Difference between revisions of "Dichanthelium laxiflorum"
Adam.Vansant (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (57 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Dichanthelium laxiflorum | | name = Dichanthelium laxiflorum | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = Dich_laxi.jpg |
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), [http://www.florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/Default.aspx Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants] |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
| classis = Liliopsida – Monocotyledons | | classis = Liliopsida – Monocotyledons | ||
| − | | ordo = | + | | ordo = Poales |
| familia = Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae | | familia = Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae | ||
| genus = ''Dichanthelium'' | | genus = ''Dichanthelium'' | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = (Lam.) Gould | | binomial_authority = (Lam.) Gould | ||
| range_map = DICH_LAXI_dist.jpg | | range_map = DICH_LAXI_dist.jpg | ||
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Dichanthelium laxiflorum'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Dichanthelium laxiflorum'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=DILA9 Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Common names: openflower rosette grass; open-flower witchgrass | ||
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: ''Panicum laxiflorum'' Lamarck; <ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: ''Dichathelium xalapense'' (Kunth) Wipff var. ''strictirameum'' (A.S. Hitchcock & Chase) Wipff; ''D. xalapense'' (Kunth) Wipff var. ''xalapense''; ''Panicum laxaiflorum''; ''P. xalapense''; ''P. xalapense'' var. ''strictirameum'' A.S. Hitchcock & Chase; ''P. xalapense'' Kunth var. ''xalapense''<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Dichanthelium laxiflorum'' is a perennial graminoid with a cespitose growth habit. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Bonnie Carswell, Kurt E. Blum, Sidney McDaniel, Lloyd H. Shinners, R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, R. Kral, Raymond Athey, John B. Nelson, S. Bennett, T. Kohlsaat, D. Kennemore, Charles N. Horn, Carolyn Kindell, W ledbetter, R.K. Godfrey, K. Craddock Burks, J. B. Phipps, Sydney Thompson, R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, A. H. Curtiss, Sidney McDaniel, James R. Burkhalter, Patricia Elliot, C. Jackson, H. Kurz, George R. Cooley, Joseph Monachino, R. Komarek, Cecil R Slaughter, Marie Victorin, Rolland Germain, Marcel Raymond, J. Kucyniak, and André. States and Counties: Alabama: Geneva and Pickens. Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Hernando, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Palm Beach, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Union, Walton, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur and Grady. Kentucky: Carlisle. Louisiana: East Feliciana. North Carolina: Wake. South Carolina: Abbeville, Fairfield, and Calhoun. Tennessee: Coffee. Texas: Freestone and Van Zandt. Other Countries: Canada</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Generally, for the ''Dichanthelium'' genus, they have "spikelets usually in panicles, round or nearly so in cross section, 2-flowered, terminal fertile, basal sterile, neutral or staminate. First glume usually present, 2nd glume and sterile lemma similar; fertile lemma and palea indurate without hyaline margins. Taxonomically our most difficult and least understood genus of grasses, more than 100 species an varieties are ascribed to the Carolinas by some authors. Note general descriptions for species groups (e.g., 1-4, 5-8, 9-13, and 26-62)." <ref name=rad> Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 142-151. Print.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specifically, for the ''D. laxiflorum'' species, they are "cespitose perennial; culms 1.5-4.5 dm tall, nodes usually bearded, internodes glabrous or scaberulous. Leaves mostly low cauline; blades to 16 cm long, 4-15 mm wide, glabrous or scaberulous. Leaves mostly low cauline; blades to 16 cm long, appressed to spreading-pilose; ligules ciliate, 0.5-1 mm long. Vernal panicle 4-9 cm long, 3-6 lipsoid, 1.6-2.3 mm long; pedicels smoothish, 1-10 mm long. First glume nerveless or 1-nerved, scarious, acute, 16-2.3 mm long. Sterile palea scarious, 1.2-1.6 mm long; fertile lemma and palea nerveless to faintly nerved, lustrous, yellowish to brownish, acute, 1.5-2 mm long. Grain whitish to yellowish, broadly ellipsoid, 1-1.5 mm long." <ref name=rad/> | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
