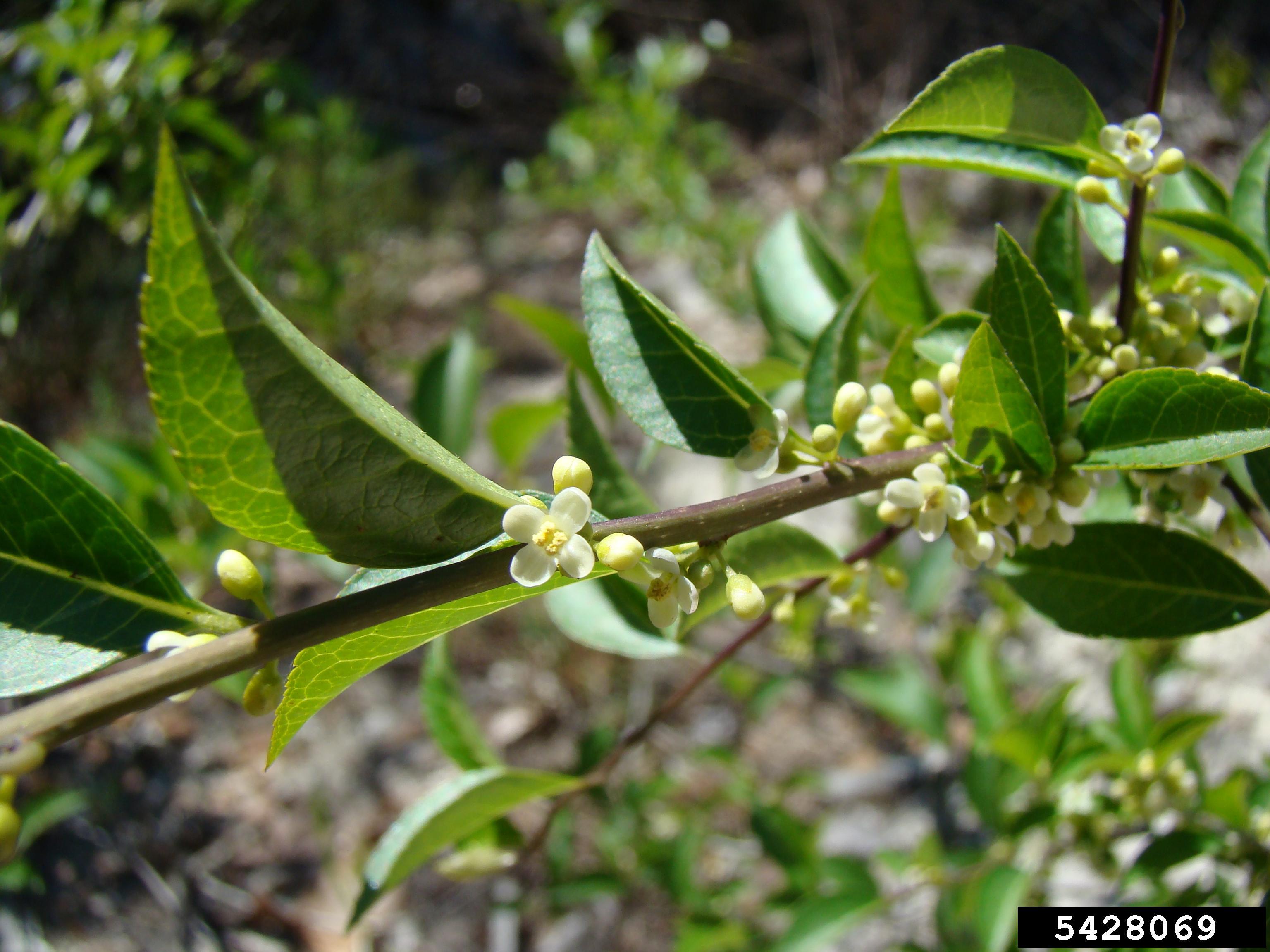
| |
| Photo by Rebekah D. Wallace, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Celastrales |
| Family: | Aquifoliaceae |
| Genus: | Ilex |
| Species: | I. ambigua |
| Binomial name | |
| Ilex ambigua (Michx.) Torr. | |
| |
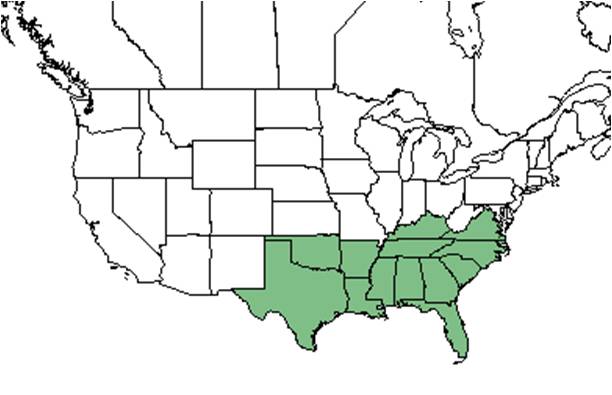
| Natural range of Ilex ambigua from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Carolina holly[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: I. montana var. mollis (A. Gray) Britton; I. montana var. beadlei W.W. Ashe) Fernald; I. beadlei W.W. Ashe; I. buswellii Small; I. beadlei var. laevis W.W. Ashe; I. caroliniana Trelease ex Small; I. mollis A. Gray.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Ilex derives from the ancient name of the European holly oak and ambigua refers to the similarity to other Ilex species.[2]
Description
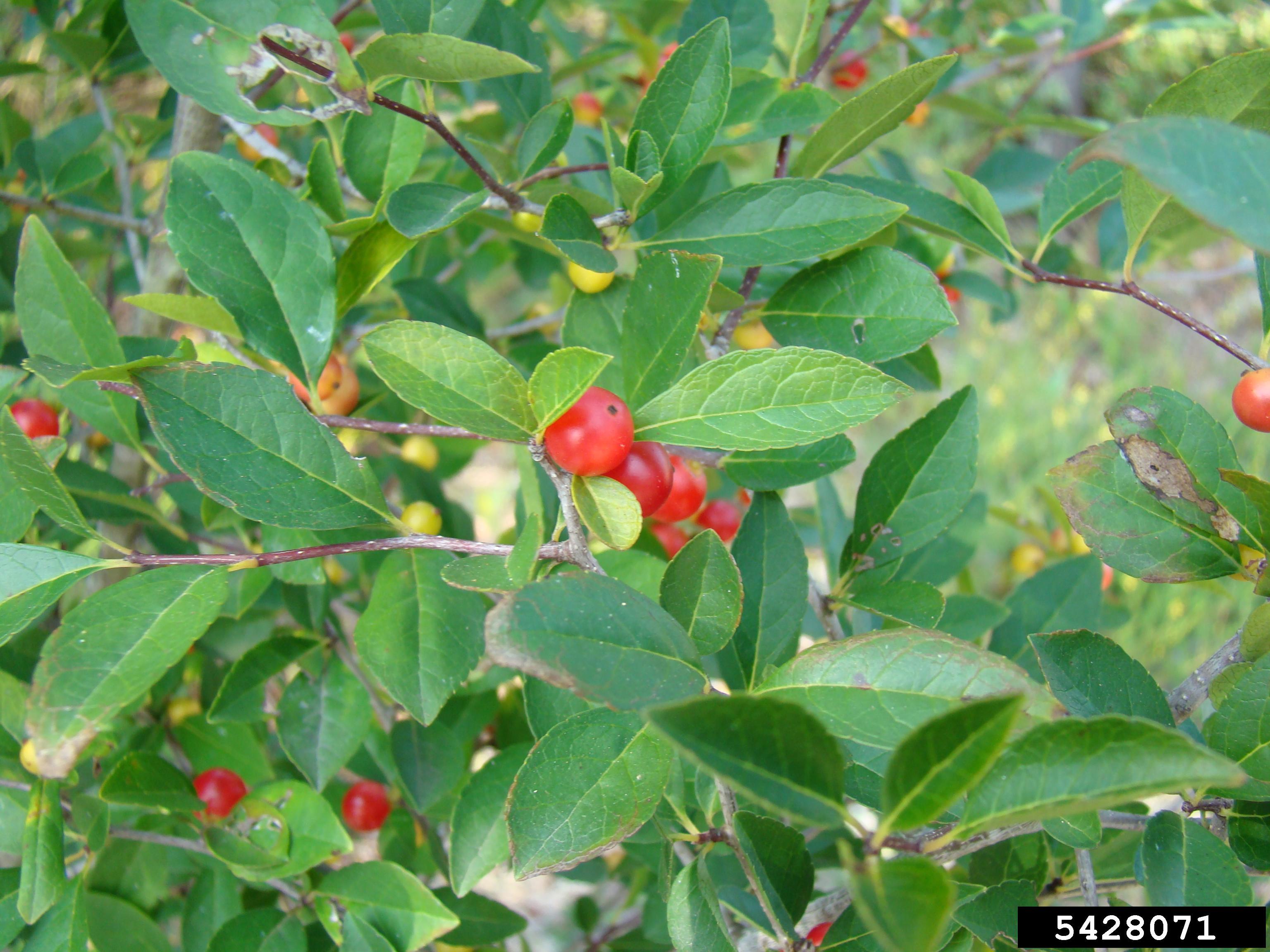
I. ambigua is a perennial large shrub or small tree that has glabrous to densely pubescent, irregular branches. The fruit is a red, translucent drupe that is eaten by animals such as birds, squirrels, and deer.[3]
"Trees or shrubs, usually with imperfect flowers. Leaves simple, entire, serrate, dentate or crenate; stipules obsolete. Flowers axillary, solitary, fascicled or in cymes, 4-7 merous, 4-8 mm broad; petals united at the base, imbricate in bud; pistillate flowers usually with nonfunctional stamens; anthers opening lengthwise; stigmas 4-7, essentially sessile. Drupe red, black or rarely yellow or white. Seeds with hard, bony endocarp (pyrenes), often grooved or ribbed on the back, 4-7 in a fruit, 1 in each locule."[4]
"Small to large shrub or small tree, branches glabrous to densely pubescent. Leaves deciduous, glabrous to densely pubescent, beneath, glabrous to slightly pubescent and dull above, lanceolate, or obovate to elliptic, 4-18 cm long, 1.5-7 cm wide, acute or acuminate, finely to coarsely serrate, or crenate-serrate; petioles 0.3-1.5 cm long. Pedicels 1-3 mm long, glabrous to densely pubescent. Staminate flowers fascicled, usually on