Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum adnatum"
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) (→Seed dispersal) |
Laurenloria (talk | contribs) (→Seed dispersal) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | This species disperses by wind. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> | + | This species disperses by wind. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> |
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
Revision as of 13:32, 18 November 2016
| Symphyotrichum adnatum | |
|---|---|
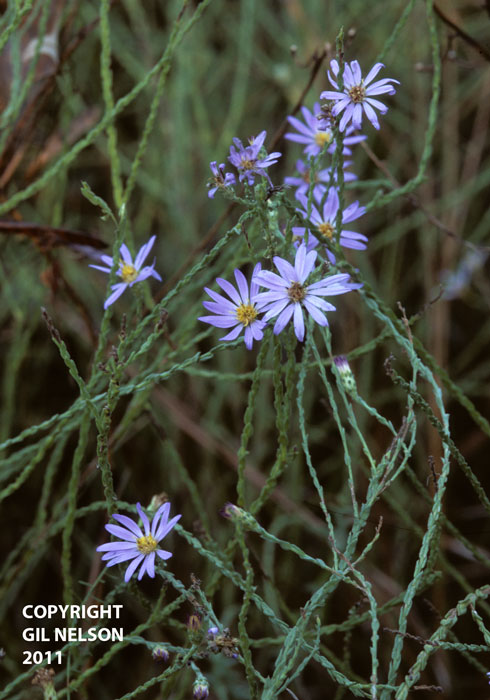

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. adnatum |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum adnatum (Nutt.) G.L. Nesom | |
| |
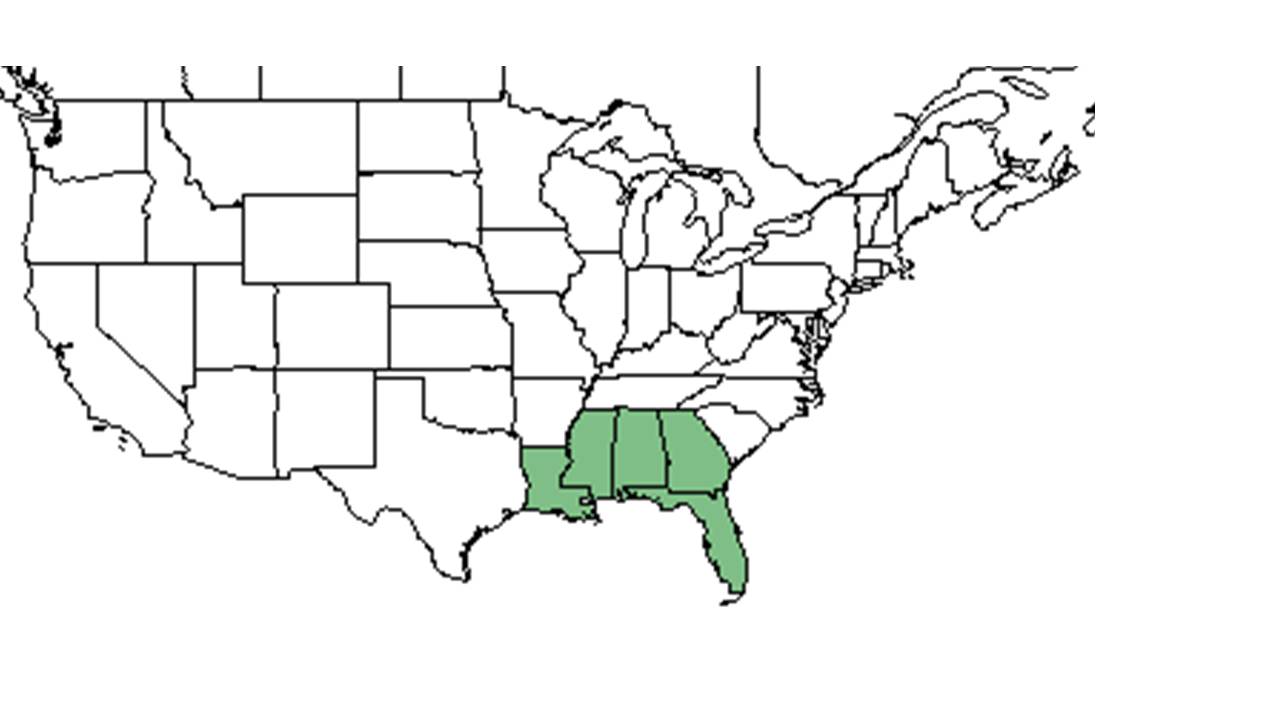
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum adnatum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Scaleleaf aster
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Aster adnatus Nuttall
Description
A description of Symphyotrichum adnatum is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, S. adnatum can be found in longleaf pine savannas, pine flatwood communities, annually burned pinelands, slash pine plantations, and open mixed woodlands. [1] It is restricted to native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinlands of South Georgia. [2] Soil types include loamy sand and sand. [1] Associated species include Euthamia minor, Andropogon virginicus, Eupatorium compositifolium, Gnaphalium obtusifolium, Chamaecrista fasciculata, Chrysopsis mariana, Diodia teres, Sericocarpus tortifolius, Aristida, Ctenium, and Sporobolus. [1]
Phenology
It has been observed to flower and fruit November and December. [1]
Seed dispersal
This species disperses by wind. [3]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Leon Neel, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, Kathleen Craddock Burks. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Leon, Wakulla, Walton. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