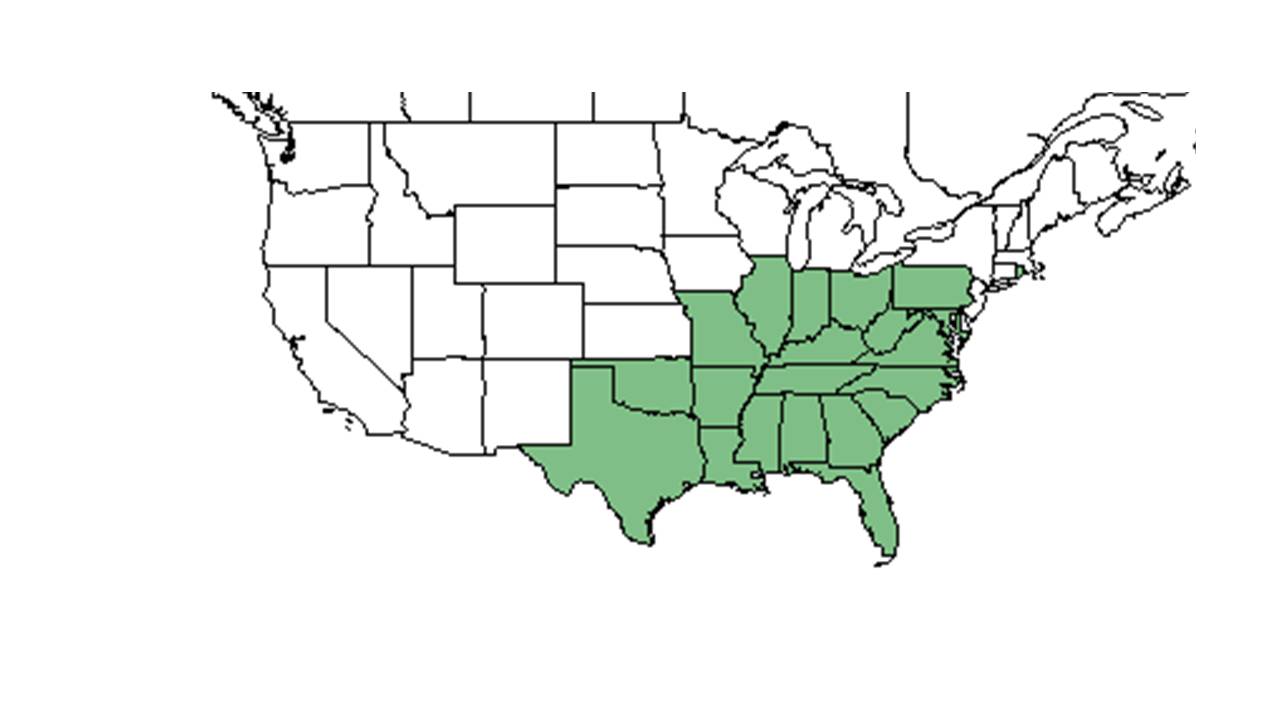
| + | ''D. laxiflorum'' is native to the eastern United States, from Maryland to Florida, west to Texas, and north to Indiana. It is also native to Mexico, Central America, and the West Indies.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | General habitats of this species is shaded to open woodlands, and most often in moist soils.<ref name=weakley/> ''D. laxiflorum'' can live in disturbed areas such as clear-cuts, thinned woods, burned areas, roadsides, power line corridors, and old fields, <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> with clay to sandy loam soil in subtropical climates.<ref name="Iglay et al 2010"/> It can also dwell in dry areas,<ref name="Taft 2003"/> like sandstone barrens communities.<ref name="Taft 2003"/> It can be found in loblolly pine communities<ref>Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest plants of the southeast, and their wildlife uses Champaign, IL, Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> and longleaf pine communities.<ref name="Cohen et al 2004"/> It also occurs in low ground hardwood communities, mesic hammocks, river banks, above lime sinks, on coastal hammocks, and near bogs. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> As well, it is a frequent component of prairie hammocks that are in the Florida dry prairie landscape.<ref>Orzell, S. L. and E. L. Bridges (2006). "Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape." Florida Ecosystem 1(3): 123-133.</ref> It is listed as a facultative and facultative upland species in various regions, where it most commonly occurs in upland non-wetland areas, but can also occasionally occur in wetland habitats.<ref name= "USDA"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''D. laxiflorum'' was found to be an increaser in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.<ref name=Dixon>Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associated species include ''Senecio, Krigia, Lolium, Hordeum, Tradescantia, Scleria, Diospyros, Rhus copallina, Hypericum mutilum, P. angustfolium, D. commutatum''. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | Common flowering time of ''D. laxiflorum'' is between April and September.<ref name=weakley/> Flowering has been observed in January through May, and November, and fruiting has been observed in January through June, and November.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/><ref>Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 29 APR 2019</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| − | It can be found in the seed bank of disturbed and undisturbed sites<ref name="Cohen et al 2004">Cohen, S., R. Braham, et al. (2004). "Seed bank viability in disturbed longleaf pine sites." Restoration Ecology 12: 503-515.</ref> | + | It can be found in the seed bank of disturbed and undisturbed sites.<ref name="Cohen et al 2004">Cohen, S., R. Braham, et al. (2004). "Seed bank viability in disturbed longleaf pine sites." Restoration Ecology 12: 503-515.</ref> It can also be found in the seed bank of a Florida flatwoods plant community.<ref>Kalmbacher, R., N. Cellinese, et al. (2005). "Seeds obtained by vacuuming the soil surface after fire compared with soil seedbank in a flatwoods plant community." Native Plants Journal 6: 233-241.</ref> This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. <ref>Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.</ref> |
| + | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| + | From observing the results of Taft's prescribed burns, fire seems to be required for germination.<ref name="Taft 2003">Taft, J. B. (2003). "Fire effects on community structure, composition, and diversity in a dry sandstone barrens." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 130: 170-192.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | This species has been found in frequently burned areas<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> as populations of ''D. laxiflorum'' have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.<ref>Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref><ref>Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.</ref> |
| − | === | + | |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | In an experiment by Iglay, Leopold, Miller, and Burger, ''D. laxiflorum'' had a positive response to dormant season prescribed fire and to imazapyr, a herbicide.<ref name="Iglay et al 2010">Iglay, R. B., B. D. Leopold, et al. (2010). "Effect of plant community composition on plant response to fire and herbicide treatments." Forest Ecology and Management 260: 543-548.</ref> Following an early dormant season, moderate-intensity burn in 1989, it rapidly increased, probably due to a stimulation if the seed bank. By 1995, ''D. laxiflorum'' occurred in 64% of the quadrants in Illinois and was the species with the greatest frequency, replacing ''Schizachyrium scoparium'' as the dominant species.<ref name="Taft 2003"/> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | |
