Difference between revisions of "Ptilimnium capillaceum"
(→Photo Gallery) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→Distribution) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | It is distributed from eastern and central United States west to Texas and south to Miami-Dade and Collier counties<ref name="regional">http://regionalconservation.org/beta/nfyn/plantdetail.asp?tx=Ptilcapi. Accessed: March 1, 2016</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 08:50, 2 March 2016
| Ptilimnium capillaceum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Ptilimnium |
| Species: | P. capillaceum |
| Binomial name | |
| Ptilimnium capillaceum (Michx.) Raf. | |
| |
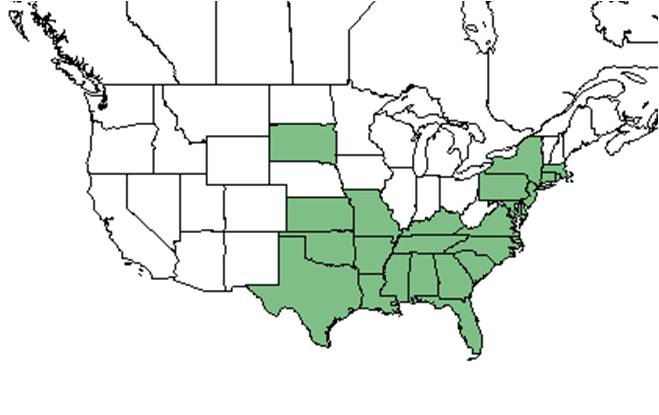
| Natural range of Ptilimnium capillaceum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Threadleaf mockbishopweed, herbwilliam
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
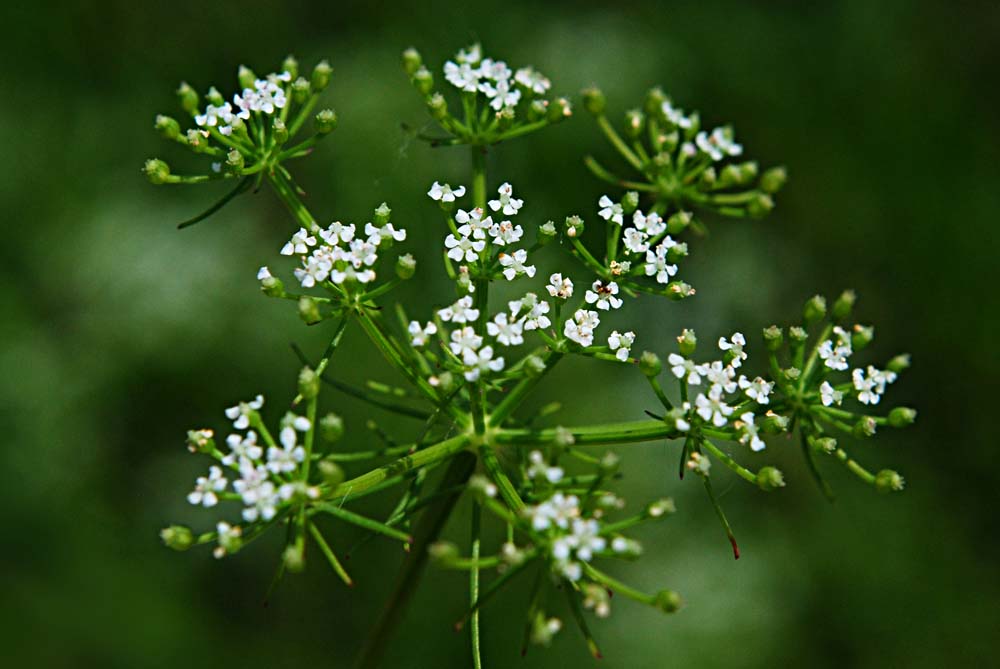
Flowers are arranged in umbels (FSU Herbarium).
"Glabrous annuals with pinnately decompound leaves or the leaves reduced to hollow, septate phyllodes. Umbels compound, terminal and axillary; involucre and involucel present; petals white. Fruit broadly ovoid to suborbicular, 1-4 mm long, glabrous, ribs prominent; mericarps semicircular in cross section." - Radford et al 1964
"Plant 1-8 dm tall. Leaves pinnately and finely decompound into numerous filiform segments 2-5 mm or more long. Peduncles 3-8 cm long; involucral bracts foliaceous, 5 mm or more long; rays 3-20, spreading, 6-21 mm long; involucel bractlets linear, about ½ length of pedicels; styles 0.2-1.5 mm long. Fruit 1.5-3 (4) mm long, 1.5 (2) mm broad." - Radford et al 1964
Distribution
It is distributed from eastern and central United States west to Texas and south to Miami-Dade and Collier counties[1].
