Difference between revisions of "Polygonum dentoceras"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | Reproduces sexually and asexually<ref name="fws"/>. Fruits and flowers all year<ref name="fnai"/>. | ||
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
Revision as of 21:08, 24 February 2016
| Polygonum dentoceras | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Polygonaceae |
| Genus: | Polygonum |
| Species: | P. dentoceras |
| Binomial name | |
| Polygonum dentoceras (Small) Horton | |
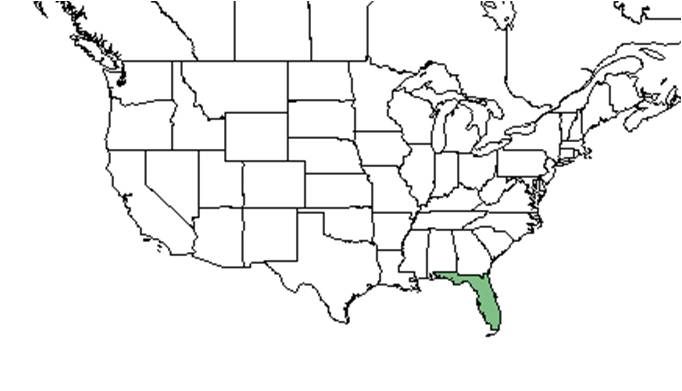
| |
| Natural range of Polygonum dentoceras from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Sandlace, Small's jointweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Polygonella myriophylla
Description
A description of Polygonum dentoceras is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
It is endemic to the ridges of central Florida[1].
Ecology
Habitat
It is found in the dry sands of Florida rosemary scrubs in central Florida[2]. It is a gap specialist and has allelopathic properties, specifically to grasses[3]
Phenology
Reproduces sexually and asexually[4]. Fruits and flowers all year[1].
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Polygonum dentoceras at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Halictidae: Lasioglossum placidensis
Leucospididae: Leucospis robertsoni
Sphecidae: Bembecinus nanus floridanus, Cerceris blakei, Tachytes pepticus
Vespidae: Leptochilus krombeini, Stenodynerus beameri
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [[1]] Florida Natural Areas Inventory. Accessed: February 24, 2016
- ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: February 2016. Collectors: L.J. Brass, D. Burch, George R. Cooley, Chas. C. Deam, Robert K. Godfrey, O. Lakela, Robert Kral, S.W. Leonard, John K. Small, D.B. Ward, Kenneth A. Wilson, Carrol E. Wood. States and Counties: Florida: DeSoto, Highlands, Polk. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Weidenhamer, J. D., D. C. Hartnett, et al. (1989). "Density-Dependent Phytotoxicity: Distinguishing Resource Competition and Allelopathic Interference in Plants." Journal of Applied Ecology 26(2): 613-624.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedfws