Difference between revisions of "Eleocharis melanocarpa"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | The tips of the culms of ''E. melanocarpa'' often arch over and root in the substrate forming a dense tangle. <ref name="Sorrie & Leonard 1999">Sorrie B. A. and Leonard S. W. (1999). Noteworthy records of Mississippi vascular plants. Sida 18:889-908.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 4 December 2017
| Eleocharis melanocarpa | |
|---|---|
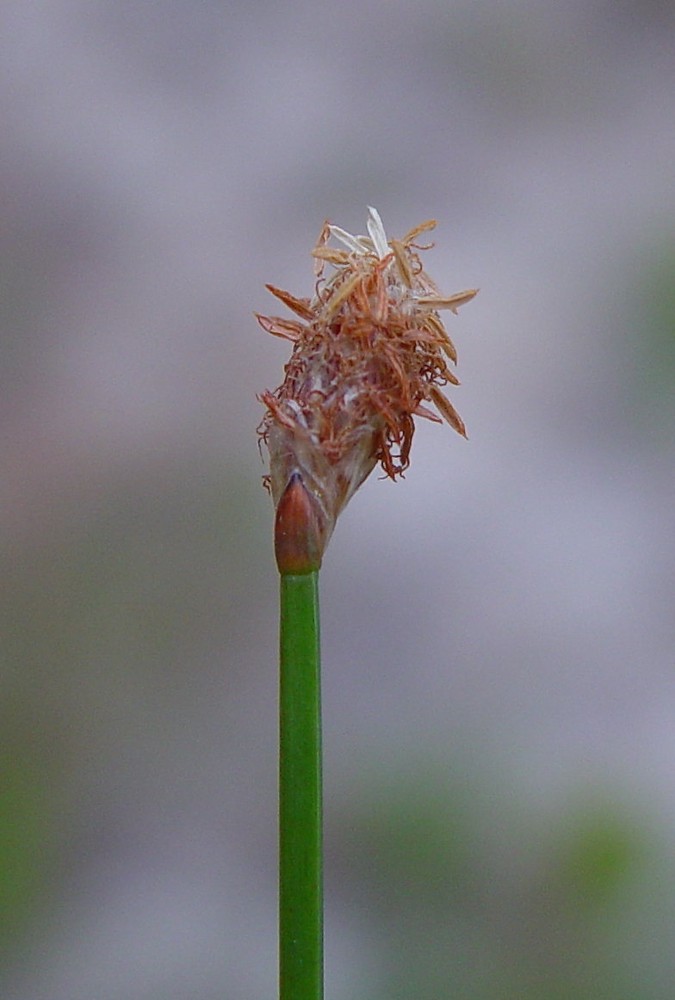

| |
| Photo by © Arthur Haines, New England Wild Flower Society | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Eleocharis |
| Species: | E. melanocarpa |
| Binomial name | |
| Eleocharis melanocarpa Torr. | |
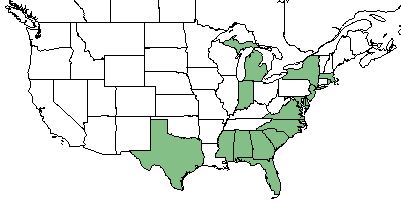
| |
| Natural range of Eleocharis melanocarpa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Black-fruited spikerush, blackfruit spikerush[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Description
The tips of the culms of E. melanocarpa often arch over and root in the substrate forming a dense tangle. [3]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 30 November 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Sorrie B. A. and Leonard S. W. (1999). Noteworthy records of Mississippi vascular plants. Sida 18:889-908.