Difference between revisions of "Lechea mucronata"
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 16:55, 8 June 2021
| Lechea mucronata | |
|---|---|

| |
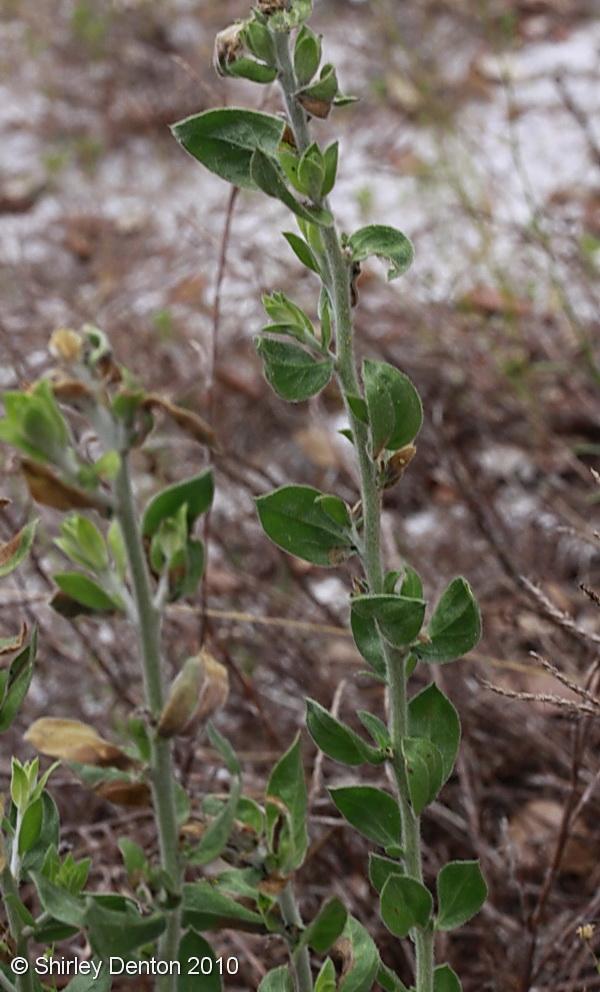
| Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Nature Photography by Shirley Denton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Violales |
| Family: | Cistaceae |
| Genus: | Lechea |
| Species: | L. mucronata |
| Binomial name | |
| Lechea mucronata Raf. | |
| |
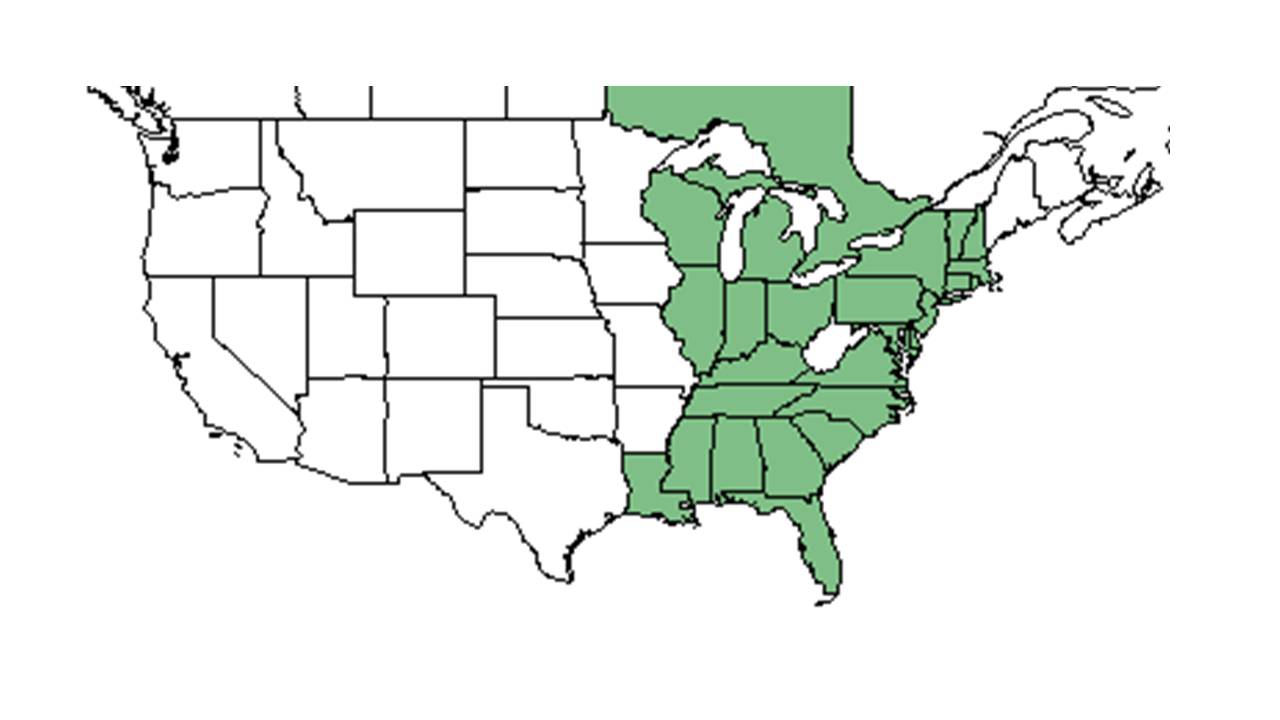
| Natural range of Lechea mucronata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Hairy pinweed[1]
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Lechea villosa Elliott; L. villosa var. typica.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
Frequent within sandhill habitats.[2]
Distribution
L. mucronata ranges from New Hampshire to Michigan and Oklahoma, them south to peninsular Florida, Texas, and northern Mexico.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species has been found in open areas in sandy soils of longleaf pine, scrub oak, wiregrass sand ridges as well as sandhills in general.[2] It has also been found in human disturbed areas around garbage dumps and powerline corridors (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Longleaf pine and wiregrass.[2] L. mucronata responds positively to soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain and longleaf pine communities.[3] It also responds positively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in the same South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as an indicator species for post-agricultural woodland.[4]
Phenology
This species has been observed flowering in June[5] and fruits July through October.[1]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by consumption by vertebrates.[6]
Fire ecology
Occurs in areas that are burned.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R.A. Norris, R.F. Doren, R. Komarek, Cecil R. Slaughter, and Lisa Keppner. States and Counties: Florida: Duval, Leon, St. Johns, and Washington. Georgia: Coffee and Grady.
- Jump up ↑ Brudvig, L.A. and E.I. Damchen. (2011). Land-use history, historical connectivity, and land management interact to determine longleaf pine woodland understory richness and composition. Ecography 34: 257-266.
- Jump up ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- Jump up ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
- Jump up ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.