Difference between revisions of "Xyris caroliniana"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | Atlantic Longleaef Flatwoods with inclusions of Atlantic Mesic Longleaf Woodland, savanna, and seepage bog (Glitzenstein et al 2003). Southern Longleaf Flatwood according to Peet and Allard 1993 (Glitzenstein et al 2003). Osceola study plots soils are spodosols (Glitzenstein et al 2003). | + | Atlantic Longleaef Flatwoods with inclusions of Atlantic Mesic Longleaf Woodland, savanna, and seepage bog (Glitzenstein et al 2003). Southern Longleaf Flatwood according to Peet and Allard 1993 (Glitzenstein et al 2003). Osceola study plots soils are spodosols (Glitzenstein et al 2003). |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, ''X. caroliniana'' has been found in mesic sandy meadows; seepage slopes with ''Rhynchospora''; sandy loam of burned wiregrass-longleaf pinewoods; sandy peat of pine-palmetto flatwoods; sand of open slash pine woodland bordering ''Hypericum'' marshes; oak scrub at margin of pine flatwoods; wiregrass-palmetto-slash pine plantation; sandy peat of flatwoods bog; upper edge of grass-sedge bog; wet pine flatwoods; mixed hardwood/cabbage palm hammocks; sandy peat of hillside bogs; mixed pine-oak woodland; dry boggy area near small stand of cypress; sandy dune hallow; sandy loam at edge of ''Ilex myrtifolia'' depression swamp; turkey oak/longleaf pine barren; and in sand around ephemeral ponds (FSU Herbarium). In disturbed habitats has been found in roadside ditches; semi-disturbed remnant of longleaf pine-saw palmetto flatwoods; borrow pit bog; and in sandy peat of drained and bulldozed flatwoods bog. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Substrate types include sandy loam, sand, sandy peat, and fine sand (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include ''Rhynchospora, Hypericum, Fuirena scirpoidea, Fimbristylis caroliniana, Juncus scirpoides, Rhexia cubensis, Seymeria, Aristida stricta, Conradina, Ilex, Lyonia, Xyris elliottii, Ilex myrtifolia, Serenoa repens, Mitreola petiolata, Xyris flexuosa, Sabatia brevifolia, Kalmia hirsuta, Balduina uniflora, Polygala lutea, Sorghastrum secundum, Quercus pumila, Liatris graminifolia'', and ''Helianthus heterophyllus'' (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 14:33, 15 October 2015
