Difference between revisions of "Desmodium glabellum"
(→Phenology) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| − | Common Names: | + | Common Names: Ticktrefoil <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref>, Smooth Beggarlice <ref name= "davis">Davis, J., J. Eric, et al. (2002). "Vascular flora of Piedmont Prairies: Evidence from several prairie remnants." Castanea 67(1): 1-12.</ref> |
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
Revision as of 19:41, 25 April 2019
Common Names: Ticktrefoil [1], Smooth Beggarlice [2]
| Desmodium glabellum | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Desmodium |
| Species: | D. glabellum |
| Binomial name | |
| Desmodium glabellum (Michx.) | |
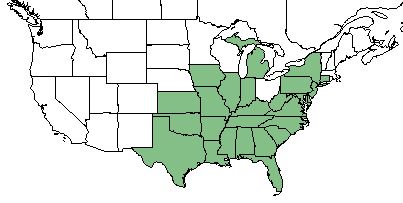
| |
| Natural range of Desmodium glabellum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: D. paniculatum, D. paniculatum var. dillenii (Darlington)
Variety: Meibomia paniculata (Linnaeus), Meibomia pubens (Torrey & A. Gray)
Description
D. glabellum is a perennial forb/herb of the Fabaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
The native distribution of D. glabellum is along hte United States east coast, west to Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
The ideal habitat for D. glabellum is with partial sun and dry conditions. Soil that has a rocky texture is ideal. Savannas, rocky upland forests, edges of more wooded areas, thickets and limestone glades are common regions for D. glabellum to be found. [1]
Phenology
D. glabellum has been observed to flower between August and October, with peak inflorescence in September. [3]
Seed dispersal
D. glabellum is a member of the pea family. It's pea pods or seeds have tiny hooked hairs on the shell that make them ideal for sticking to passing fur bearing animals for dispersal.[1] This species is thought to be dispersed by translocation on animal fur or feathers. [4]
Seed bank and germination
Firm seedbed is required for germination to be successful.[1]
Pollination
Bees are the primary pollinator for D. glabellum.[1]
Use by animals
Seeds from D. glabellum are eaten by birds, rodents, wild turkey, rabbits, groundhogs, and many livestocks. [3]
Diseases and parasites
White mold can occur on D. glabellum. Adult Japanese beetles will feed on the plant. [1]
Conservation and Management
D. glabellum has been placed on the special concern list for the state of Connecticut. [1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Davis, J., J. Eric, et al. (2002). "Vascular flora of Piedmont Prairies: Evidence from several prairie remnants." Castanea 67(1): 1-12.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 21 MAY 2018 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Pan Flora" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.