Difference between revisions of "Cuscuta gronovii"
(→Conservation and Management) |
|||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| − | One technique to reduce the emergence of ''C. gronovii'' is to bury seeds under at least 2.5 cm of sand ( | + | One technique to reduce the emergence of ''C. gronovii'' is to bury seeds under at least 2.5 cm of sand. The use of glyphosate on glyphsate-resistant crops are reported to effectively control dodder. (as cited in <ref name="Sandler 2010"/>). |
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 26 January 2018
| Cuscuta gronovii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Cuscutaceae |
| Genus: | Cuscuta |
| Species: | C. gronovii |
| Binomial name | |
| Cuscuta gronovii Willd | |
| |
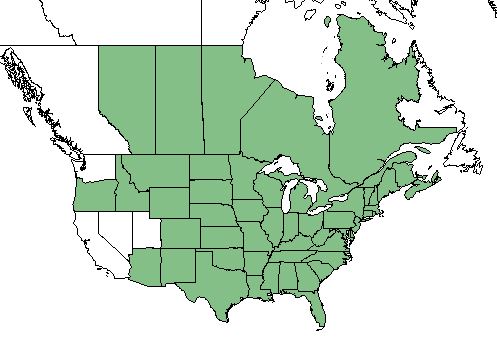
| Natural range of Cuscuta gronovii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name: swamp dodder; common dodder;[1] scaldweed[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Grammica gronovii[1]
Varieties: C. gronovii var. gronovii;[1][2] C. gronovii var. latiflora;[1] C. gronovii var. calyptrata[2]
Description
C. gronovii is a dioecious perennial that grows as a forb/herb or vine.[2] Scales can produce up to five axillary branches, which can then become their own plant after contacting a host.[3] Its seeds weight 2.3 g and is reported to have 22,900 seeds in a single clump.[4] Although, seed production may also be influenced by the species its host (as cited in [5]). Other dodder species have a very limited photosynthetic ability that decreases with age. It is likely C. gronovii is similar in this regard.[6]
Distribution
This species is found in all of the lower 48 United States except for Washington, California, Nevada, and Utah. It is also found in Canada from Alberta eastward to Quebec, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found on a wide variety of herbaceous and woody plants within stream banks, bottomland forests, bogs, marshes, swamps, wet fields, and wet disturbed areas.
Phenology
Flowering occurs from late July through November in the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States.[1]
Seed bank and germination
C. gronovii seeds are known to survive in dry storage for up to 30 years and a 12 year study in simulated bog environments supports such lengthy longevity in the seed bank (reviewed in [5]). Seeds germinate in soil, but roots die off as the plant twines around a host and sends out suckers that penetrate the host's tissues and obtain nutrients.[7] While searching for a host, seedlings have shown a preference for taller hosts (as cited in [5]). Embryogenesis studies reveal no primary root meristem in this species.[3]
Fire ecology
Because scarification increases the germination rate of C. gronovii (reviewed in [5]), fire has the potential to increase the abundance of C. gronovii.
Conservation and Management
One technique to reduce the emergence of C. gronovii is to bury seeds under at least 2.5 cm of sand. The use of glyphosate on glyphsate-resistant crops are reported to effectively control dodder. (as cited in [5]).
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 25 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Truscott FH (1966) Some aspects of morphogenesis in Cuscuta gronovii. American Journal of Botany 53(7):739-750.
- ↑ Stevens OA (1957) Weights of seeds and numbers per plant. Weeds 5(1):46-55.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Sandler HA (2010) Managing Cuscuta gronovii (swamp dodder) in cranberry requires an integrated approach. Sustainability 2:660-683.
- ↑ Pattee HE, Allred KR, Wiebe HH (1965) Photosynthesis in dodder. Weeds 13(3):193-195.
- ↑ Plant database: Cuscuta gronovii. (25 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=CUGR