Difference between revisions of "Pinus palustris"
(→Conservation and Management) |
(→Fire ecology) |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
Germination needs mineral soil and 1-2 weeks after dispersal. Most germination occurs during the fall and spring. Only after the first two years of development, seedlings will begin to develop stems and growth in height begins to occur rapidly. During the first two years, the root system is developing, preparing for a rapid growth to extreme heights. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | Germination needs mineral soil and 1-2 weeks after dispersal. Most germination occurs during the fall and spring. Only after the first two years of development, seedlings will begin to develop stems and growth in height begins to occur rapidly. During the first two years, the root system is developing, preparing for a rapid growth to extreme heights. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
===Fire ecology=== | ===Fire ecology=== | ||
| − | ''P. palustris'' requires frequent burning for a healthy environment. Without frequent burning, hardwood species will begin to overtake the habitat. ''P. palustris'' has a high fire tolerance. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | + | ''P. palustris'' requires frequent burning for a healthy environment. Without frequent burning, hardwood species will begin to overtake the habitat. The species requires burning to regenerate and seed. ''P. palustris'' has a high fire tolerance. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> |
| − | <!--===Pollination===--> | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| + | |||
===Use by animals=== | ===Use by animals=== | ||
Birds and small mammals eat the large seeds, ants will eat the seeds that are germinating, and razorback hogs eat the roots of the seedlings.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | Birds and small mammals eat the large seeds, ants will eat the seeds that are germinating, and razorback hogs eat the roots of the seedlings.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | ||
Revision as of 12:44, 7 June 2018
Common Names: Longleaf pine [1]
| Pinus palustris | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Pinales |
| Family: | Pinaceae |
| Genus: | Pinus |
| Species: | P. palustris |
| Binomial name | |
| Pinus palustris Mill. | |
| |
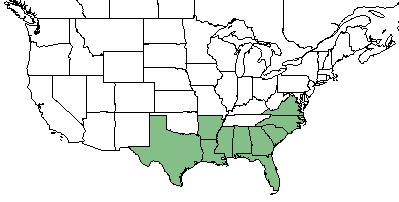
| Natural range of Pinus palustris from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: P. australis (Michaux)
Variety: none
Description
Pinus palustris is a perennial tree of the Pinaceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
P. palustris is found throughout the southeastern United States; specifically in Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Virginia, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, Arkansas, and Texas. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitat falls largely within the southeastern Atlantic coastal plain and Gulf coastal plain. They require warm, wet, and temperate climates that have a steady reliable annual precipitation of 43-69 inches. It is common in sandy, well-drained soils close to sea level. [1]
Specimens have been collected from hardwood hammocks, longleaf pine scrub oak ridge, sandy soils with many oak species, and old longleaf stands. [2]
Being historically known to the southeastern coastal plains, the longleaf pine stands have been an ideal habitat for herbaceous diversity. [3]
Seed bank and germination
Germination needs mineral soil and 1-2 weeks after dispersal. Most germination occurs during the fall and spring. Only after the first two years of development, seedlings will begin to develop stems and growth in height begins to occur rapidly. During the first two years, the root system is developing, preparing for a rapid growth to extreme heights. [1]
Fire ecology
P. palustris requires frequent burning for a healthy environment. Without frequent burning, hardwood species will begin to overtake the habitat. The species requires burning to regenerate and seed. P. palustris has a high fire tolerance. [1]
Use by animals
Birds and small mammals eat the large seeds, ants will eat the seeds that are germinating, and razorback hogs eat the roots of the seedlings.[1]
The tree provides habitats for bobwhite quail, white tailed deer, wild turkey, and fox squirrel. [1]
Red-cockaded woodpecker will use the old growth stands for nesting. [1]
Diseases and parasites
Hogs eat the seedlings during the initial stages of development.[1]
The brown spot needle disease can cause defoliation of the P. palustris tree. It is a fungus that occurs with a build up of dead grass on the forest floor and can spread to the young trees and seedlings. Frequent burning can reduce the likelihood of this disease spreading. [1]
Conservation and Management
Frequent fire is necessary to maintain a healthy forest of P. palustris. They grow in the place of dead trees, allowing for many tree of the same age to disperse to the same area where old trees have fallen. [1]
Excessive grazing of the forest floor will reduce the P. palustris in the region. [1]
Pinus palustris stands have been declining since European settlement with an increase in logging, agricultural conversion, and suppressing natural fires that are key to the health of long-leaf pine land. [4] They were once considered the most abundant ecosystem in North America with over 37 million ha to only 1.5 ha in 1985. [5]
Cultivation and restoration
P. palustris is ideal for reforestation in the proper climates; dry, seep sands in the southeastern United States. [1]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R.K. Godfrey, Cecil R. Slaughter, Kurt Blum, S.W. Leonard, A. S. Jensen, S. L. Beckwith, Sidney McDaniel, S. Snedaker, D. B. Ward, Patricia Elliot, L. B. Trott, J. P. Gillespie, R. Komarek, Leon Neel, K. M. Meyer, A. Townesmith, Annie Schmidt States and counties: Florida (Franklin, Leon, Putnam, Washington, Orange, Citrus, Nassau, Marion, Wakulla, Liberty) Georgia (Harris)
- ↑ Andreu, M. G., et al. (2009). "Can managers bank on seed banks when restoring Pinus taeda L. plantations in Southwest Georgia?" Restoration Ecology 17: 586-596.
- ↑ Aschenbach, T. A., et al. (2010). "The initial phase of a longleaf pine-wiregrass savanna restoration: species establishment and community responses." Restoration Ecology 18(5): 762-771.
- ↑ Brockway, D. G. and C. E. Lewis (1997). "Long-term effects of dormant-season prescribed fire on plant community diversity, structure and productivity in a longleaf pine wiregrass ecosystem." Forest Ecology and Management 96: 167-183.