Difference between revisions of "Gelsemium sempervirens"
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Generally, ''G. sempervirens'' flowers from February to early May, and fruits from September to November.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed to flower from January to April with peak inflorescence in February.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016</ref> Although it usually blooms briefly in the early spring, it can begin flowering as early as December and also bloom again in the early fall.<ref name= "lady bird"/> | + | Generally, ''G. sempervirens'' flowers from February to early May, and fruits from September to November.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed to flower from January to April with peak inflorescence in February.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016</ref> Although it usually blooms briefly in the early spring, it can begin flowering as early as December and also bloom again in the early fall. Greatest inflorescence is in full sun.<ref name= "lady bird"/> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 09:52, 17 May 2019
| Gelsemium sempervirens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Gentianales |
| Family: | Loganiaceae |
| Genus: | Gelsemium |
| Species: | G. sempervirens |
| Binomial name | |
| Gelsemium sempervirens (L.) W.T. Aiton | |
| |
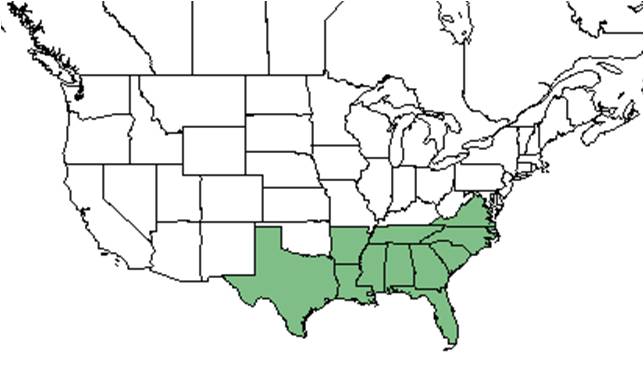
| Natural range of Gelsemium sempervirens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Evening trumpetflower; Yellow jessamine; Carolina jessamine
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
"High climbing or trailing vines, twining upward from left to right. Leaves evergreen, opposite, lanceolate to elliptic, 3-7 cm long, 1-2.5 cm wide, acute to acuminate, entire, base rounded to cuneate; petioles 2-7 mm long. Flowers actinomorphic, heterostylic, axillary, solitary or in cymes; pedicels short, bracteate. Sepals 5, separate to base, lanceolate,, 3-5 mm long, 1-2 mm wide; corolla 5-lobed, yellow, 2-3.8 cm long, the tube gradually flaring upward, lobes 7-10 mm long, spreading; stamens 5, attached to lower part of corolla tube, anthers sagittate; pistil 1, slender styled, 2-cleft, each divided again and appearing 4-cleft. Capsule compressed; seeds many, dull brown, the body roughly papillose." [1]
"Leaf base cuneate to rounded. Flowers very fragrant, usually solitary, rarely in 2-3 flowered cymes. Speals obtuse to subacute. Capsule oblong, 1.4-2 cm long, 0.8-1.2 cm broad, abruptly rounded to a beaked apex; seeds 0.7-1 cm long, membranously winged apically."[1]
Distribution
This species is generally found along the southeastern coastal plain from Virginia and Tennessee south to Florida and west to Texas and Arkansas.[2] More specifically, it can be found from Virginia, southeastern Tennessee, and Arkansas south to central peninsular Florida and eastern Texas. It is also disjunct in Mexico and Guatemala.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found in a large range of habitats, including swamp forests to even dry uplands as well as thickets, and it is also commonly an ornamental plant otherwise. It commonly climbs to the tops of trees.[3] As well, it is frequently found in abandoned fields, and can grow into a mound of tangled stems if left untouched.[4]
Phenology
Generally, G. sempervirens flowers from February to early May, and fruits from September to November.[3] It has been observed to flower from January to April with peak inflorescence in February.[5] Although it usually blooms briefly in the early spring, it can begin flowering as early as December and also bloom again in the early fall. Greatest inflorescence is in full sun.[4]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [6]
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Gelsemium sempervirens at Archbold Biological Station: [7]
Apidae: Bombus griseocollis, B. impatiens, Habropoda laboriosa
Use by animals
It consists of approximately 5-10% of the diet for large mammals and various terrestrial birds.[8] The leaves, roots, and flowers are poisonous for humans and livestock, and can be lethal. The nectar can also be toxic for honeybees if too much is consumed, and the nectar may also be toxic for humans.[4]
Diseases and parasites
Due to it being tenacious and adaptable overall, G. sempervirens does not have any serious insect or disease problems.[4]
Conservation and management
It is considered a species of special concern by the Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation, Natural Heritage Program.[2]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 17 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 [[1]] Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. Accessed: May 17, 2019
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.