Difference between revisions of "Asplenium platyneuron"
(→Conservation and Management) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
Is fed on by two aphids: ''Amphorophora ampullata'' and '' Idiopterus nephrelepidis''<ref name="illinois">[[http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/grasses/plants/eb_spleenwort.htm]]Illinois Wildflowers. Accessed: April 1, 2016</ref>. | Is fed on by two aphids: ''Amphorophora ampullata'' and '' Idiopterus nephrelepidis''<ref name="illinois">[[http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/grasses/plants/eb_spleenwort.htm]]Illinois Wildflowers. Accessed: April 1, 2016</ref>. | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation and management== |
| + | |||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 20 June 2016
| Asplenium platyneuron | |
|---|---|
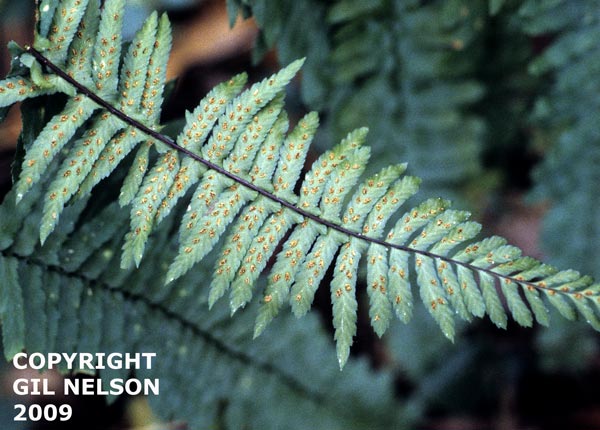

| |
| photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pteridophyta - Ferns |
| Class: | Filicopsida |
| Order: | Polypodiales |
| Family: | Acanthaceae |
| Genus: | Asplenium |
| Species: | A. platyneuron |
| Binomial name | |
| Asplenium platyneuron (L.) Britton, Sterns & Poggenb. | |
| |
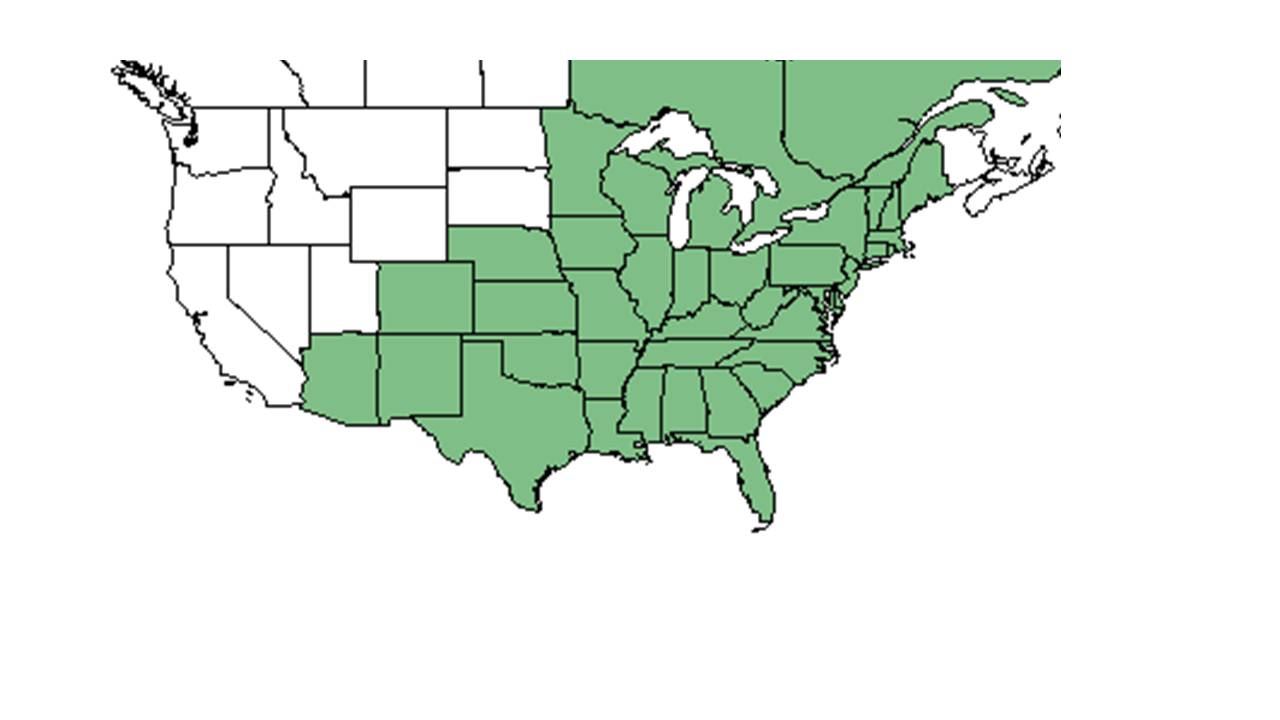
| Natural range of Asplenium platyneuron from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Ebony Spleenwort
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Asplenium platyneuron var. platyneuron; A. platyneuron var. bacculum-rubrum (Featherman) Fernald; A. platyneuron var. incisum (Howe ex Peck) B.L.
Description
A description of Asplenium platyneuron is provided in The Flora of North America.
It can be easily confused with Christmas fern (Polystichum acrostichoides), however, the stem of Christmas fern is green and scaly and the spores cover a back of a leaflet[1].
Distribution
It is one of the most common and widespread of the eastern North American spleenwort[2]. Listed as critically imperiled in Arizona and Colorado[3].
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats include rocks, rotting logs, swamps, marshes, crotches of hardwood trees, and savannas[4][5]. It also grwos in disturbed areas such as fallow fields and near field edges. It does well in moist, loamy sand in fully shaded environments to areas with full sun[5].
Associated species include cypress, moss, magnolia, oak, and beech[5].
Phenology
Reproduces with proliferating buds that form near the base of the stipe and when covered with soil, can grow into new individuals as the frond that bore them dies. Also propagates by spores and can hybridize with other spleenworts[6].
Fire ecology
It does well in fire dependent environments[5].
Use by animals
Is fed on by two aphids: Amphorophora ampullata and Idiopterus nephrelepidis[7].
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ [[1]]Minnesota wildflowers. Accessed: April 1, 2016
- ↑ Taylor, W. C., R. H. Mohlenbrock, et al. (1976). "Variation in North American Asplenium platyneuron." American Fern Journal 66(2): 63-68.
- ↑ [[2]]NatureServe. Accessed: April 1, 2016
- ↑ [[3]]Daily Press. Accessed: April 1, 2016
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Karen MacClendon, R.K. Godfrey, Wilson Baker, R. F. Doren, Roy Komarek, and Jeffrey M. Kane. States and Counties: Florida: Wakulla, Calhoun, Franklin, Leon, and Gadsden. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ [[4]]inaturalist.Accessed: April 1, 2016
- ↑ [[5]]Illinois Wildflowers. Accessed: April 1, 2016