Difference between revisions of "Bignonia capreolata"
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Bignonia capreolata'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.sc.egov.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=BICA Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Bignonia capreolata'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.sc.egov.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=BICA Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: | + | Common name: cross-vine |
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
Synonyms: ''Anisostichus capreolata'' (Linnaeus) Bureau; ''Anisostichus crucigera'' (Linnaeus) Bureau<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | Synonyms: ''Anisostichus capreolata'' (Linnaeus) Bureau; ''Anisostichus crucigera'' (Linnaeus) Bureau<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:27, 13 July 2023
| Bignonia capreolata | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Bignoniaceae |
| Genus: | Bignonia |
| Species: | B. capreolata |
| Binomial name | |
| Bignonia capreolata L. | |
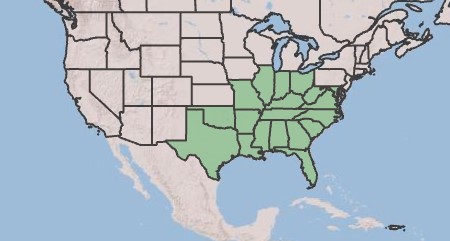
| |
| Natural range of Bignonia capreolata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: cross-vine
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Anisostichus capreolata (Linnaeus) Bureau; Anisostichus crucigera (Linnaeus) Bureau[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
B. capreolata is a climbing vine often found in the crowns and mid-stories of hardwood trees. Its natural communities include mixed pine-hardwood forests and forest edges, annually burned savannas, mesic hammocks, old hardwood forests, sandhill slopes, ravines, and floodplains. B. capreolata can grow in low or upland areas in loamy sand.[2]
Associated species of B. capreolata include Liquidambar styraciflua, Vitis rotundifolia, Quercus spp., and Myrica cerifera.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2023. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Chris Buddenhagen, Kevin England, Robert K. Godfrey, Brian R. Keener, R. Komarek, and John B. Nelson. States and counties: Alabama: Limestone. Florida: Holmes, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Grady