| − | == | + | <!--===Pollination===--> |
| + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> | ||
| + | ''Dichanthelium laxiflorum'' consists of approximately 2-5% of the diet for large mammals and about 10-25% of the diet for various terrestrial birds.<ref>Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> Significant use of this species is during the winter.<ref>Gee, K. L., et al. (1994). White-tailed deer: their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.</ref> | ||
| + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | ''D. laxiflorum'' is listed as endangered by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.<ref name= "USDA">USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 29 April 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.</ref> | ||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
| + | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 19:03, 1 August 2024
| Dichanthelium laxiflorum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. laxiflorum |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium laxiflorum (Lam.) Gould | |
| |
| Natural range of Dichanthelium laxiflorum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: openflower rosette grass; open-flower witchgrass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Panicum laxiflorum Lamarck; [1]
Varieties: Dichathelium xalapense (Kunth) Wipff var. strictirameum (A.S. Hitchcock & Chase) Wipff; D. xalapense (Kunth) Wipff var. xalapense; Panicum laxaiflorum; P. xalapense; P. xalapense var. strictirameum A.S. Hitchcock & Chase; P. xalapense Kunth var. xalapense[1]
Description
Dichanthelium laxiflorum is a perennial graminoid with a cespitose growth habit. [2]
Generally, for the Dichanthelium genus, they have "spikelets usually in panicles, round or nearly so in cross section, 2-flowered, terminal fertile, basal sterile, neutral or staminate. First glume usually present, 2nd glume and sterile lemma similar; fertile lemma and palea indurate without hyaline margins. Taxonomically our most difficult and least understood genus of grasses, more than 100 species an varieties are ascribed to the Carolinas by some authors. Note general descriptions for species groups (e.g., 1-4, 5-8, 9-13, and 26-62)." [3]
Specifically, for the D. laxiflorum species, they are "cespitose perennial; culms 1.5-4.5 dm tall, nodes usually bearded, internodes glabrous or scaberulous. Leaves mostly low cauline; blades to 16 cm long, 4-15 mm wide, glabrous or scaberulous. Leaves mostly low cauline; blades to 16 cm long, appressed to spreading-pilose; ligules ciliate, 0.5-1 mm long. Vernal panicle 4-9 cm long, 3-6 lipsoid, 1.6-2.3 mm long; pedicels smoothish, 1-10 mm long. First glume nerveless or 1-nerved, scarious, acute, 16-2.3 mm long. Sterile palea scarious, 1.2-1.6 mm long; fertile lemma and palea nerveless to faintly nerved, lustrous, yellowish to brownish, acute, 1.5-2 mm long. Grain whitish to yellowish, broadly ellipsoid, 1-1.5 mm long." [3]
Distribution
D. laxiflorum is native to the eastern United States, from Maryland to Florida, west to Texas, and north to Indiana. It is also native to Mexico, Central America, and the West Indies.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
General habitats of this species is shaded to open woodlands, and most often in moist soils.[1] D. laxiflorum can live in disturbed areas such as clear-cuts, thinned woods, burned areas, roadsides, power line corridors, and old fields, [2] with clay to sandy loam soil in subtropical climates.[4] It can also dwell in dry areas,[5] like sandstone barrens communities.[5] It can be found in loblolly pine communities[6] and longleaf pine communities.[7] It also occurs in low ground hardwood communities, mesic hammocks, river banks, above lime sinks, on coastal hammocks, and near bogs. [2] As well, it is a frequent component of prairie hammocks that are in the Florida dry prairie landscape.[8] It is listed as a facultative and facultative upland species in various regions, where it most commonly occurs in upland non-wetland areas, but can also occasionally occur in wetland habitats.[9]
D. laxiflorum was found to be an increaser in its long-term response following cessation of repeated soil disturbance.[10]
