Difference between revisions of "Rhynchosia reniformis"
(→Seed dispersal) |
|||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ''R. reniformis'' is a legume found in frequently burned longleaf pine savannas | + | ''R. reniformis'' is a legume found in frequently burned longleaf pine savannas. <ref name=brew> Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle 2003. Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica). Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.</ref> <ref name=hiers> Hiers, J. K. and R. J. Mitchell 2007. The influence of burning and light availability on N-2-fixation of native legumes in longleaf pine woodlands. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 398-409.</ref> It was observed to resprout one month after a fire in July of 1993 (Pavon 1995). In a burning x no shade treatment, ''R. reniformis'' was found to have elevated levels of N2-fixation. <ref name=hiers/> Herbivory damage for ''R. reniformis'' does not increase with time since fire. <ref name=knight> Knight, T. M. and R. D. Holt 2005. Fire generates spatial gradients in herbivory: an example from a Florida sandhill ecosystem. Ecology 86: 587-593. </ref> |
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
Revision as of 16:45, 12 April 2016
| Rhynchosia reniformis | |
|---|---|
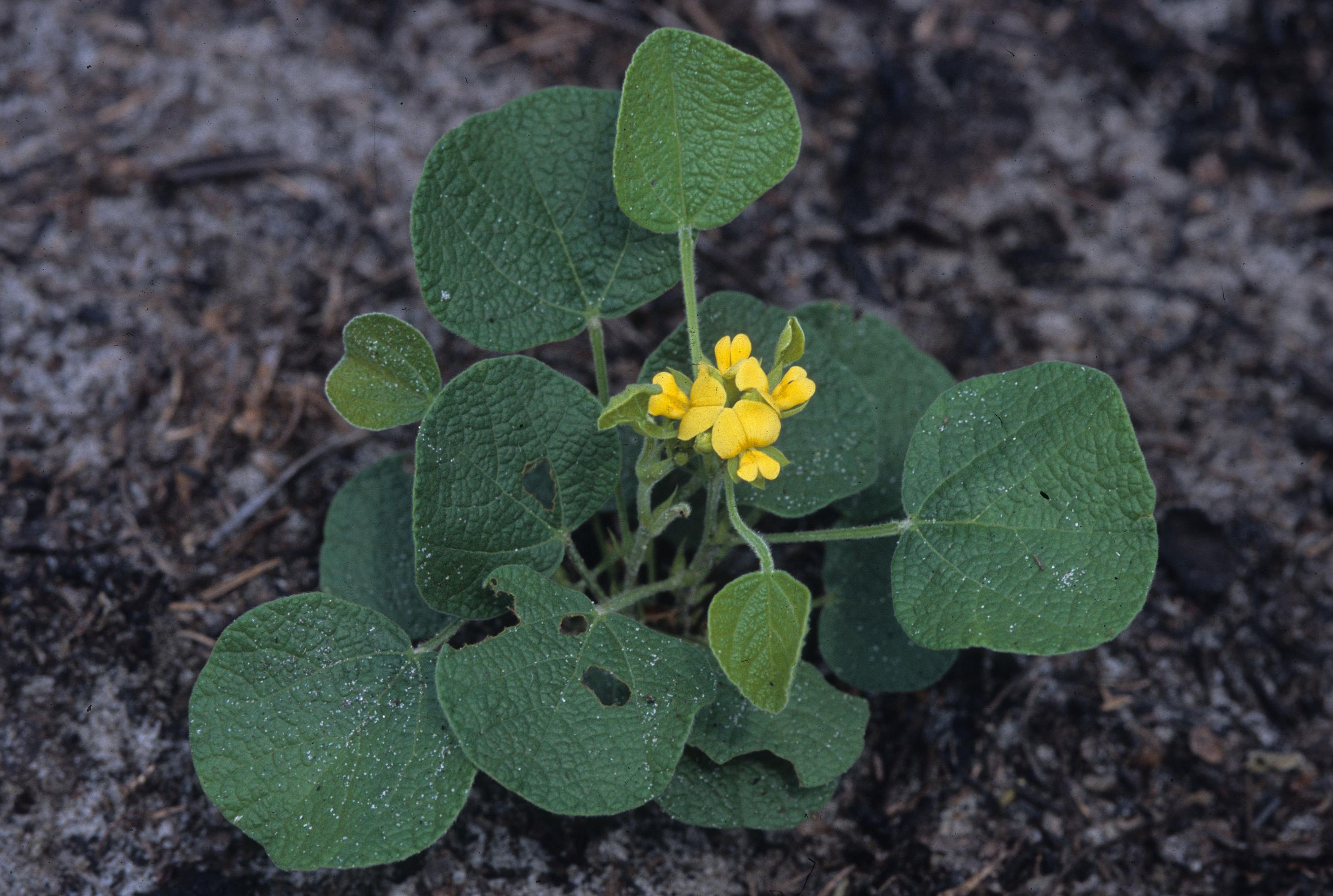

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Rhynchosia |
| Species: | R. reniformis |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchosia reniformis DC. | |
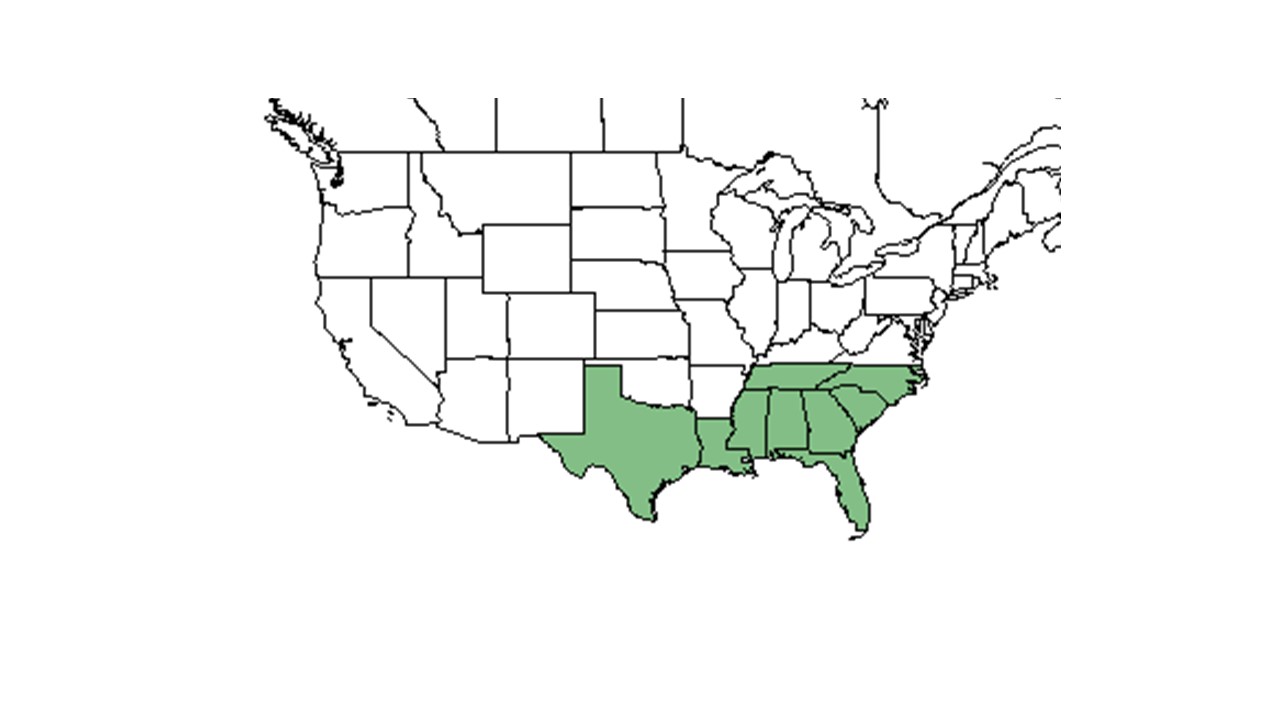
| |
| Natural range of Rhynchosia reniformis from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Dollarleaf (Nelson 2005).
