Difference between revisions of "Eupatorium perfoliatum"
(→Ecology) |
(→Habitat) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===Habitat=== | ===Habitat=== | ||
''E. perfoliatum'' has been found in pine-sweetgum forests, magnolia-live oak floodplain communities, hardwood swamps, and cabbage palm-slash pine hammocks. It can grow in open to semi-shaded conditions, usually in wet, sandy or loamy soils. | ''E. perfoliatum'' has been found in pine-sweetgum forests, magnolia-live oak floodplain communities, hardwood swamps, and cabbage palm-slash pine hammocks. It can grow in open to semi-shaded conditions, usually in wet, sandy or loamy soils. | ||
| − | ''E. perfoliatum can also occur in areas with soil disturbance | + | ''E. perfoliatum'' can also occur in areas with soil disturbance including roadsides, right-of-ways, clearings, forest edges and areas rooted by hogs.<ref name = fsu> Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2023. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Andre F. Clewell, R. F. Doren, W. R. Fryar, Mark A. Garland, J. P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Gary R. Knight, H. Larry, Robert L. Lazor, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., E. Stripling, Victoria I. Sullivan, and Ginny Vail. States and counties: Florida: Alachua, Citrus, Dixie, Franklin, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Taylor, Union, and Wakulla.</ref> |
Associated species of ''E. perfoliatum'' include ''[[Eupatorium capillifolium]]'' and ''Eupatoruim x pinnatifidum''.<ref name=fsu/> | Associated species of ''E. perfoliatum'' include ''[[Eupatorium capillifolium]]'' and ''Eupatoruim x pinnatifidum''.<ref name=fsu/> | ||
Latest revision as of 14:49, 26 May 2023
| Eupatorium perfoliatum | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Genus: | Eupatorium |
| Species: | E. perfoliatum |
| Binomial name | |
| Eupatorium perfoliatum Linnaeus | |
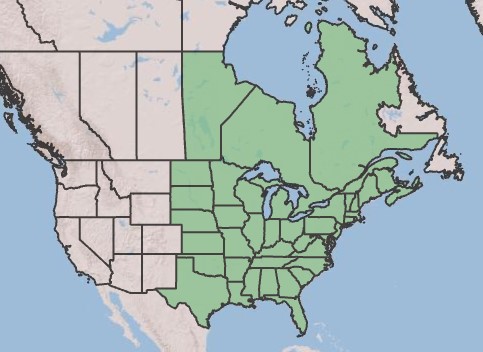
| |
| Natural range of Eupatorium perfoliatum from USDA NRCS [1]. | |
Common name: boneset, common boneset
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: E. perfoliatum var. perfoliatum; E. cuneatum Engelmann (actually a hybrid)[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
E. perfoliatum has been found in pine-sweetgum forests, magnolia-live oak floodplain communities, hardwood swamps, and cabbage palm-slash pine hammocks. It can grow in open to semi-shaded conditions, usually in wet, sandy or loamy soils. E. perfoliatum can also occur in areas with soil disturbance including roadsides, right-of-ways, clearings, forest edges and areas rooted by hogs.[2]
Associated species of E. perfoliatum include Eupatorium capillifolium and Eupatoruim x pinnatifidum.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2023. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Andre F. Clewell, R. F. Doren, W. R. Fryar, Mark A. Garland, J. P. Gillespie, Robert K. Godfrey, Gary R. Knight, H. Larry, Robert L. Lazor, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., E. Stripling, Victoria I. Sullivan, and Ginny Vail. States and counties: Florida: Alachua, Citrus, Dixie, Franklin, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Taylor, Union, and Wakulla.