Difference between revisions of "Amianthium muscitoxicum"
m |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Pollination=== | ||
| + | The distance of pollinating neighbors has some influence on the production and weight of seeds. However, heterogeneity between plants accounted for a greater amount of variance between seed production and weight.<ref name="Redmond et al 1989">Redmond AM, Robbins LE, Travis J (1989) The effects of pollination distance on seed production in three populations of ''Amianthium muscaetoxicum'' (Liliaceae). Oecologia 79:260-264.</ref> | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 16:54, 21 February 2018
| Amianthium muscitoxicum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Liliaceae |
| Genus: | Amianthium |
| Species: | A. muscitoxicum |
| Binomial name | |
| Amianthium muscitoxicum (Walter) A. Gray | |
| |
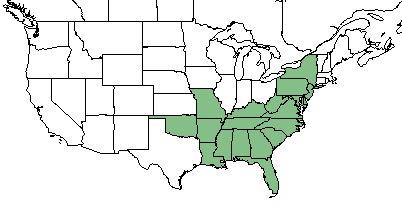
| Natural range of Amianthium muscitoxicum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: A. muscaetoxicum;[1] Chrosperma muscaetoxicum; Zigadenus muscitoxicus;[1][2]
Description
Amianthium muscitoxicum is a monoecious perennial forb/herb.[2] It has narrow elongated leaves and reaches lengths of 12-24 in (30-61 cm). Flowers are initially white, but turn a bronzy-green, and occur in dense showy racemes. All parts of the plant are poisonous, containing a very toxic alkaloid.[3]
Distribution
This species occurs from southern New York, Pennsylvania, Missouri, and Oklahoma, southward to the Florida panhandle, Mississippi, and Arizona.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
A. muscitoxicum occurs from 5-1,600 m in elevation across a wide variety of mesic to dry forests, pine savannas, sandhills, and meadows.[1]
Phenology
In the Southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, flowering occurs from May through July and fruiting from July through September.[1]
Pollination
The distance of pollinating neighbors has some influence on the production and weight of seeds. However, heterogeneity between plants accounted for a greater amount of variance between seed production and weight.[4]
Use by animals
Humans use it to kill flies by taking the pulp from crushed bulbs and mixing it with sugar.[3] Native Americans would also use A. muscitoxicum to kill crows and as a severe cure for the itch.[5]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Propagation can be performed by planting seeds when ripe in the spring or through rood divisions.[3]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 21 February 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Plant database: Amianthium muscitoxicum. (21 February 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=AMMU
- ↑ Redmond AM, Robbins LE, Travis J (1989) The effects of pollination distance on seed production in three populations of Amianthium muscaetoxicum (Liliaceae). Oecologia 79:260-264.
- ↑ Witthoft J (1947) Ethnology - An early Cherokee ethnobotanical note. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences 37(3):73-75.