Difference between revisions of "Eleocharis melanocarpa"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | ''E. eleocharis'' blooms for 6-7 months per year.<ref name="Harper 1918">Harper R. M. (1918). The vegetation of the Hempstead Plains. Proceedings of the semi-centennial anniversary of the Torry Botanical Club. Memoirs of the Torrey Botanical Club 17:262-286.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 38: | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| + | ''E. eleocharis'' has no organs for attracting insects for pollination. Instead, it relies on the wind to disseminate pollen.<ref name="Harper 1918"/> | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 18:06, 5 December 2017
| Eleocharis melanocarpa | |
|---|---|
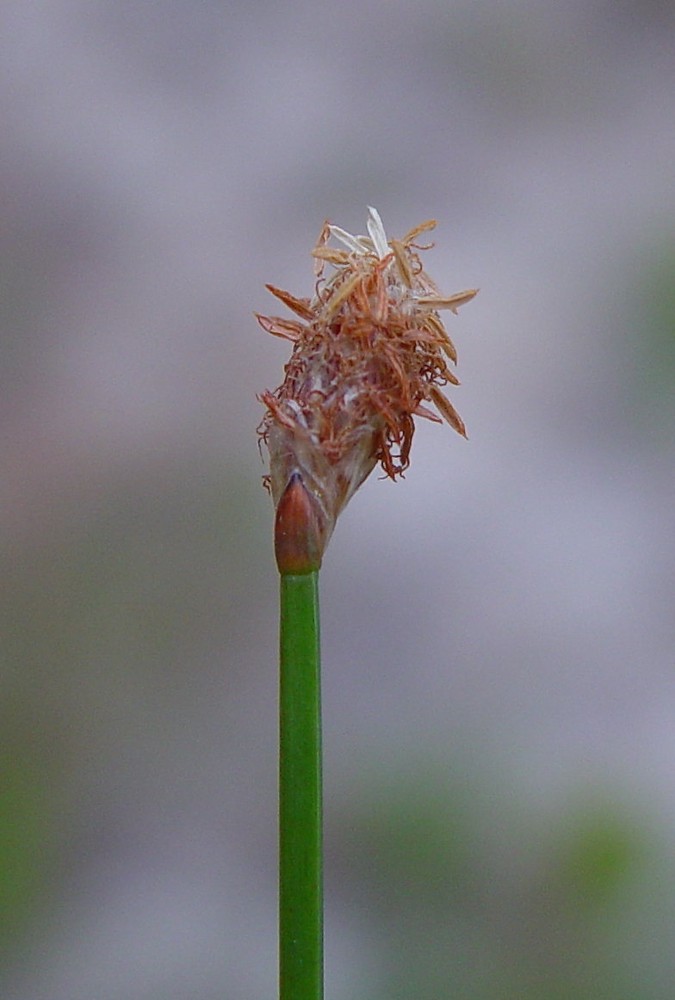

| |
| Photo by © Arthur Haines, New England Wild Flower Society | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Eleocharis |
| Species: | E. melanocarpa |
| Binomial name | |
| Eleocharis melanocarpa Torr. | |
| |
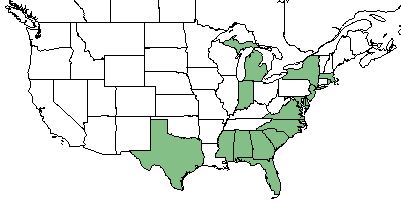
| Natural range of Eleocharis melanocarpa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Black-fruited spikerush, blackfruit spikerush[1][2]
Contents
Description
E. melanocarpa is a perennial, monoecious, graminoid, sedge.[2] On its seed, the tubercle is very short and dilated with its projecting edge rolled over and surrounding the top of the nut.[3] The tips of the culms of E. melanocarpa often arch over and root in the substrate forming a dense tangle. [4] It commonly grows in stools containing several roots and five to 20 stems. Stems range in length from 1 to 3.6 ft (0.3 to 1.1 m) in length. Stools are commonly bunched together into clusters 1 ft (0.3 m) or more in diameter.[3]
Distribution
E. melanocarpa ranges from Massachusetts to Florida and Mississippi, disjunct to eastern Texas, southern Michigan, and northern Indiana. [2][4][1] Despite most studies not listing E. melanocarpa as occurring in Louisiana, the species has been found in parts of Bienville Parish in 2008 suggesting a more connective distribution along its southern range.[5][6]
Ecology
Habitat
E. melanocarpa is a facultative wetland species found in moist to wet ditches and freshwater pond margins.[7] Such occurrences in these habitats are often ephemeral, sandy, and can range from sunny to shady.[5]
E. eleocharis blooms for 6-7 months per year.[8]
Fire ecology
Despite typically inhabiting wet areas, fires from adjacent habitats (e.g. long-leaf pine savannas, sand-hill pines, Oldfield, etc.) are thought to burn into drawn-down areas of wet ponds/ditches. Such burns likely maintain more open canopy conditions benefiting populations of E. melanocarpa. [5]
E. eleocharis has no organs for attracting insects for pollination. Instead, it relies on the wind to disseminate pollen.[8]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 30 November 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hill E. J. (1894). Eleocharis melanocarpa a proliferous plant. Bulletin of the Torrey Botanical Club. 25(7):392-394.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Sorrie B. A. and Leonard S. W. (1999). Noteworthy records of Mississippi vascular plants. Sida 18:889-908.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Reid C. S. and Faulkner P. L. (2010). Louisiana. Castanea 75(1):138-140.
- ↑ Sorrie B. A. and Weakley A. S. (2001). Coastal plain vascular plant endemics: Phytogeographic patterns. Castanea 66(1/2):50-82.
- ↑ Contributions to the flora of Florida: 8, Eleocharis (Cyperaceae). Castanea 40(1):16-36.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Harper R. M. (1918). The vegetation of the Hempstead Plains. Proceedings of the semi-centennial anniversary of the Torry Botanical Club. Memoirs of the Torrey Botanical Club 17:262-286.