Ecology
Habitat
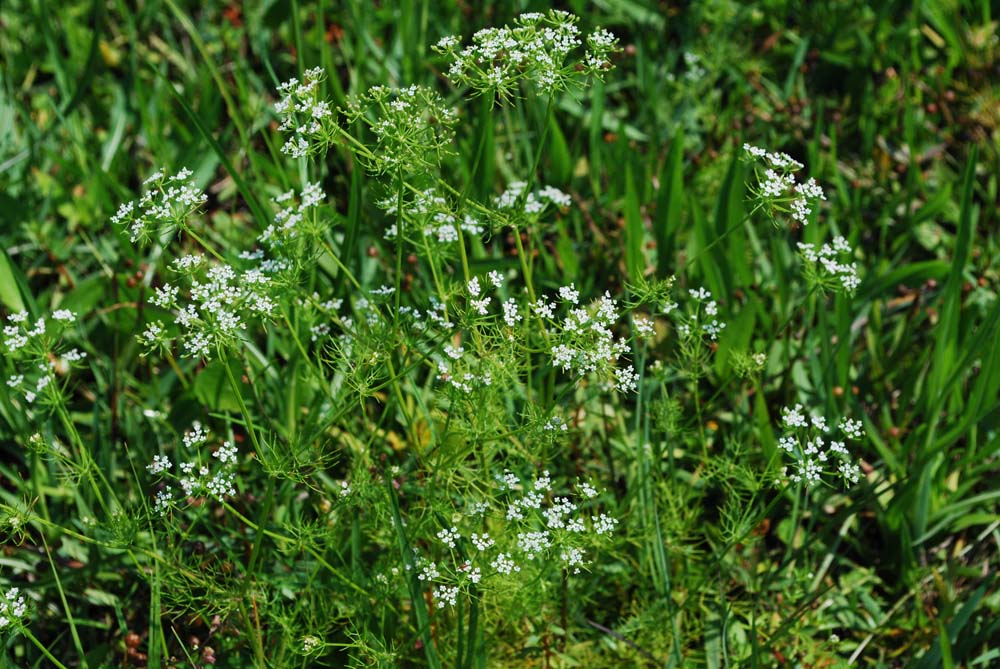
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, P. capillaceum has occurred in wiregrass/slashpine communities; the edge of a small cattail swale; mucky soils of floodplains; dry pond in a coastal hammock; cabbage palm hammocks; scrubby flatwoods adjacent to cypress swamps; slough edges; wet ditches bordering flatwoods; borders of salt flats; wet sands near a salt marsh; gum depressions; low depressions amongst sand dunes; middle of a lake growing on a tree stump; and cypress-sweetgum floodplains. It has also been observed in disturbed areas such as roadsides, a grazed cabbage palm hammock, moist roadside ditches, along railroad beds, marsh in a drainage canal bordering a swamp forest, permanently flooded pits, drained clearing of a wet hammock, exposed peat beneath pond cypresses ringing a lake after draining, and powerline transects across pine flatwoods (FSU Herbarium). Soil types include loamy sand, sand, sandy loam, sandy peat, clay, and peaty soil (FSU Herbarium). It has been observed to grow in both full sun and very shaded locations (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Anagallis minima, Eleocharis albida, Bacopa monnieri, Dichromena colorata and Sagittaria (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It flowers and fruits April through July (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It has been observed in an annually burned boggy draw in a pine forest (FSU Herbarium).
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Ptilimnium capillaceum at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Epeolus floridensis
Colletidae: Colletes mandibularis
Halictidae: Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum tamiamensis
Sphecidae: Epinysson basilaris, E. mellipes, Hoplisoides denticulatus denticulatus, Liris argentata, L. muesebecki, Oxybelus laetus fulvipes, Tachytes intermedius, T. mergus
Vespidae: Euodynerus megaera, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus bicornis, P. fulvipes rufovestris
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
Flowers of Ptilimnium capillaceum Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: William P. Adams, Loran C. Anderson, Kurt E. Blum, Dave Breil, Sidney T. Brinson, G. Fleming, P. Genelle,, C.S. Gidden, R.K. Godfrey, Darren Jackson, D.E. Kennemore Jr., G. Knight, Mabel Kral, R. Kral, Robert J. Lamaire, S.W. Leonard, Sidney McDaniel, William Lindsey,W. Miley, Marc Minno, Richard Mitchell, John B. Nelson, Elmer C. Prichard, Ronald A. Pursell, Gwynn W. Ramsey, P.L. Redfearn Jr., A. Redman, Grady W. Reinert, V. Rosario, Cecil R. Slaughter, Bian Tan, D.B. Ward, S.S. Ward, Jean W. Wooten. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bradford, Brevard, Calhoun, Charlotte, Citrus, Columbia, DeSoto, Dixie, Escambia, Franklin, Hamilton, Hernando, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, Orange, Polk, Putnam, St. Johns, Sumter, Suwannee, Taylor, Union, Volusia, Wakulla. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 784. Print.
- ↑ http://regionalconservation.org/beta/nfyn/plantdetail.asp?tx=Ptilcapi. Accessed: March 1, 2016
