Difference between revisions of "Coleataenia anceps"
(→Ecology) |
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
Synonyms: ''Panicum anceps'' (Michaux) | Synonyms: ''Panicum anceps'' (Michaux) | ||
| − | + | Subspecies: ''Coleataenia anceps'' (Michaux) Soreng ssp. ''rhizomata'' (A.S. Hitchcock & Chase) Soreng | |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Revision as of 18:19, 26 June 2018
Common Names: Beaked Panicgrass [1]
| Coleataenia anceps | |
|---|---|
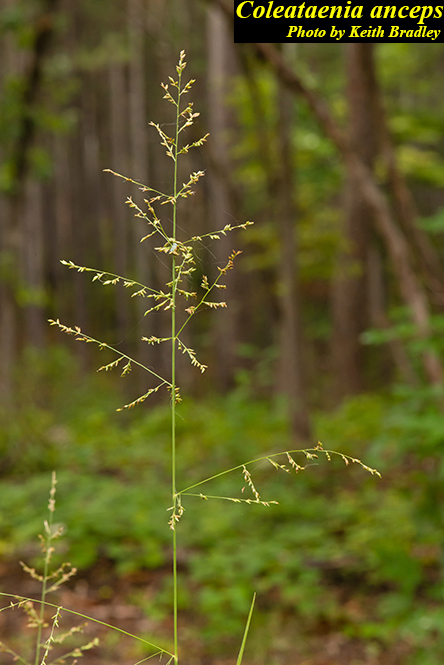

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Coleataenia |
| Species: | C. anceps |
| Binomial name | |
| Coleataenia anceps Michx. | |
| |
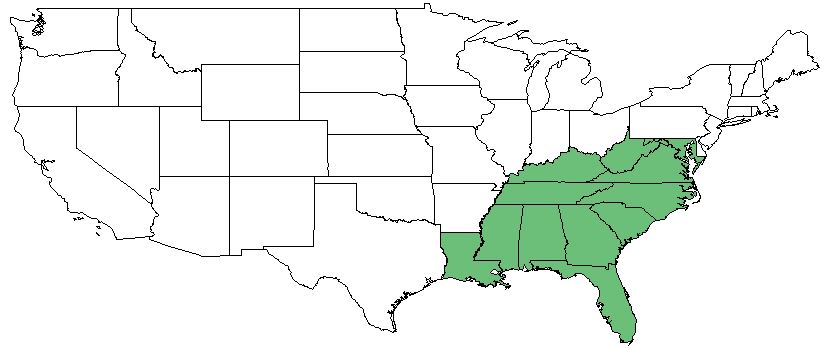
| Natural range of Coleataenia anceps from Weakley [2] | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Panicum anceps (Michaux)
Subspecies: Coleataenia anceps (Michaux) Soreng ssp. rhizomata (A.S. Hitchcock & Chase) Soreng
Description
C. anceps is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
This weedy graminoid can be found in the United States, from the east coast west to Illinois and Texas. [3]
Ecology
Habitat
C. anceps is tolerant of a variety of habitats such as dry sandy soil and standing water regions; however, swamp regions are its ideal habitat, with partial shade. [1]
Specimens of C. anceps have been collected from habitats including upper tidal swamps, edge of rivers, in dune swale, ind rying sandy loam of open flatwoods, burned over cypress swamp, pine flatwoods, moist sands of roadsides, moist sands in hammock clearing, and longleaf pine flatwoods. [4]
Phenology
once a year the C. anceps flowers, in the fall, and produces its seeds that are germinated in the fall and early winter. [1]
Use by animals
Deer graze on the grass and birds and waterfowl eat the seeds. [1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
This grassy wwed has been used for restoring regions used for mining, logging, timber roads, and other eroded sites by reintroducing vegetation.[1]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1320 pp.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: M. Darst, R. Mattson, G. Mahon, J. Good, Loran Anderson, Ann F. Johnson, R.K. Godfrey, R. Fral, J.P. Gillespie, Richard S. Mitchell, William Reese, Paul Redfearn, R.E. Perdue. States and counties: Florida (Dixie, Wakulla, Bay, Leon, Franklin, Nassau, Madison, Taylor, Jackson, Jefferson, Clay, Levy, Baker) Georgia (Grady)