spur shoots. Pistillate flowers axillary, solitary, usually on short sour growths. Flowers 4-merous. Drupe red, translucent, globose, 5-9 mm in diam.; pyrenes 4, with fairly deep furrows on the back, 4-7 mm long. This is probably our most polymorphic species and is here recognized by two fairly distinct varieties: var. ambigua and var. montana."[4]
Distribution
The native range includes the Coastal Plain from North Carolina, northern Georgia, northern Alabama, central Arkansas, and southeastern Oklahoma south to central Florida, the Gulf Coast, and eastern Texas.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, Ilex ambigua occurs in well-drained sites such as magnolia-hickory hammocks, longleaf pine-turkey oak sand ridges, edges of limestone sinks, Pinus clausa/Ceratolia scrubs, stabilized sand dunes, and calcareous slopes in mesic deciduous woodlands.[5] Stephenson (1986) found that I. ambigua is one of the leading dominants in successional areas that were once dominated by the American chestnut. It appears in disturbed areas such as old fields, railroad beds, and disturbed pine flatwoods.[5] Soils include loam, sand, loamy sand, and reddish clay.[5] Associated species include Ilex vomitoria, I. opaca, I. glabra, Panicum commutatum, Calamintha georgiana, Parthenocissus quinquefolia, Castanea pumila, Crataegus, Desmodium ochroleucum, and Commelina erecta.[5]
Phenology
This is a dioecious species that produces sessile, red, translucent, drupes when fertilized.[3] The fruits are elliptical, rather than round, and fall quickly after ripening.[6] This species flowers April through May[7] and fruits April through December.[5]
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by animals.[3]
Seed bank and germination
No specific information is available for seed germination requirements.[3]
Fire ecology
It occurs in Florida sand pine scrubs which are maintained by fire every 10 to 100 years; however, it may be eliminated from the understory in communities that are subject to frequent fires. When fire is suppressed in sand pine scrubs, I. ambigua is one of the early successional hardwoods that appear.[3]
