Difference between revisions of "Coleataenia anceps"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| + | Common Names: Beaked Panicgrass <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
Revision as of 20:05, 11 June 2018
Common Names: Beaked Panicgrass [1]
| Coleataenia anceps | |
|---|---|
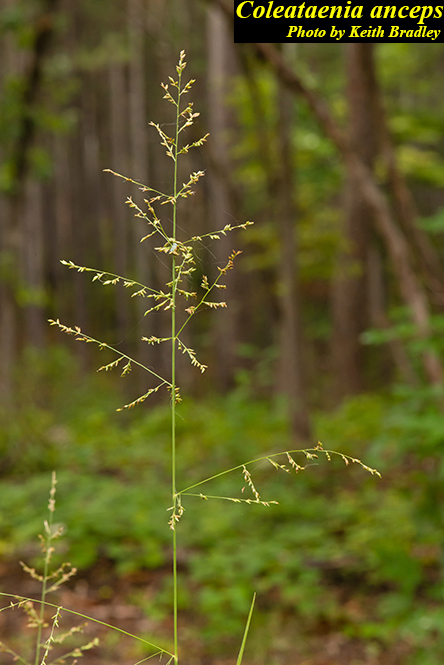

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Coleataenia |
| Species: | C. anceps |
| Binomial name | |
| Coleataenia anceps Michx. | |
| |
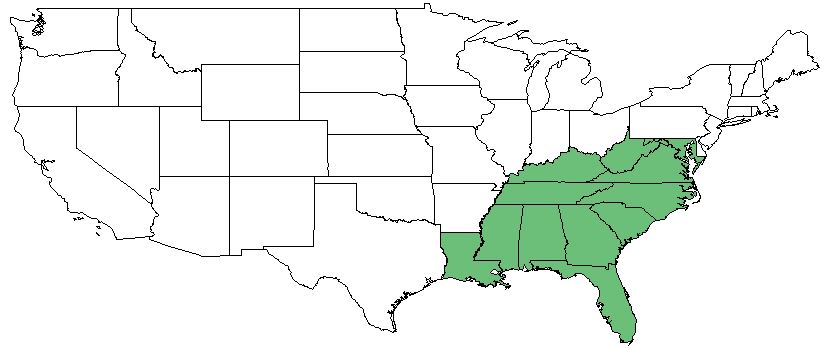
| Natural range of Coleataenia anceps from Weakley [2] | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Panicum anceps (Michaux)
Variety: none
Description
C. anceps is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
This weedy graminoid can be found in the United States, from the east coast west to Illinois and Texas. [3]
Ecology
Habitat
C. anceps is tolerant of a variety of habitats such as dry sandy soil and standing water regions; however, swamp regions are its ideal habitat, with partial shade. [1]
Phenology
once a year the C. anceps flowers, in the fall, and produces its seeds that are germinated in the fall and early winter. [1]
Use by animals
Deer graze on the grass and birds and waterfowl eat the seeds. [1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
This grassy wwed has been used for restoring regions used for mining, logging, timber roads, and other eroded sites by reintroducing vegetation.[1]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Weakley, Alan S. 2015. Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States: Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. 1320 pp.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.