Difference between revisions of "Apios americana"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Effects on understory vegetation. International Journal of Wildland Fire 10:91-101.</ref> | Effects on understory vegetation. International Journal of Wildland Fire 10:91-101.</ref> | ||
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | ===Pollination and use by animals=== |
| − | The only pollinator identified for ''A. americana'' are bees of the family Megachilidae, though it has been speculated that they are fly pollinated.<ref name="Bruneau & Anderson 1994">Bruneau A, Anderson GJ (1994) To bee or not to bee?: The pollination biology of ''Apios americana'' (Leguminosae). Plant Systematics and Evolution 192:147-149.</ref> | + | The only pollinator identified for ''A. americana'' are bees of the family Megachilidae, though it has been speculated that they are fly pollinated.<ref name="Bruneau & Anderson 1994">Bruneau A, Anderson GJ (1994) To bee or not to bee?: The pollination biology of ''Apios americana'' (Leguminosae). Plant Systematics and Evolution 192:147-149.</ref> Additionally, this species has been observed to host ''Lygus lineolaris'' (family Miridae).<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> ''A. americana'' has been found to be consumed by white-tailed deer, but not commonly.<ref name= "Harlow">Harlow, R. F. (1961). "Fall and winter foods of Florida white-tailed deer." The Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 24(1): 19-38.</ref> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ''A. americana'' has been found to be consumed by white-tailed deer, but not commonly.<ref name= "Harlow">Harlow, R. F. (1961). "Fall and winter foods of Florida white-tailed deer." The Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 24(1): 19-38.</ref> | ||
==Diseases and parasites== | ==Diseases and parasites== | ||
Revision as of 15:09, 10 June 2021
| Apios americana | |
|---|---|
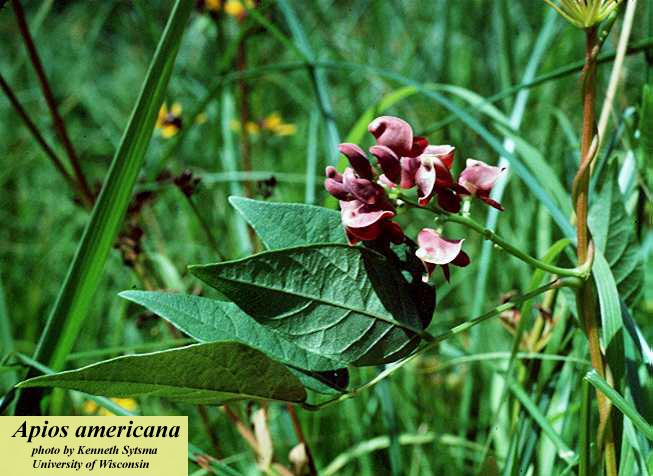

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Apios |
| Species: | A. americana |
| Binomial name | |
| Apios americana Medikus | |
| |
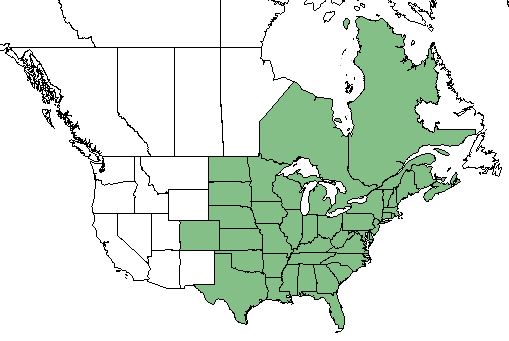
| Natural range of Apios americana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Names: Common Groundnut;[1] Groundnut;[2][3] Wild Potato; Indian Potato;[3]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Glycine apios Linnaeus. [4]
Varieties: none.[4]
Description
A. americana is a dioeceious perennial that grows as a forb/herb or a vine.[2] As a vine, it can reach 1-6 m in length[5] and produces maroon or reddish-brown pea-like flowers in compact racemes arising from leaf axils. Leaves are green and alternate.[3] The legume fruit is indehiscent and with usually 1 seed, and the seeds are oblong or square in shape with a dark brown wrinkled surface.[2]
Distribution
This species occurs from Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, and Quebec, westward to Minnesota and South Dakota, southward to southern Florida and Texas.[1] The plant can also be found cultivated in Europe.[6]
Ecology
Habitat
A. americana occurs in marshes (tidal and non-tidal), wet thickets, streambanks, and bottomland forests,[1] and has been observed along the borders of bodies of water and wet flatwoods, in loamy sand and calcareous soil, and in disturbed areas like roadsides.[7] It has been reported as common in a lakeshore cypress swamp on the east side of Lake Arbuckle, Polk County, FL.[8] In Washington D.C. marshes, relative cover of vegetation in reference sites was 1.60% and the relative density of seedlings emerging from seed bank samples was 1.12%.[9]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from June through August and fruiting from July though September.[1] On the Florida panhandle, A. americana has been observed flowering in April and June through September, with a peak inflorescence between August and September.[10] Flowering in large numbers during the winter month of January has been reported in the central peninsular Florida Polk County.[8]
Fire ecology
In southern Illinois brown shale barrens, Apios americana was absent in preburn sampling but present postburn, suggesting the species may require, or at least do well, in burned habitats.[11] A different study in Michigan white pine/red pine stands showed the mean percent coverage was greatest when burned once (1.62%) over a five year period (1991-1995). Biennial burn frequencies had a mean percent coverage of 1.09% and unburned areas covered 0.29%.[12]
Pollination and use by animals
