Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum undulatum"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''S. undulatum'' can be found in upland oak-hickory woods, limestone glades, and along pine-oak woodlands.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann F. Johnson. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Associated species include ''Pinus, Quercus,'' and ''Carya.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''S. undulatum'' can be found in upland oak-hickory woods, limestone glades, and along pine-oak woodlands.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann F. Johnson. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Pinus, Quercus,'' and ''Carya.''<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
''S. undulatum'' responds negatively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as an indicator species for remnant woodland.<ref>Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.</ref> | ''S. undulatum'' responds negatively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as an indicator species for remnant woodland.<ref>Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:32, 21 June 2021
| Symphyotrichum undulatum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken and permission granted by Jeff Pippen, JeffPippen.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. undulatum |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum undulatum (L.) G.L. Nesom | |
| |
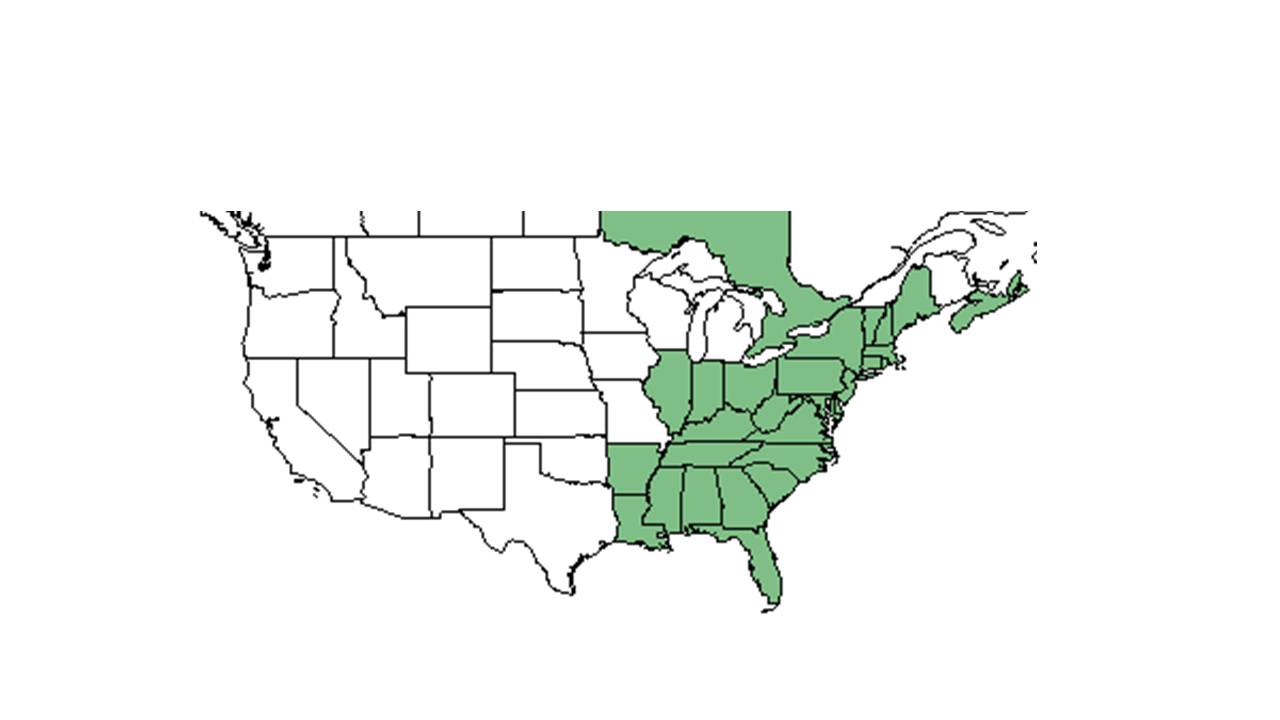
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum undulatum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Wavyleaf aster
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Aster undulatus Linnaeus; A. undulatus var. loriformis E.S. Burgess; A. undulatus var. diversifolius (Michaux) A. Gray; A. asperifolius E.S. Burgess; A. linguiformis E.S. Burgess; A. loriformis (E.S. Burgess) E.S. Burgess; A. mohrii E.S. Burgess; A. claviger E.S. Burgess; A. corrigiatus E.S. Burgess; A. gracilescens E.S. Burgess; A. proteus E.S. Burgess; A. sylvestris E.S. Burgess; A. triangularis (E.S. Burgess) E.S. Burgess; A. truellius E.S. Burgess; A. undulatus; A. undulatus Linnaeus var. asperulus (Torrey & A. Gray) Wood.[1]
Description
A description of Symphyotrichum undulatum is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, S. undulatum can be found in upland oak-hickory woods, limestone glades, and along pine-oak woodlands.[2]
Associated species include Pinus, Quercus, and Carya.[2] S. undulatum responds negatively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as an indicator species for remnant woodland.[3]
Phenology
It has been observed flowering in January, October and November.[2][4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
Symphyotrichum undulatum flowers Photos taken and permission granted by Jeff Pippen, JeffPippen.com
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann F. Johnson. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson, Jefferson. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021

