Difference between revisions of "Hibiscus aculeatus"
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<!--===Habitat===--> <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | <!--===Habitat===--> <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology===<!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | ''H. aculeatus'' has been observed to flower May to September with peak inflorescence in July.<ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> | |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
==Conservation and management== | ==Conservation and management== | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 2 November 2018
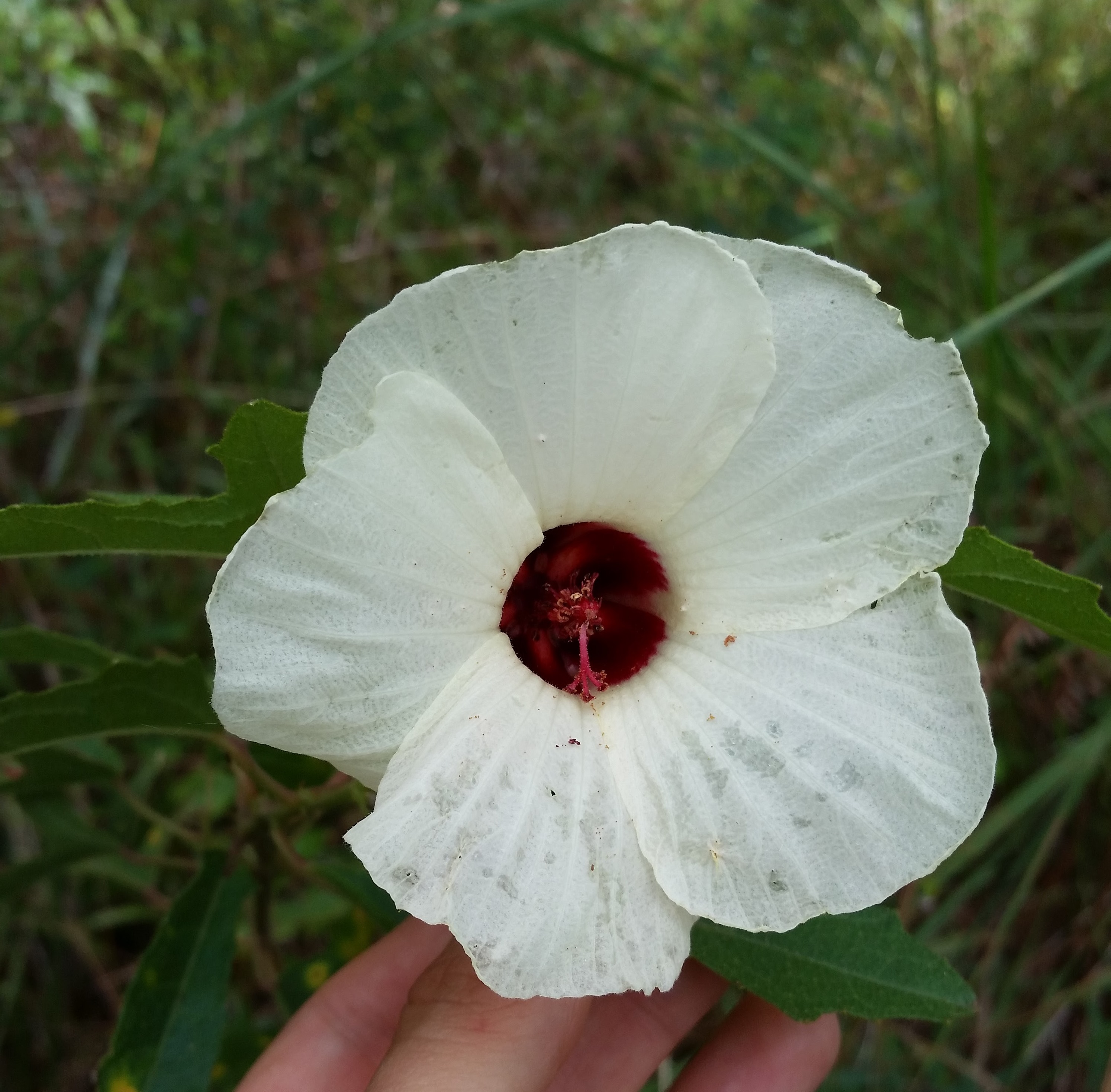
Common name: Comfortroot
| Hibiscus aculeatus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Hibiscus aculeatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Dicots |
| Order: | Malvales |
| Family: | Malvaceae |
| Genus: | Hibiscus |
| Species: | H. aculeatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Hibiscus aculeatus Walter | |
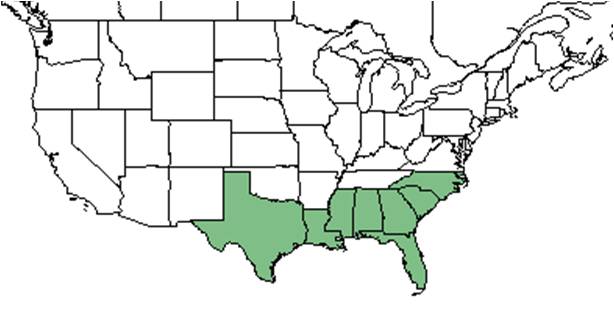
| |
| Natural range of Hibiscus aculeatus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Hibiscus scaber Michx. USDA NRCS Plants Database
Description
"Shrubs or perennial or annual herbs with stellate pubescence. Leaves unlobed to palmately lobed or dissected; petioles usually long; stipules present, usually caduceus flowers solitary in the upper leaf axils, or in terminal racemes; peduncles and pedicels present or the peduncle obsolete, often elongating in fruit. Involucral bracts 7-15, linear. Sepals 5, widely triangular to triangular-lanceolate, enlarged in fruit; petals oblanceolate to obovate, apex rounded; stamens usually numerous; stigmas 5, capitate, styles free near apex. Capsule 5-locular." [1]
"Perennial with spreading-ascending or, less frequently erect branches to 1m tall. Trichomes of stems, petioles, leaves and pedicels short, bristly, stellate, scabrous. Leaves palmately 3-5 cleft or lobed, 3-9 cm long, mostly wider than long, coarsely and irregularly serrate, truncate to cleft with an inverted broad, V-shaped sinus; petioles 2-10 cm long. Flowers in leafly-bracteate racemes, bracts less divided than the leaves or entire; peduncles obsolete or to 2 mm long; pedicels 5-12 mm long, elongated slightly in fruit, usually with a few long white trichomes; Involucral bracts 8-10, linear, 1-2 cm long, usually palmately or pinnately cleft at apex. Calyx lobes triangular-lanceolate, 8-12 mm long, acute, elongated in fruit, distinctly keeled to the apex and with a thickened margin resembling the keel, pubescent with long stiff, postulate-based trichomes; petals cream, turning a deeper yellow and finally fading to pink, crimson marked at base, 5-6 cm long. Capsule gradually contracted to a beak, 1.7-2 cm long, pubescent with mixed short and long, bristle-like trichomes. Seeds brown, with fine reticulations and with a few whitish papillate, 3.5-4 mm long." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Phenology
H. aculeatus has been observed to flower May to September with peak inflorescence in July.[2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 704-6. Print.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016