| Xyris caroliniana | |
|---|---|

| |
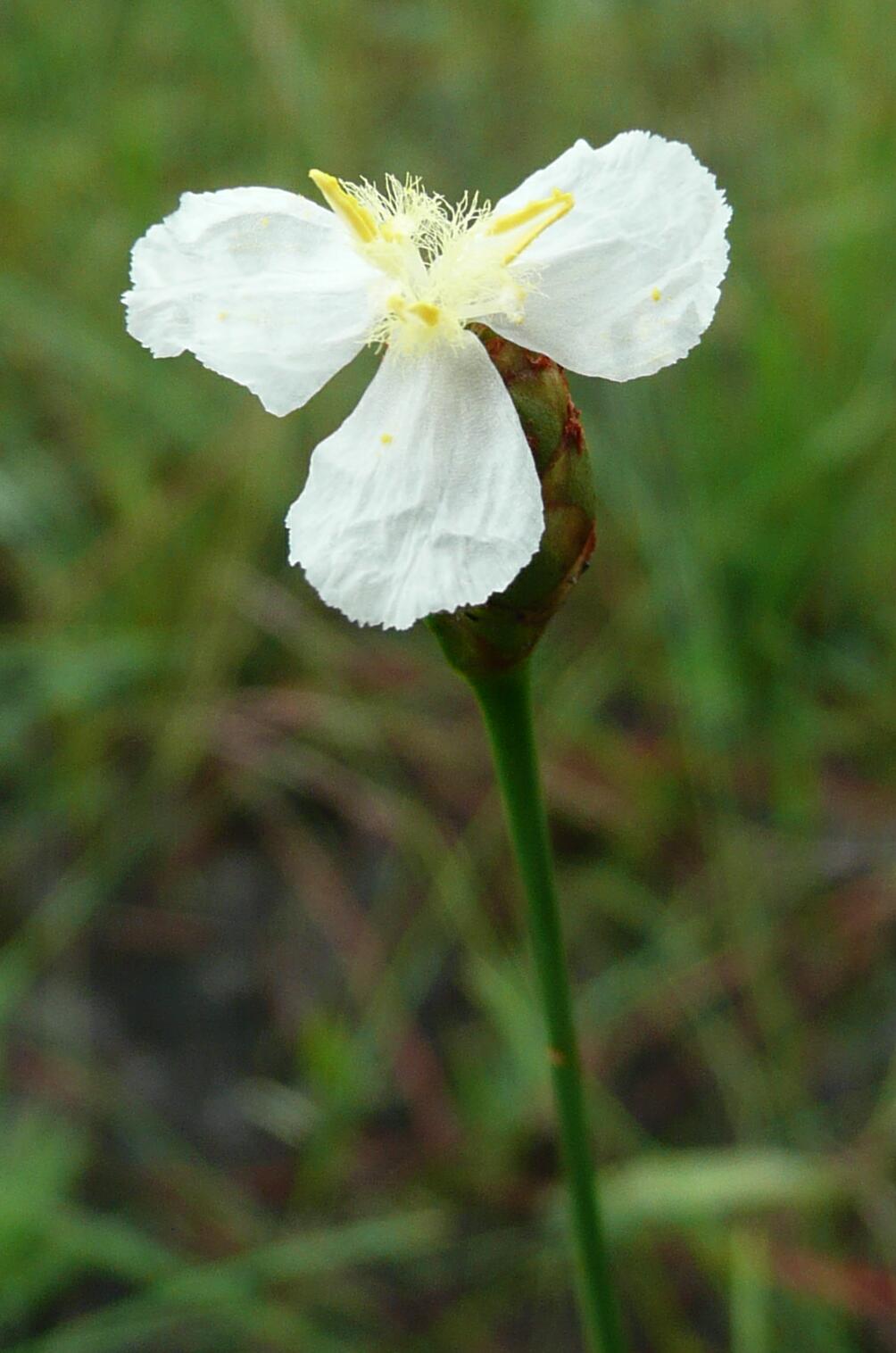
| Xyris caroliniana, the Peninsular Florida white-flowered form | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Commelinales |
| Family: | Xyridaceae |
| Genus: | Xyris |
| Species: | X. caroliniana |
| Binomial name | |
| Xyris caroliniana Walter | |
| |
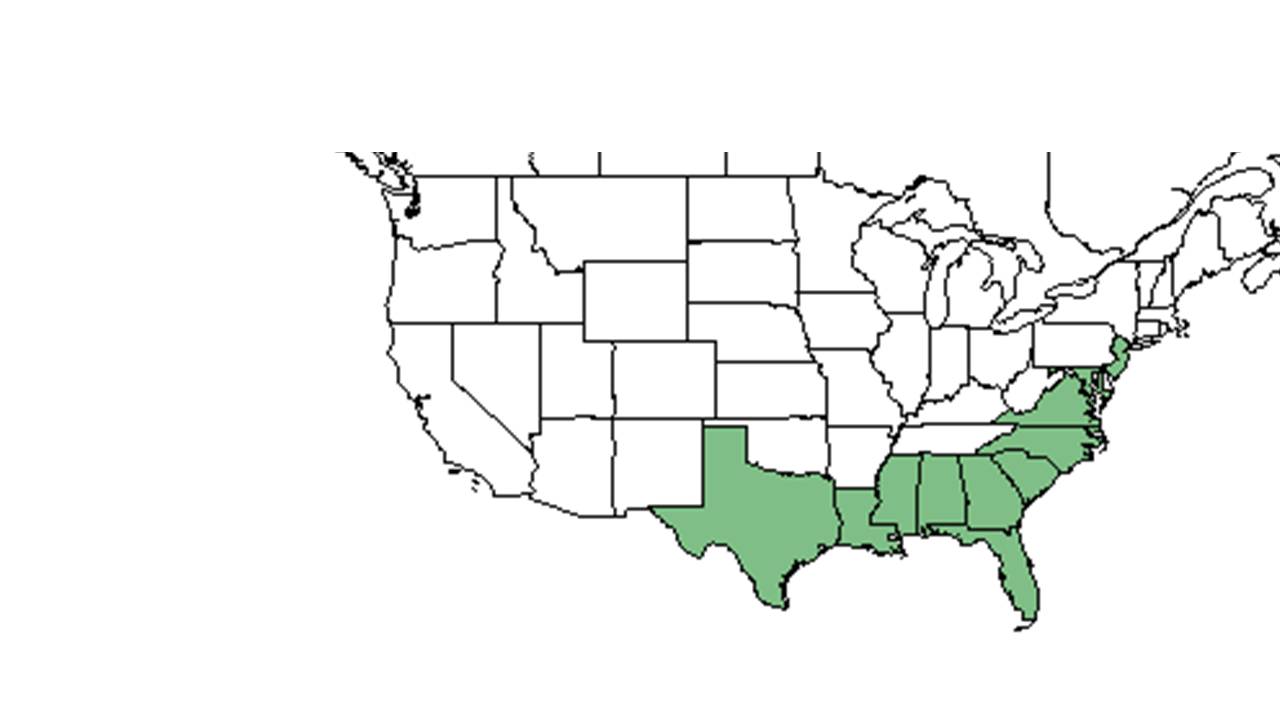
| Natural range of Xyris caroliniana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Carolina yelloweyed grass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Solitary or in small tufts, the bases deeply set in the substrate, perennating by means of pale, elongated, fleshy lateral buds. Outer leaves scaly, castaneous; longer leaves linear, 2-5 (-7) dm long, 2-5 mm broad, twisted and flexuous, mostly smooth, minutely tuberculate along the margins, base abruptly dilated, dark brown, shiny, long-persistent as scales. Sheath of the scape shorter than the leaves, tight below, loose toward the oblique orifice which is tipped by a very short blade. Scapes linear, 5-10 dm long, twisted, flexuous, smooth, terete and minutely ridged below, the ridges minutely tuberculate, becoming oval in cross-section and smooth to 1-ridged above. Spikes 1-3 cm long, elliptic to narrowly lanceolate in outline, blunt to acute, of few to many closely imbricate bracts. Fertile bracts 0.5-1.3 cm long, oblong to obovate, entire or emarginate, becoming erose, the center ovate area gray-green, the wide margin light tan or brown. Lateral sepals linear, slightly to conspicuously exserted, tan to reddish brown with a broad keel which is entire below but fimbriate at its exserted apex. Petal blades obovate, 8-9 mm long, yellow in n. Fla., becoming more typically white in peninsular Fla., in most populations opening in the afternoon. Seeds fusiform, narrow, 0.8-1 mm long, translucent, with about 20 pale, stripelike longitudinal lines, the vertical lines apparent.
