Difference between revisions of "Collinsonia punctata"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = Walter | | binomial_authority = Walter | ||
| range_map = COLL_PUNC_DIST.JPG | | range_map = COLL_PUNC_DIST.JPG | ||
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Collinsonia punctata''<ref>Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Collinsonia punctata''<ref name= "Weakley 2015">Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common Names: Florida | + | Common Names: Florida Horsebalm;<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> Blue Ridge Horsebalm;<ref name="USDA">USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 15 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> |
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
Revision as of 13:27, 15 April 2019
| Collinsonia punctata | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo by from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Collinsonia |
| Species: | C. punctata |
| Binomial name | |
| Collinsonia punctata Walter | |
| |
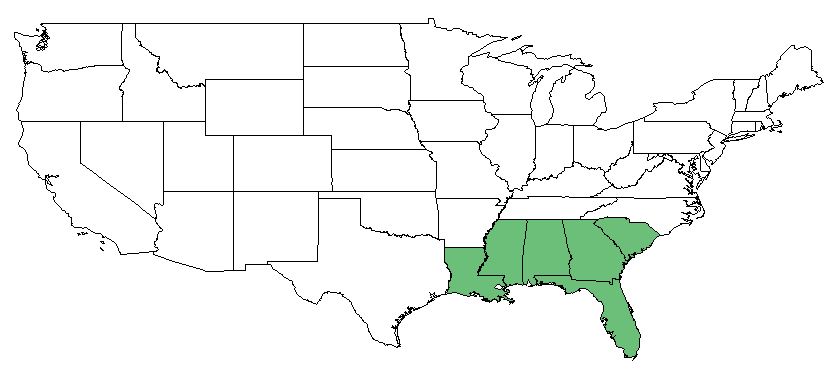
| Natural range of Collinsonia punctata[1] | |
Common Names: Florida Horsebalm;[1] Blue Ridge Horsebalm;[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: C. serotina;[1][2] C. canadensis var. punctata; Hypogon verticillata; Micheliella anisata[2]
The taxanomic identification of this species seems highly debated in the literature.[3] Collinsonia punctata is almost identical to Collinsonia anisata except for its different scent and the number of stamen (two).[4][5] In a 2006 manuscript, C. punctata is recognized as having two stamens instead of four and being an intermediate between C. canadensis and Collinsonia anisata.[3]
Description
Collinsonia punctata is a dioecious perennial forb/herb.[2]
Distribution
This species occurs from southern South Carolina to eastern Louisiana along the coastal plain.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
C. punctata is found in rich woods.[1]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs in late August to mid-October and fruiting from September through October.[1]
Use by animals
C. serotina composes 2-5% of the diet for some terrestrial birds.[6]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 15 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Peirson JA, Cantino PD, Ballard, Jr. HE (2006) A taxonomic revision of Collinsonia (Lamiaceae) based on phenetic analyses of morphological variation. Systematic Botany 31(2):398-409.
- ↑ Sims J (1809) Collinsonia anisata Curtis's Botanical Magazine 30:t.1213.
- ↑ Ward DB (2014) Thomas Walter typification project, VII: Observations on the genus Collinsonia (Labiatae) and a neotype for C. serotina Walter. Phytoneuron 89:1-5.
- ↑ Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.