The only pollinator identified for A. americana are bees of the family Megachilidae, though it has been speculated that they are fly pollinated.[6] Additionally, this species has been observed to host Lygus lineolaris (family Miridae).[13] A. americana has been found to be consumed by white-tailed deer, but not commonly.[14]
Diseases and parasites
In Baton Rouge, Louisiana, cucumber mosaic virus and Desmodium yellow mottle virus are reported to be causal agents of diseases in A. americana.[15]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
The cord-like rootstalk contains edible tubers that have been eaten historically by Native Americans and the Pilgrims in soups, stews, or fried like potatoes. Cooked seeds can also be consumed by humans.[3] It was a food source for multiple Native American tribes, including the Omaha, Dakota, Santee Sioux, Cheyenne, Osage, Pawnee, and Hidatsa. Groundnuts were eaten raw, cooked, dried, or even ground for flour. As well, the rhizomes were stored by boiling, peeling, and drying them, and the seeds are cooked and eaten like peas during the summer.[2][16]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 16 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Plant database: Apios americana. (16 February 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL:https://www.wildflower.org/plants/search.php?search_field=&newsearch=true
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Reynolds BD, Blackmon WJ, Wickremesinhe E, Wells MH, Constantin RJ (1988) Domestication of Apios americana. Janick J, Simon JE (eds.) In Advances in new crops: Proceedings of the first national symposium 'New crops: research, development, economics'. Indianapolis, Indiana. 23-26 October 1988.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Bruneau A, Anderson GJ (1994) To bee or not to bee?: The pollination biology of Apios americana (Leguminosae). Plant Systematics and Evolution 192:147-149.
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: March 2019. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, H. L. Blomquist, Frank Bowers, L. J. Brass, S. g. C., C. C. Christensen, R. F. Christensen, Delzie Demaree, David M. DuMond, Patricia Elliot, Robert K. Godfrey, C. C. Harris, Randy Haynes, Ron Hughes, S. K., J. M. Kane, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, R. Komarek, R. Kral, B. Kuser, Sidney McDaniel, Geo M. Merrill, John Morrill, John B. Nelson, Mary E. Nolan, Deborah Paul, James D. Ray, Jr., H. R. Reed, Fr. Edmond Roy, F. H. Sargent, A. J. Sharp, Al Skorepa, R. Stastny, John W. Thieret, L. J. Uttal, Mary E. Wharton, Rodie White, Roomie Wilson, D. R. Windler, and Jean W. Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Dixie, Franklin, Gulf, Highlands, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Nassau, Putnam, Sarasota, St Johns, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Alabama: Jackson. Arkansas: Pulaski and St Francis. Georgia: Decatur, Grady, Rabun, Thomas, and Walker. Kentucky: Powell. Louisiana: Iberia, St Mary, and Tangipahoa. Maryland: Dorchester. Massachusetts: Essex and Franklin. Mississippi: Oktibbeha, Pearl River, and Quitman. New Hampshire: Carroll. North Carolina: Carteret. South Carolina: Clarendon, Fairfield, and Richland. Tennessee: Polk. Texas: Freestone. Virginia: Mecklenburg, Montgomery, and Prince Edward.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Observation by Edwin Bridges at the east side of Lake Arbuckle, Polk County, FL, January 8, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group January 9, 2016.
- ↑ Baldwin AH, Derico EF (1999) The seed bank of a restored tidal freshwater marsh in Washington, DC. Urban Ecosystems 3:5-20.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 16 FEB 2018
- ↑ Heikens AL, West KA, Robertson PA (1994) Short-term response of chert and shale barrens vegetation to fire in southwestern Illinois. Castanea 59(3):274-285.
- ↑ Neumann DD, Dickmann DI (2001) Surface burning in a mature stand of Pinus resinosa and Pinus strobus in Michigan: Effects on understory vegetation. International Journal of Wildland Fire 10:91-101.
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]
- ↑ Harlow, R. F. (1961). "Fall and winter foods of Florida white-tailed deer." The Quarterly Journal of the Florida Academy of Sciences 24(1): 19-38.
- ↑ Valverde RA, Provvidenti R, Clark CA (1990) Cucumber mosaic virus and Desmodium yellow mottle virus infections in wild groundnut (Apios americana). Plant Disease 74:151-153.
- ↑ Gilmore, M. R. (1919). Uses of plants by the indians of the Missouri River region. B. o. A. E. Smithsonian Institution. 33rd Annual Report.