Difference between revisions of "Helianthus heterophyllus"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
|||
| (39 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = Nutt. | | binomial_authority = Nutt. | ||
| range_map = HELI_HETE_dist.jpg | | range_map = HELI_HETE_dist.jpg | ||
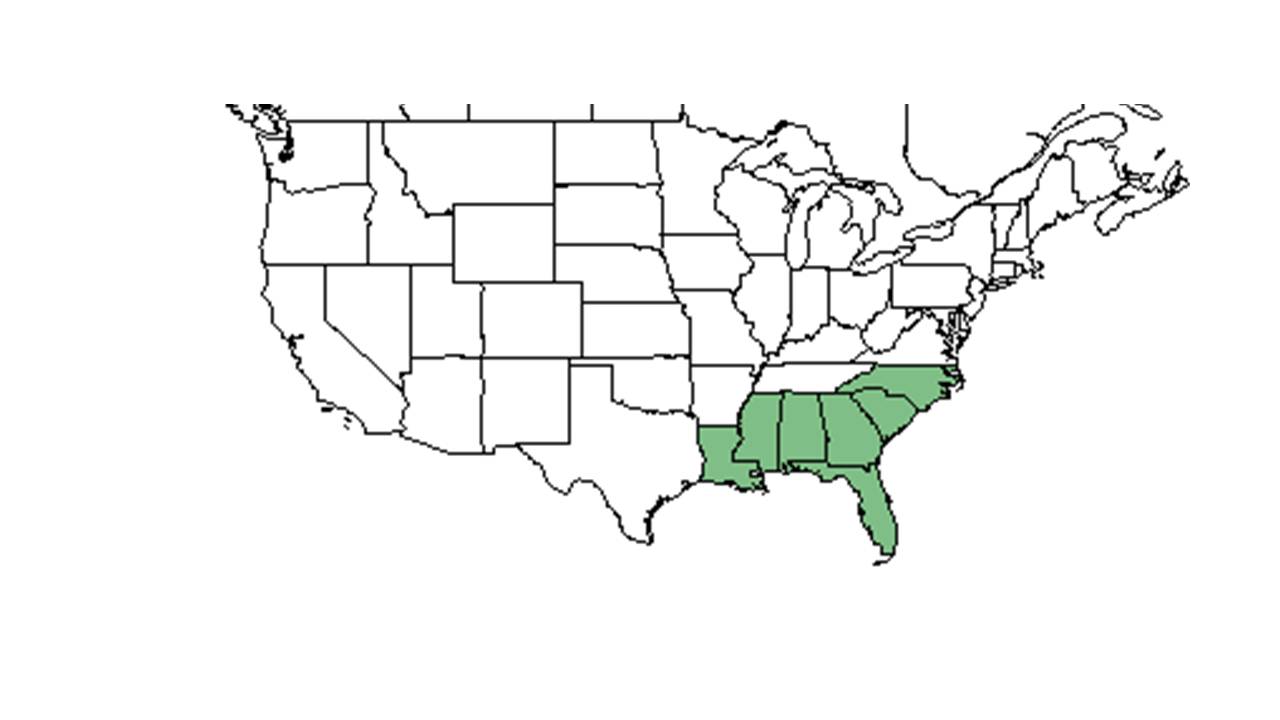
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Helianthus heterophyllus'' from USDA NRCS [http:// | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Helianthus heterophyllus'' from USDA NRCS [http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=HEHE4 Plants Database]. |
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Common names: variableleaf sunflower; wetland sunflower; savanna sunflower | ||
| + | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: none<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | A description of ''Helianthus heterophyllus'' is provided in [http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=250066885 The Flora of North America]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Helianthus heterophyllus'' is a perennial herbaceous species. | ||
| + | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | This plant is a southeastern Coastal Plain endemic. It occurs from southeastern North Carolina, south to Panhandle Florida, and west to southeastern Louisiana.<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | ''H. heterophyllus'' tends to grow on moist sandy soils at lower elevations.<ref name=fsu>Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Ann F. Johnson, R. Kral, R.K. Godfrey, John Morrill, Jean W. Wooten, Robert A. Norris, Sidney McDaniel, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, Nancy E. Jordan, Harry E. Ahles, Joseph Ewan, J R Massey, W. Thomas, Victoria I. Sullivan, S. W. Leonard, A. E. Radford, Samuel B. Jones, Jr., O. M. Freeman, Michael B. Brooks, Almut G. Jones, and Robert L. Lazor. States and Counties: Alabama: Baldwin, Conecuh, and Mobile. Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Escambia, Franklin, Gulf, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, and Washington. Louisiana: St Tammany and Washington. Mississippi: Forrest, Harrison, and Jackson. North Carolina: Columbus and Robeson. South Carolina: Horry.</ref> It is commonly found on sand, loamy sand, sandy peat, sandy clay, and Lynchburg soils (Aeric Paleaquults). It can be found in natural communities such as wiregrass savannas, pine flatwoods, grass-sedge bogs, low hillside seepage bogs with wiregrass and ''Sarracenia'', ''Sphagnum'' ditches, and pine-saw palmetto flatwoods. This species also occurs in disturbed habitat including roadsides, ditches, disturbed pineland, old fields, pine plantations, and clobbered pine fields. Associated species include ''Pinus palutris, Aristida stricta, Sarracenia, Pinus elliottii, Serenoa repens, Helianthus radula, Bigelowia, Liatris, Marshallia, Eupatorium, Diodia virginiana, Euthamia minor, Pteridium aquilnum, Solidago fistulosa,'' and ''Agalinis fasciulata.''<ref name=fsu/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Helianthus heterophyllus'' is an indicator species for the Lower Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).<ref>Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | ===Seed dispersal=== | + | ''H. heterophyllus'' has been observed to flower in January, July, September, October, and December.<ref name=fsu/><ref>Nelson, G. [http://www.gilnelson.com/ PanFlora]: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016</ref> |
