Difference between revisions of "Hexalectris spicata"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) (→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Blooming from June through August.<ref name=nelson/> It has also been observed fruiting in June and August.<ref name=fsu/> | + | Blooming from June through August.<ref name=nelson/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021</ref> It has also been observed fruiting in June and August.<ref name=fsu/> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
Revision as of 20:08, 7 June 2021
| Hexalectris spicata | |
|---|---|
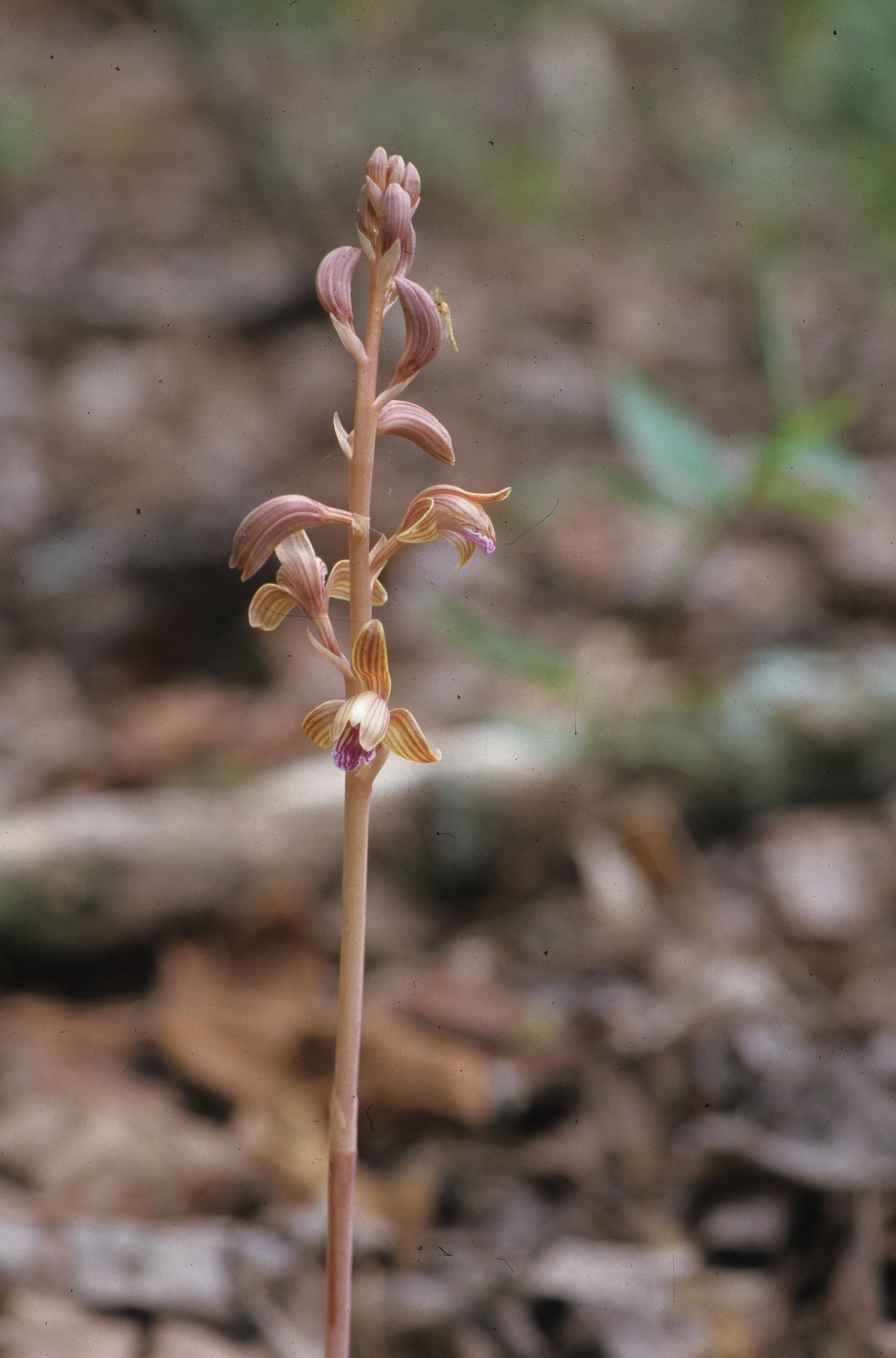

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Orchidales |
| Family: | Orchidaceae |
| Genus: | Hexalectris |
| Species: | H. spicata |
| Binomial name | |
| Hexalectris spicata (Walter) Barnhart | |
| |
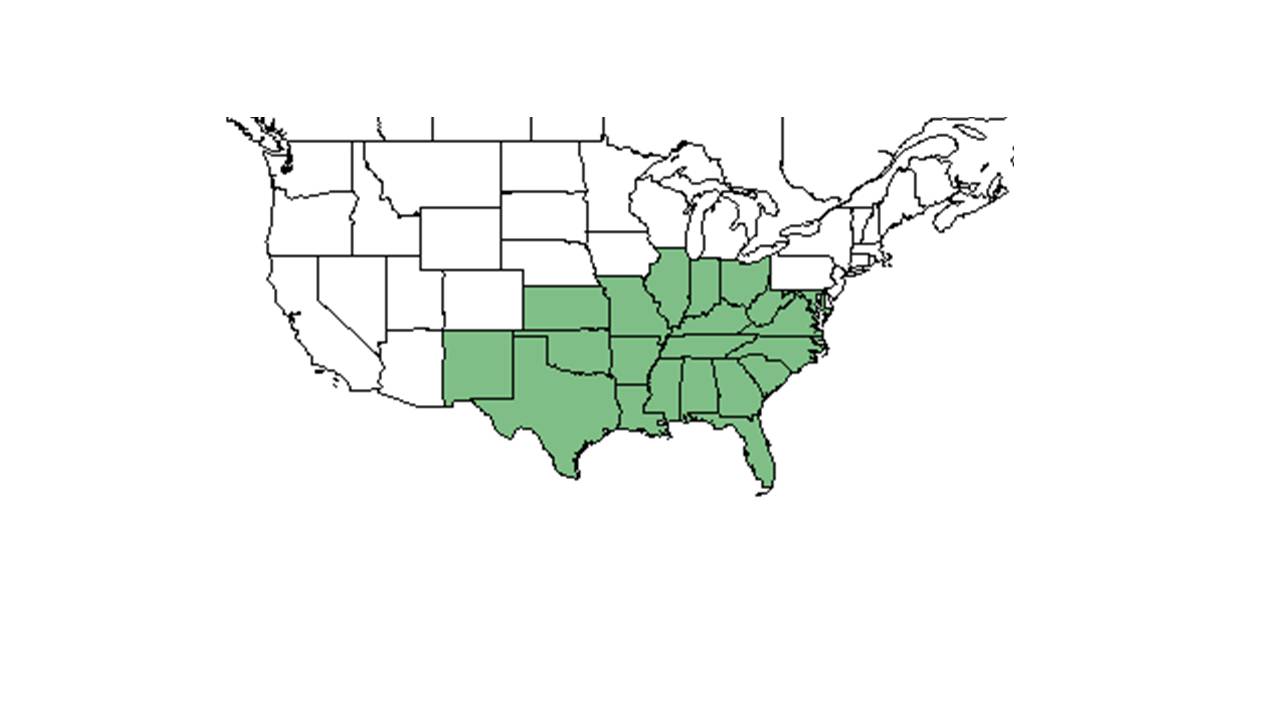
| Natural range of Hexalectris spicata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Crested coralroot (Nelson 2005)
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
A description of Hexalectris spicata is provided in The Flora of North America.
Hexalectris spicata is a perennial herbaceous species with rhizomes.[2]
Distribution
This plant's range extends from Maryland, Ohio, and Missouri to Florida and southwestern Texas.[1]
Ecology
H. spicata is a saprophytic orchid.[3]
Habitat
It is found in rich woods, stream banks, hardwood slope forests, mixed pine and hardwood forests, and shortleaf pine-oak-hickory forests.[3]
Phenology
Blooming from June through August.[3][4] It has also been observed fruiting in June and August.[2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Harry E. Ahles, Loran C. Anderson, Bill & Pam Anderson, A. F. Clewell, A. Gholson Jr., Robert K. Godfrey, John G. Haesloop, Dale R. Jackson, Rob Jemson, R. Kral, Mark Ludlow, Richard S. Mitchell, Jamie Trescott, Rodie White, and Lovett E. Williams. States and Counties: Alabama: Houston and Wilcox. Florida: Calhoun, Dixie, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Okaloosa, Suwannee, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Grady, and Seminole. South Carolina: Bamberg.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Nelson, Gil. East Gulf Coastal Plain Wildflowers. A Field Guide to the Wildflowers of the East Gulf Coastal Plain, including Southwest Georgia, Northwest Florida, Southern Alabama, Southern Mississippi, and Parts of Southeastern Louisiana. Guilford, CT: Falcon, 2005. 234. Print.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 19 MAY 2021
