Difference between revisions of "Strophostyles umbellata"
(→Photo Gallery) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Common name: pink fuzzybean | Common name: pink fuzzybean | ||
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
Revision as of 15:33, 14 October 2015
| Strophostyles umbellata | |
|---|---|

| |
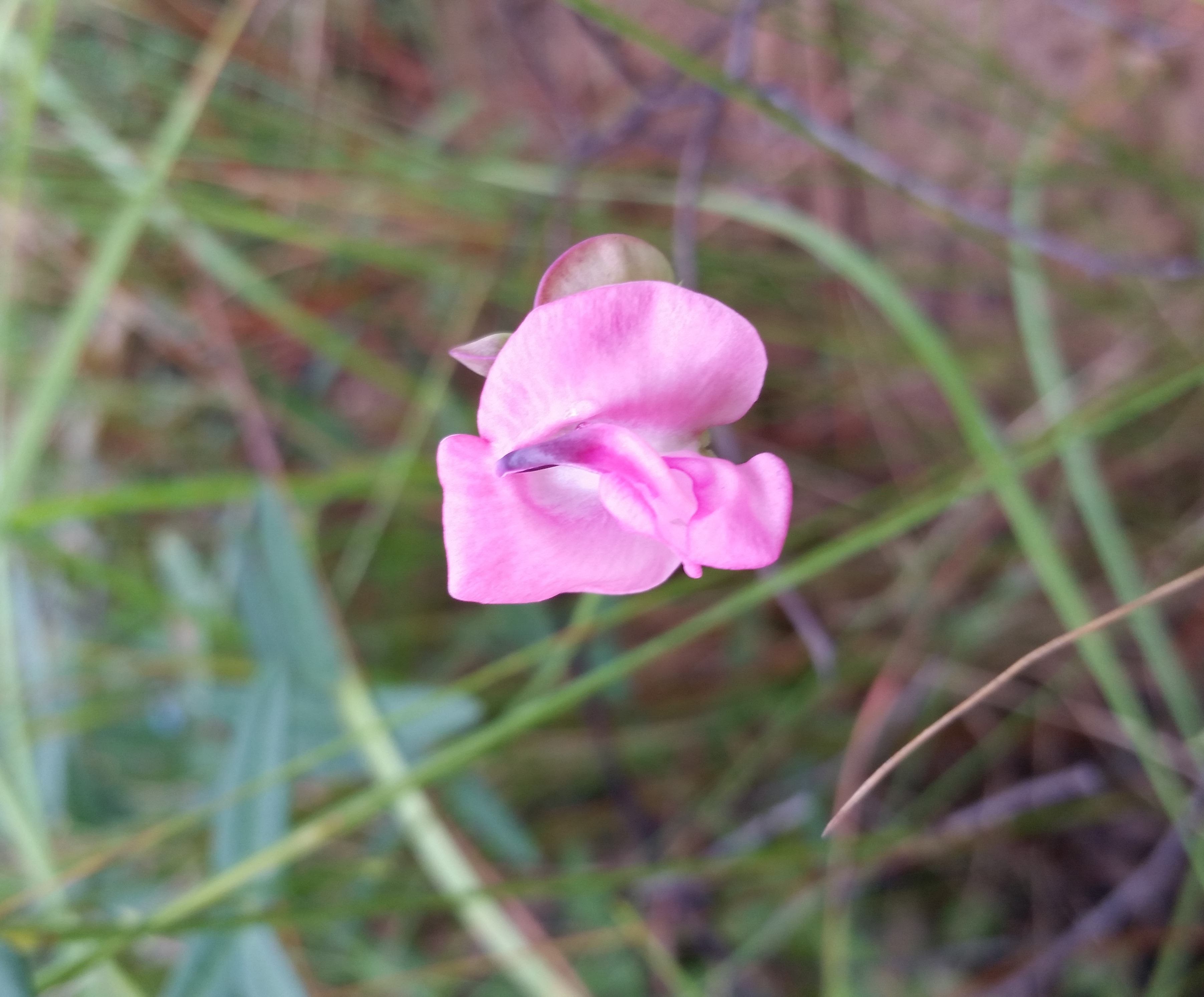
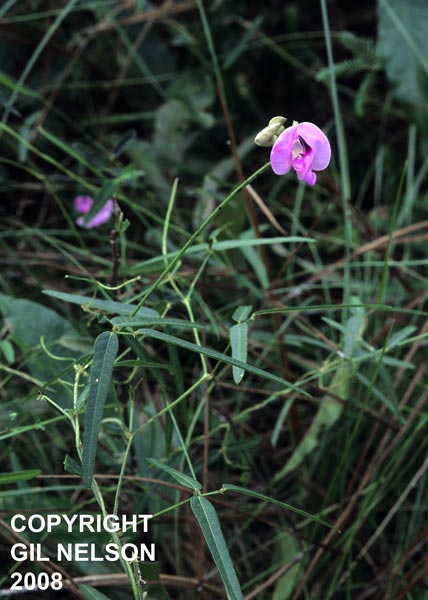
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Strophostyles |
| Species: | S. umbellata |
| Binomial name | |
| Strophostyles umbellata (Muhl. ex Willd.) Britton | |
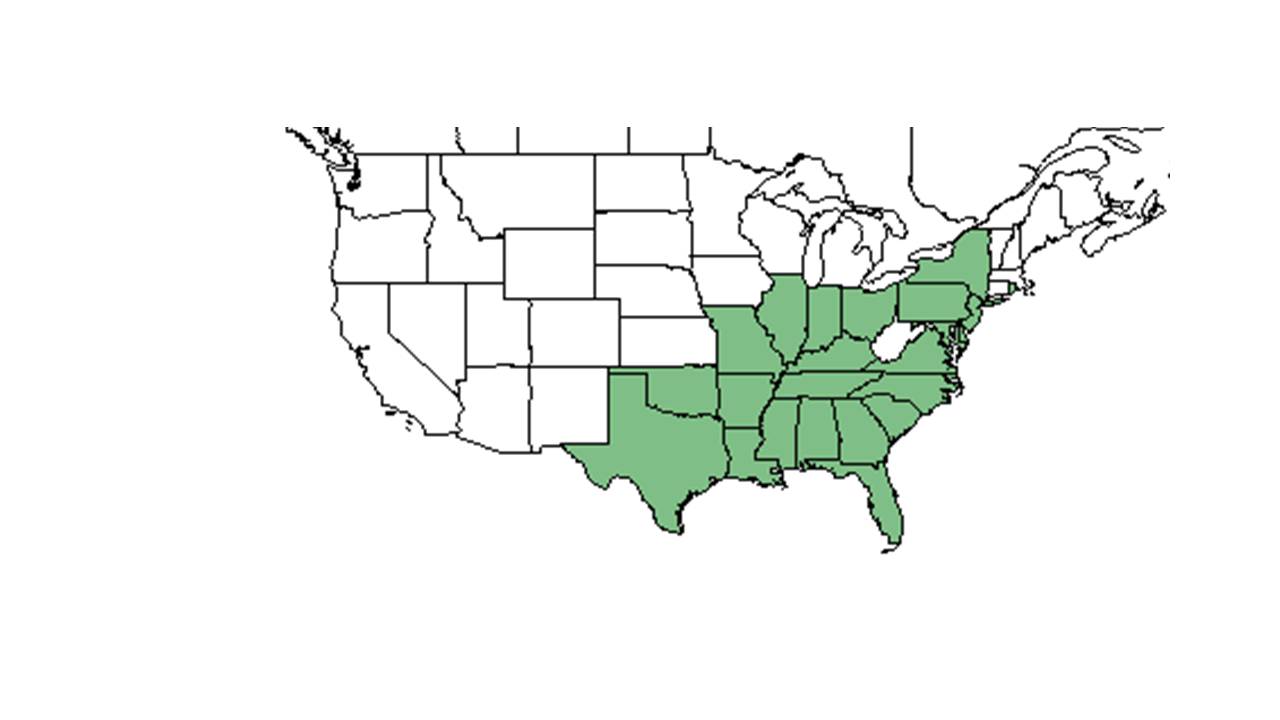
| |
| Natural range of Strophostyles umbellata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: pink fuzzybean
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It is associated with longleaf pine-wiregrass communities (Hainds et al 1999). Is found in limestone glades in Leavenworth Barrens Nature Preserve in Crawford County, Indiana where burning is important (Wade and Menges 1986). Strophostyles umbellata is predominately in native groundcover with a statistical affinity in upland pinelands of South Georgia (Ostertag and Robertson 2007).
Phenology
It blooms from late June to early July (Hainds et al 1999).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It occurs in areas that are frequently burned (Hainds et al 1999).
Pollination
Use by animals
It is included in bobwhite quail diet (Sweeney 1981).
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Hainds, M. J., R. J. Mitchell, B. J. Palik, L. R. Boring and D. H. Gjerstad. 1999. Distribution of native legumes (Leguminoseae) in frequently burned longleaf pine (Pinaceae)-wiregrass (Poaceae) ecosystems. American Journal of Botany 86:1606-1614.
Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.
Sweeney, J. M., C. R. Wenger and N. S. Yoho. 1981. Bobwhite quail food in young Arkansas loblolly pine plantations. Arkansas Experiment Station bulletin 852. Fayetteville, AR, University of Arkansas, Divisionn of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station.
Wade, K. A. and E. S. Menges. 1987. Effects of fire on invasion and community structure of a southern Indiana cedar barrens. Indiana Academy of Science 96:273-286.
