Difference between revisions of "Ceanothus americanus"
(→Description) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
| − | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | + | ===Habitat=== |
| + | The ''C. americanus'' is largely found in in sandy soil within woodlands and prairies. <ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
| + | <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| − | + | ===Seed bank and germination=== | |
| − | + | Seedling ''C. americanus'' are more likely to thrive when planted in late fall or early winter. <ref name= "USDA"/> | |
| − | + | ===Fire ecology=== | |
| − | + | ''C. americanus'' has a high tolerance to drought and fire is a management technique for the spread of the species. <ref name= "USDA"/> | |
| − | + | <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | |
| + | ===Pollination=== | ||
| + | Bees may collect pollen from the plant and other insects such as butterflies and moths may just collect nectar. <ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
| + | ===Use by animals=== | ||
| + | Many animals such as rabbit, elk and deer eat the grass from ''C. americanus'' while others will eat the fruit, turkey and quail for instance. <ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
| + | <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | ==Diseases and parasites== | ||
| + | This species can acquire leaf spot and powdery mildew. <ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 18 May 2018
| Ceanothus americanus | |
|---|---|
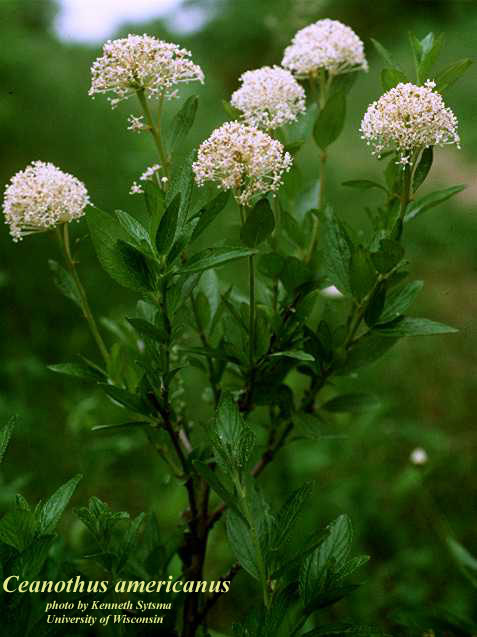

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Rhamnales |
| Family: | Rhamnaceae |
| Genus: | Ceanothus |
| Species: | C. americanus |
| Binomial name | |
| Ceanothus americanus L. | |
| |
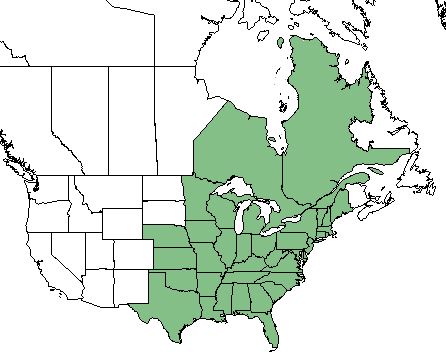
| Natural range of Ceanothus americanus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Ceanothus intermedius (Pursh)
Variety: none
Description
C. americanus is a perennial shrub/subshrub of the Rhamnaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
While it is more commonly found along the coastal plains of the eastern United States and Canada, C. americanus can be found inland as far west as Louisiana. [2]
Ecology
Habitat
The C. americanus is largely found in in sandy soil within woodlands and prairies. [1]
Seed bank and germination
Seedling C. americanus are more likely to thrive when planted in late fall or early winter. [1]
Fire ecology
C. americanus has a high tolerance to drought and fire is a management technique for the spread of the species. [1]
Pollination
Bees may collect pollen from the plant and other insects such as butterflies and moths may just collect nectar. [1]
Use by animals
Many animals such as rabbit, elk and deer eat the grass from C. americanus while others will eat the fruit, turkey and quail for instance. [1]
Diseases and parasites
This species can acquire leaf spot and powdery mildew. [1]