Additoinal description information of Xyris caroliniana is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Moist sands of pine flatwoods or savannas, well-drained sands or moist depressions of mesic to scrubby flatwoods, sandhills, and scrub. Summer-Fall. Common throughout Florida. Coastal Plain. New Jersey; southeast Virginia, south to Florida, west to southeast Texas.
Ecology
Habitat
Atlantic Longleaef Flatwoods with inclusions of Atlantic Mesic Longleaf Woodland, savanna, and seepage bog (Glitzenstein et al 2003). Southern Longleaf Flatwood according to Peet and Allard 1993 (Glitzenstein et al 2003). Osceola study plots soils are spodosols (Glitzenstein et al 2003).
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, X. caroliniana has been found in mesic sandy meadows; seepage slopes with Rhynchospora; sandy loam of burned wiregrass-longleaf pinewoods; sandy peat of pine-palmetto flatwoods; sand of open slash pine woodland bordering Hypericum marshes; oak scrub at margin of pine flatwoods; wiregrass-palmetto-slash pine plantation; sandy peat of flatwoods bog; upper edge of grass-sedge bog; wet pine flatwoods; mixed hardwood/cabbage palm hammocks; sandy peat of hillside bogs; mixed pine-oak woodland; dry boggy area near small stand of cypress; sandy dune hallow; sandy loam at edge of Ilex myrtifolia depression swamp; turkey oak/longleaf pine barren; and in sand around ephemeral ponds (FSU Herbarium). In disturbed habitats has been found in roadside ditches; semi-disturbed remnant of longleaf pine-saw palmetto flatwoods; borrow pit bog; and in sandy peat of drained and bulldozed flatwoods bog.
Substrate types include sandy loam, sand, sandy peat, and fine sand (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Rhynchospora, Hypericum, Fuirena scirpoidea, Fimbristylis caroliniana, Juncus scirpoides, Rhexia cubensis, Seymeria, Aristida stricta, Conradina, Ilex, Lyonia, Xyris elliottii, Ilex myrtifolia, Serenoa repens, Mitreola petiolata, Xyris flexuosa, Sabatia brevifolia, Kalmia hirsuta, Balduina uniflora, Polygala lutea, Sorghastrum secundum, Quercus pumila, Liatris graminifolia, and Helianthus heterophyllus (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.