Difference between revisions of "Euphorbia curtisii"
(→References and notes) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
''E. curtisii'' was absent before herbicide treatments near the end of the growing season but present after. This might be because of increased availability of resources.<ref>Bohn, K. K., P. Minogue, et al. (2011). "Control of invasive Japanese Climbing Fern (Lygodium japonicum) and response of native ground cover during restoration of a disturbed longleaf pine ecosystem." Ecological Restoration 29: 346-356.</ref> | ''E. curtisii'' was absent before herbicide treatments near the end of the growing season but present after. This might be because of increased availability of resources.<ref>Bohn, K. K., P. Minogue, et al. (2011). "Control of invasive Japanese Climbing Fern (Lygodium japonicum) and response of native ground cover during restoration of a disturbed longleaf pine ecosystem." Ecological Restoration 29: 346-356.</ref> | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | This has been found in wet pine flatwoods, in Longleaf pinelands and savannas (FSU Herbarium). This has also been spotted in human disturbed areas such as along roadsides and in edges of flatwoods (FSU Herbarium). | + | This has been found in wet pine flatwoods, in Longleaf pinelands and savannas (FSU Herbarium). This has also been spotted in human disturbed areas such as along roadsides and in edges of flatwoods (FSU Herbarium). May be associated with areas that have been disturbed where the soil is a heavy sticky clay type (FSU Herbarium). |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 13 July 2015
| Euphorbia curtisii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Euphorbia |
| Species: | E. curtisii |
| Binomial name | |
| Euphorbia curtisii Engelm. | |
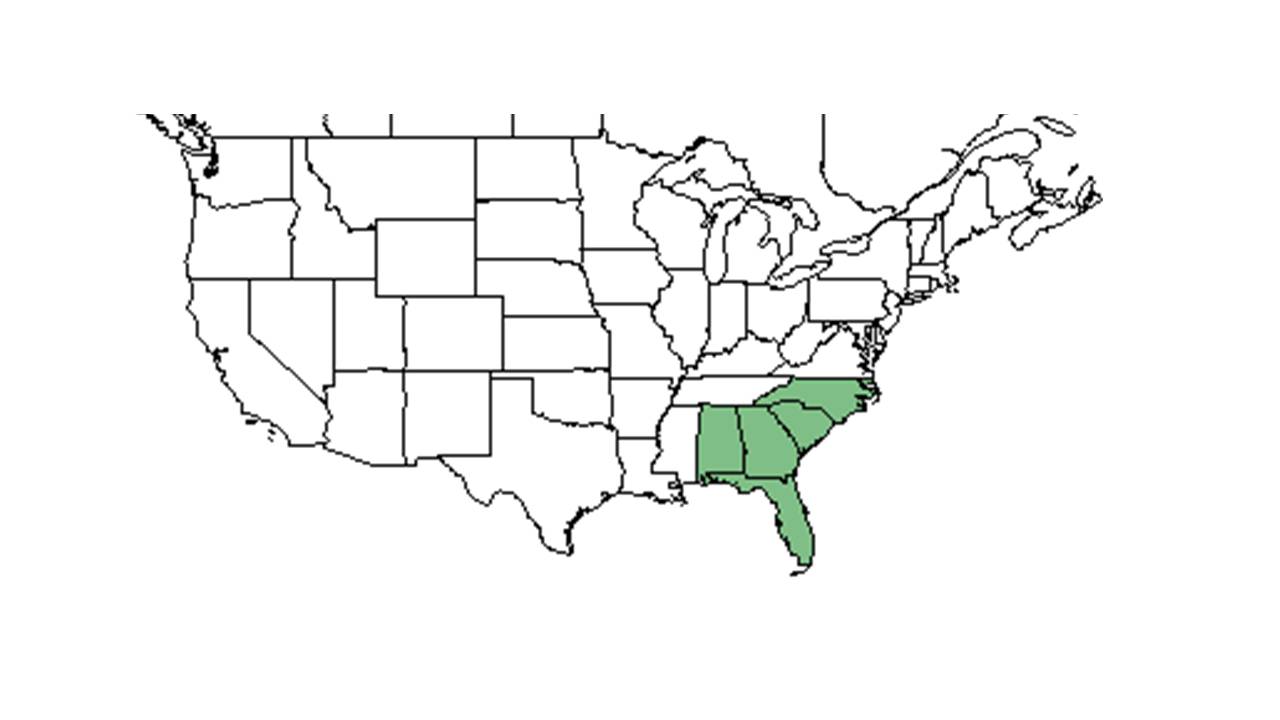
| |
| Natural range of Euphorbia curtisii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: Curtis' spurge
Distribution
Ecology
E. curtisii was absent before herbicide treatments near the end of the growing season but present after. This might be because of increased availability of resources.[1]
Habitat
This has been found in wet pine flatwoods, in Longleaf pinelands and savannas (FSU Herbarium). This has also been spotted in human disturbed areas such as along roadsides and in edges of flatwoods (FSU Herbarium). May be associated with areas that have been disturbed where the soil is a heavy sticky clay type (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.
Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey and Roy Komarek.
States and Counties: Florida: Jefferson, Leon, and Wakulla. Georgia:Thomas.
- ↑ Bohn, K. K., P. Minogue, et al. (2011). "Control of invasive Japanese Climbing Fern (Lygodium japonicum) and response of native ground cover during restoration of a disturbed longleaf pine ecosystem." Ecological Restoration 29: 346-356.