Difference between revisions of "Euphorbia pubentissima"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) (→Taxonomic notes) |
|||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | ==Cultural use== |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Revision as of 15:08, 8 June 2021
| Euphorbia pubentissima | |
|---|---|
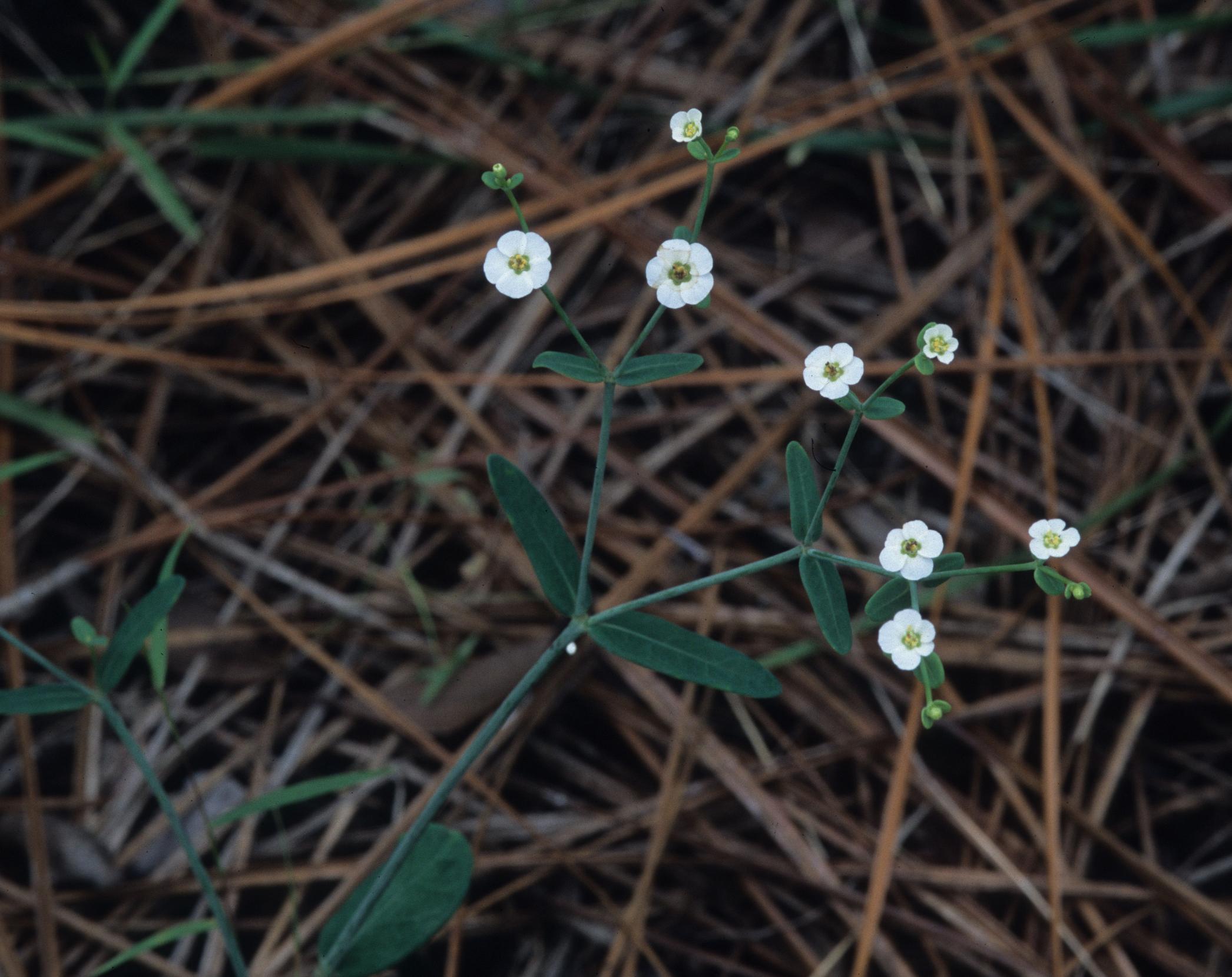

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Euphorbia |
| Species: | E. pubentissima |
| Binomial name | |
| Euphorbia pubentissima Michx. | |
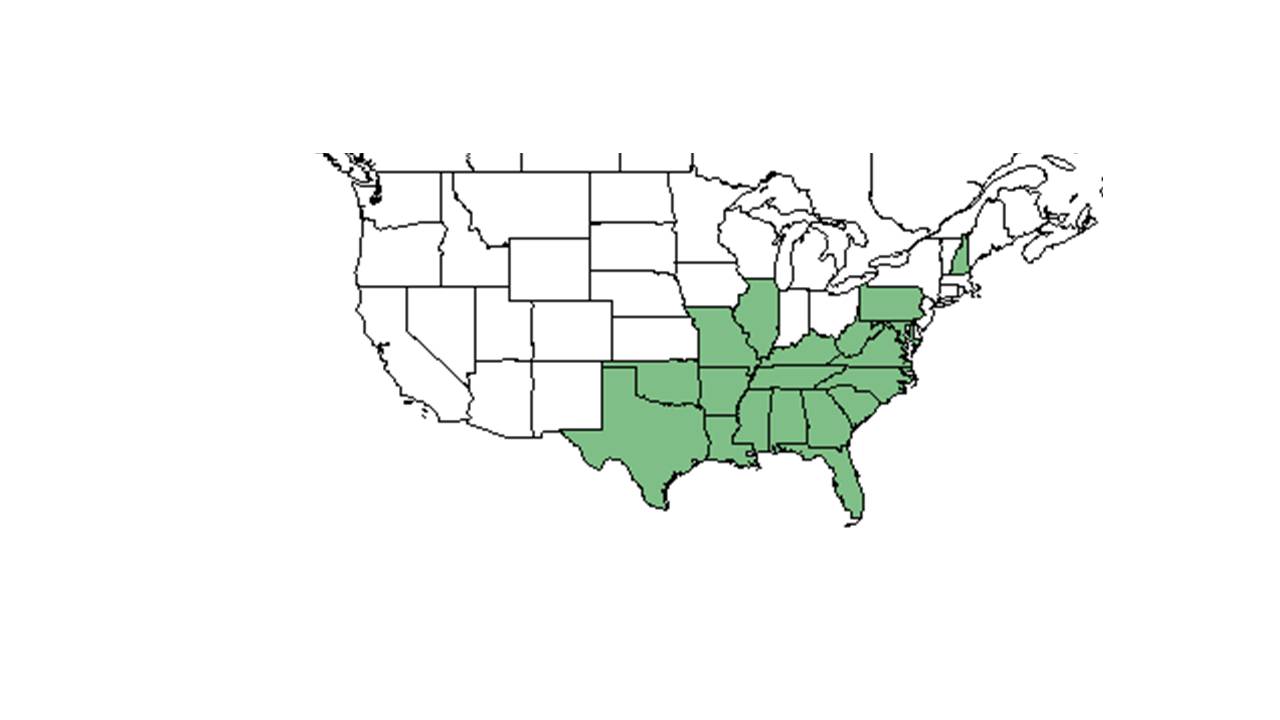
| |
| Natural range of Euphorbia pubentissima from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: False flowering spurge; Southeastern flowering spurge
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Agaloma pubentissima (Michaux) D.B. Ward; E. apocynifolia Small; E. corollata Linnaeus var. corollata; E. corollata var mollis Millspaugh; E. corollata var. paniculata Boissier; E. corollata Linnaeus var. zinniiflora (Small) H.E. Ahles; E. zinniiflora Small; Tithymalopsis apocynifolia (Small) Small; T. paniculata (Boissier) Small; T. zinniiflora (Small) Small.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in mesic wooded slopes of a ravine and also in a nature park.[2] E. pubentissima responds negatively to soil disturbance by agriculture in Southwest Georgia.[3]
Phenology
E. pubentissima has been observed flowering in October, after a prescribed burn in July, at Pebble Hill Plantation, Grady County, GA by Michelle M. Smith. It has also been observed flowering in May, September, and November.[4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by ants and/or explosive dehiscence. [5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden.
- ↑ Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. (2004). Journal of Ecology 92(3):409-421.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.