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
“Erect, trailing or climbing, perennial herbs or shrubs. Leaves pinnately 3-foliolate or occasionally 1-foliolate; leaflets usually entire and often bearing amber glands, usually estipellate; stipules ovate to lanceolate. Flowers papilionaceous, rarely solitary or in pairs but usually in axillary or occasionally also terminal racemes, several to numerous, loose to compactly clustered, pedicellate, each subtended by a caduceus bract. Calyx tube campanulate or tubular, nearly regular, lobes equal or nearly so in size but with the 2 uppermost partially united; petals yellow in ours, often equaling or even shorter than the calyx; stamens diadelphous, 9 and 1. Legume usually oblong and flattened, 1-2 seeded, dehiscent.” – Radford et al 1964
"Erect herb 0.5-2.5 dm tall with strongly angled, densely short-pubescent stems. Leaves mostly 1-foliolate or rarely the lowermost 3-foliolate; leaflets suborbicular to reniform, 2-5 cm long, usually wider than long, thick and conspicuously reticulate, sparsely to densely pubescent especially along the veins on both surfaces, inconspicuously beset with numerous, minute, amber glands above and below, stipels persistent, 1.5-2.5 mm long; stipules persistent, linear-lanceolate, 5-10 mm long. Racemes axillary and terminal, sessile or peduncles to 2 cm long with rachises mostly 1-3 cm long, with numerous, closely clustered flowers on pedicels 1.5-3 mm long each subtended by a linear-subulate bract 3-5 mm long. Calyx densely hirsute to villous with numerous, inconspicuous, amber glands, tube 1.5-2 mm long, lobes subequal, lanceolate, 6-9 mm long, long-acuminate to subulate; petals yellow, 6-8 mm long. Legume 1-1.8 cm long, 5-7 mm broad, densely short-pubescent, inconspicuously glandular." - Radford et al 1964
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain region, R. reniformis can be found in burned longleaf pine-wiregrass stands, burned upland longleaf pine forests, loamy sands of longleaf pine-oak scrubs, sandhills, savannas, sandy open areas, sandpine flatwoods, pineflatwoods on limerock, recently burned scrubs of cutover pinewoods, and turkey oak sand ridges (FSU Herbarium, Nelson 2005). It can also be found in open powerlines, clobbered slash pine forests, fallow longleaf pine-scrub oaks, and railroad embankments. Associated species include Galactia mollis, Desmodium floridanum, Desmodium strictum, R. tomentosa, Pinus palustris, Aristida stricta, slash pine, sand pine, Lactuca floridana, Serenoa repens, turkey oak, Acanthospermum, Polygala and Onosmodium (FSU Herbarium).
Soil types include dry sand, sandy loam, loamy sand, limerock and gravelly sand (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It inconsistently flowers from April to September (Nelson 2005).
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). [1]
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
R. reniformis is a legume found in frequently burned longleaf pine savannas. [2] [3] It was observed to resprout one month after a fire in July of 1993 (Pavon 1995). In a burning x no shade treatment, R. reniformis was found to have elevated levels of N2-fixation. [3] Herbivory damage for R. reniformis does not increase with time since fire. [4]
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle 2003. Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica). Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert L. Lazor, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, Gary R. Knight, James R. Burkhalter, R.K. Godfrey, A. F. Clewell, Cheryl Vaughan, Robert Kral, Mable Kral, Gwynn W. Ramsey, R. S. Mitchell, Travis MacClendon, Karen MacClendon, Rodie White, Walter Kittredge, Kevin Oakes, Richard R. Clinebell II, Clarke Hudson, Charles M. Allen, Cecil R Slaughter, H. R. Reed, A. B. Seymour, F. S. Earle, S. B. Jones, Carleen Jones, S. W. Leonard, A. E. Radford, Henrietta Laing, Delzie Demaree, Lisa Keppner. States and Counties: Florida: Baker, Calhoun, Clay, Dade, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Hernando, Highlands, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, St. Johns, Seminole, Suwannee, Union, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Georgia: Baker, Grady, Seminole, Thomas. Mississippi: Clarke, Harrison, Ocean Springs, Pearl River, Pike. Louisiana: Allen. North Carolina: Harnett, Moore. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Hiers, J. K. and R. J. Mitchell 2007. The influence of burning and light availability on N-2-fixation of native legumes in longleaf pine woodlands. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 398-409.
Knight, T. M. and R. D. Holt 2005. Fire generates spatial gradients in herbivory: an example from a Florida sandhill ecosystem. Ecology 86: 587-593.
Nelson, Gil. East Gulf Coastal Plain. a Field Guide to the Wildflowers of the East Gulf Coastal Plain, including Southwest Georgia, Northwest Florida, Southern Alabama, Southern Mississippi, and Parts of Southeastern Louisiana. Guilford, CT: Falcon, 2005. 184. Print.
Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 636. Print.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Brewer, J. S. and S. P. Cralle 2003. Phosphorus addition reduces invasion of a longleaf pine savanna (southeastern USA) by a non-indigenous grass (Imperata cylindrica). Plant Ecology 167: 237-245.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hiers, J. K. and R. J. Mitchell 2007. The influence of burning and light availability on N-2-fixation of native legumes in longleaf pine woodlands. Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 134: 398-409.
- ↑ Knight, T. M. and R. D. Holt 2005. Fire generates spatial gradients in herbivory: an example from a Florida sandhill ecosystem. Ecology 86: 587-593.