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> |
| + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | This species occurs in habitat that is maintained by fire.<ref name=fsu/> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | === | + | This species has been observed to host leafcutting bees such as ''Megachile xylocopoides'' (family Megachilidae).<ref>Discoverlife.org [https://www.discoverlife.org/20/q?search=Bidens+albaDiscoverlife.org|Discoverlife.org]</ref> |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | <!--===Herbivory and toxicology===--> |
| − | ==Conservation and | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
| + | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Latest revision as of 16:40, 30 May 2023
| Helianthus heterophyllus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Helianthus |
| Species: | H. heterophyllus |
| Binomial name | |
| Helianthus heterophyllus Nutt. | |
| |
| Natural range of Helianthus heterophyllus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: variableleaf sunflower; wetland sunflower; savanna sunflower
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
A description of Helianthus heterophyllus is provided in The Flora of North America.
Helianthus heterophyllus is a perennial herbaceous species.
Distribution
This plant is a southeastern Coastal Plain endemic. It occurs from southeastern North Carolina, south to Panhandle Florida, and west to southeastern Louisiana.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
H. heterophyllus tends to grow on moist sandy soils at lower elevations.[2] It is commonly found on sand, loamy sand, sandy peat, sandy clay, and Lynchburg soils (Aeric Paleaquults). It can be found in natural communities such as wiregrass savannas, pine flatwoods, grass-sedge bogs, low hillside seepage bogs with wiregrass and Sarracenia, Sphagnum ditches, and pine-saw palmetto flatwoods. This species also occurs in disturbed habitat including roadsides, ditches, disturbed pineland, old fields, pine plantations, and clobbered pine fields. Associated species include Pinus palutris, Aristida stricta, Sarracenia, Pinus elliottii, Serenoa repens, Helianthus radula, Bigelowia, Liatris, Marshallia, Eupatorium, Diodia virginiana, Euthamia minor, Pteridium aquilnum, Solidago fistulosa, and Agalinis fasciulata.[2]
Helianthus heterophyllus is an indicator species for the Lower Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[3]
Phenology
H. heterophyllus has been observed to flower in January, July, September, October, and December.[2][4]
Fire ecology
This species occurs in habitat that is maintained by fire.[2]
Pollination
This species has been observed to host leafcutting bees such as Megachile xylocopoides (family Megachilidae).[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, Ann F. Johnson, R. Kral, R.K. Godfrey, John Morrill, Jean W. Wooten, Robert A. Norris, Sidney McDaniel, Steve L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, Nancy E. Jordan, Harry E. Ahles, Joseph Ewan, J R Massey, W. Thomas, Victoria I. Sullivan, S. W. Leonard, A. E. Radford, Samuel B. Jones, Jr., O. M. Freeman, Michael B. Brooks, Almut G. Jones, and Robert L. Lazor. States and Counties: Alabama: Baldwin, Conecuh, and Mobile. Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Escambia, Franklin, Gulf, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, and Washington. Louisiana: St Tammany and Washington. Mississippi: Forrest, Harrison, and Jackson. North Carolina: Columbus and Robeson. South Carolina: Horry.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]