Associated species include Senecio, Krigia, Lolium, Hordeum, Tradescantia, Scleria, Diospyros, Rhus copallina, Hypericum mutilum, P. angustfolium, D. commutatum. [2]
Phenology
Common flowering time of D. laxiflorum is between April and September.[1] Flowering has been observed in January through May, and November, and fruiting has been observed in January through June, and November.[2][11]
Seed dispersal
It can be found in the seed bank of disturbed and undisturbed sites.[7] It can also be found in the seed bank of a Florida flatwoods plant community.[12] This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [13]
Seed bank and germination
From observing the results of Taft's prescribed burns, fire seems to be required for germination.[5]
Fire ecology
This species has been found in frequently burned areas[2] as populations of D. laxiflorum have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.[14][15]
In an experiment by Iglay, Leopold, Miller, and Burger, D. laxiflorum had a positive response to dormant season prescribed fire and to imazapyr, a herbicide.[4] Following an early dormant season, moderate-intensity burn in 1989, it rapidly increased, probably due to a stimulation if the seed bank. By 1995, D. laxiflorum occurred in 64% of the quadrants in Illinois and was the species with the greatest frequency, replacing Schizachyrium scoparium as the dominant species.[5]
Dichanthelium laxiflorum consists of approximately 2-5% of the diet for large mammals and about 10-25% of the diet for various terrestrial birds.[16] Significant use of this species is during the winter.[17]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
D. laxiflorum is listed as endangered by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.[9]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Bonnie Carswell, Kurt E. Blum, Sidney McDaniel, Lloyd H. Shinners, R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, R. Kral, Raymond Athey, John B. Nelson, S. Bennett, T. Kohlsaat, D. Kennemore, Charles N. Horn, Carolyn Kindell, W ledbetter, R.K. Godfrey, K. Craddock Burks, J. B. Phipps, Sydney Thompson, R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, A. H. Curtiss, Sidney McDaniel, James R. Burkhalter, Patricia Elliot, C. Jackson, H. Kurz, George R. Cooley, Joseph Monachino, R. Komarek, Cecil R Slaughter, Marie Victorin, Rolland Germain, Marcel Raymond, J. Kucyniak, and André. States and Counties: Alabama: Geneva and Pickens. Florida: Alachua, Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Hernando, Holmes, Jackson, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Palm Beach, Putnam, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Union, Walton, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur and Grady. Kentucky: Carlisle. Louisiana: East Feliciana. North Carolina: Wake. South Carolina: Abbeville, Fairfield, and Calhoun. Tennessee: Coffee. Texas: Freestone and Van Zandt. Other Countries: Canada
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 142-151. Print.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Iglay, R. B., B. D. Leopold, et al. (2010). "Effect of plant community composition on plant response to fire and herbicide treatments." Forest Ecology and Management 260: 543-548.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Taft, J. B. (2003). "Fire effects on community structure, composition, and diversity in a dry sandstone barrens." Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 130: 170-192.
- ↑ Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest plants of the southeast, and their wildlife uses Champaign, IL, Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Cohen, S., R. Braham, et al. (2004). "Seed bank viability in disturbed longleaf pine sites." Restoration Ecology 12: 503-515.
- ↑ Orzell, S. L. and E. L. Bridges (2006). "Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape." Florida Ecosystem 1(3): 123-133.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 29 April 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Dixon, C. M., K. M. Robertson, A. M. Reid and M. T. Rother. 2024. Mechanical soil disturbance in a pine savanna has multiyear effects on plant species composition. Ecosphere 15(2):e4759.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 29 APR 2019
- ↑ Kalmbacher, R., N. Cellinese, et al. (2005). "Seeds obtained by vacuuming the soil surface after fire compared with soil seedbank in a flatwoods plant community." Native Plants Journal 6: 233-241.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Gee, K. L., et al. (1994). White-tailed deer: their foods and management in the cross timbers. Ardmore, OK, Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.