Pollination and use by animals
The drupes are eaten by animals such as birds, white-tailed deer, and squirrels.[3]
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Ilex ambigua at the Archbold Biological Station:[8]
Bees from the family Apidae: Apis mellifera
Sweat bees from the family Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Lasioglossum pectoralis
Wasps from the family Leucospididae: Leucospis slossonae
Spider wasps from the family Pompilidae: Anoplius marginalis
Thread-waisted wasps from the family Sphecidae: Cerceris fumipennis, Isodontia mexicana
Wasps from the family Vespidae: Euodynerus boscii boharti, Polistes metricus, Stenodynerus lineatifrons, Zethus spinipes
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
This species is listed threatened by Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services[3].
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Flowers of Ilex ambigua Photo by Rebekah D. Wallace, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org
References and notes
Stephenson, S. L. (1986). "Changes in a Former Chestnut-Dominated Forest after a Half Century of Succession." American Midland Naturalist 116(1): 173-179.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ [[1]] Accessed: January 6, 2016
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 [[2]]USDA Forest Service. Accessed: January 6, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 679-81. Print.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, George R. Cooley, Kathleen Craddock Burks, A. Gholson Jr., Robert K. Godfrey, Mary G. Henry, Melvin Jackson, Lisa Keppner, R. Kral, Sidney McDaniel, Mary E. Nolan, R.A. Norris, James D. Ray Jr. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Holmes, Jackson, Lake, Leon, Liberty, Okaloosa, Orange, Sarasota, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Baker, Decatur, Grady, Marion. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ [[3]] Accessed: January 6, 2016
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
