Difference between revisions of "Ipomoea cordatotriloba"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
''I. cordatotriloba'' is found in dunes, sandy areas on barrier islands, and other sandy habitats. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from sand of roadside depression, sand floodplain, and margin of thin woods. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. Komarek, R.k. Godfrey, Andre Clewell, Pat Ferral, John Nelson, Loran C. Anderson, J.M. Kane. States and counties: Florida (Leon, Liberty, Jefferson, Franklin) Georgia (Thomas) South Carolina (Georgetown)</ref> | ''I. cordatotriloba'' is found in dunes, sandy areas on barrier islands, and other sandy habitats. <ref name= "Weakley 2015"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium. </ref> Specimens have been collected from sand of roadside depression, sand floodplain, and margin of thin woods. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. Komarek, R.k. Godfrey, Andre Clewell, Pat Ferral, John Nelson, Loran C. Anderson, J.M. Kane. States and counties: Florida (Leon, Liberty, Jefferson, Franklin) Georgia (Thomas) South Carolina (Georgetown)</ref> | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ''I. cordatotriloba'' | + | ''I. cordatotriloba'' has been observed to flower in June, July, and September. <ref name= "PanFlora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018 </ref> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| + | |||
===Fire ecology=== | ===Fire ecology=== | ||
It has been observed flowering in recently burned wetland. <ref name ="FFE">Observation by Edwin Bridges in Big Cypress National Preserve, Collier COunty, Septmber 30, 2009, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group January 2017. </ref> | It has been observed flowering in recently burned wetland. <ref name ="FFE">Observation by Edwin Bridges in Big Cypress National Preserve, Collier COunty, Septmber 30, 2009, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group January 2017. </ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:08, 2 November 2018
Common name: tievine [1], coastal morning-glory [2]
| Ipomoea cordatotriloba | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Southeastern Flora Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Convolvulaceae |
| Genus: | Ipomoea |
| Species: | I. cordatotriloba |
| Binomial name | |
| Ipomoea cordatotriloba Dennst. | |
| |
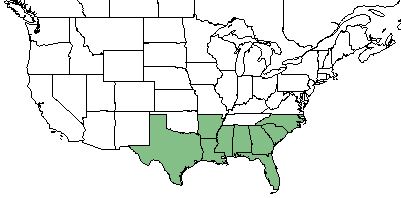
| Natural range of Ipomoea cordatotriloba from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: I. trifida
Varieties: none
Description
I. cordatotriloba is a perennial forb/herb/vine of the Convolvulaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
I. cordatotriloba is found along the southeastern coast of the United States from Texas to North Carolina. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
I. cordatotriloba is found in dunes, sandy areas on barrier islands, and other sandy habitats. [2] Specimens have been collected from sand of roadside depression, sand floodplain, and margin of thin woods. [3]
Phenology
I. cordatotriloba has been observed to flower in June, July, and September. [4]
Fire ecology
It has been observed flowering in recently burned wetland. [5]
Use by animals
Butterflies are commonly found in proximity to I. cordatotriloba, skippers in particular. [5]
Conservation and Management
I. cordatotriloba is listed as a noxious weed by the Arizona Department of Agriculture Plant Services Division and the Arkansas State Plant Board. [1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=IPCOC2
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- Jump up ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R. Komarek, R.k. Godfrey, Andre Clewell, Pat Ferral, John Nelson, Loran C. Anderson, J.M. Kane. States and counties: Florida (Leon, Liberty, Jefferson, Franklin) Georgia (Thomas) South Carolina (Georgetown)
- Jump up ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 Observation by Edwin Bridges in Big Cypress National Preserve, Collier COunty, Septmber 30, 2009, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group January 2017. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "FFE" defined multiple times with different content