Difference between revisions of "Eupatorium altissimum"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
(→Distribution) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| − | It is seen as far noth as CT; stretches south to Florida, and to Texas. <ref name= | + | It is seen as far noth as CT; stretches south to Florida, and to Texas.<ref name=weakley/> It is mostly seen in the midwest on limestone substrates, but uncommon east of the mountains.<ref name=weakley/> |
| + | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 14:40, 26 May 2023
| Eupatorium altissimum | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo by Jennifer Anderson, hosted by the USDA-NRCS PLANTS Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Eupatorium |
| Species: | E. altissimum |
| Binomial name | |
| Eupatorium altissimum L. | |
| |
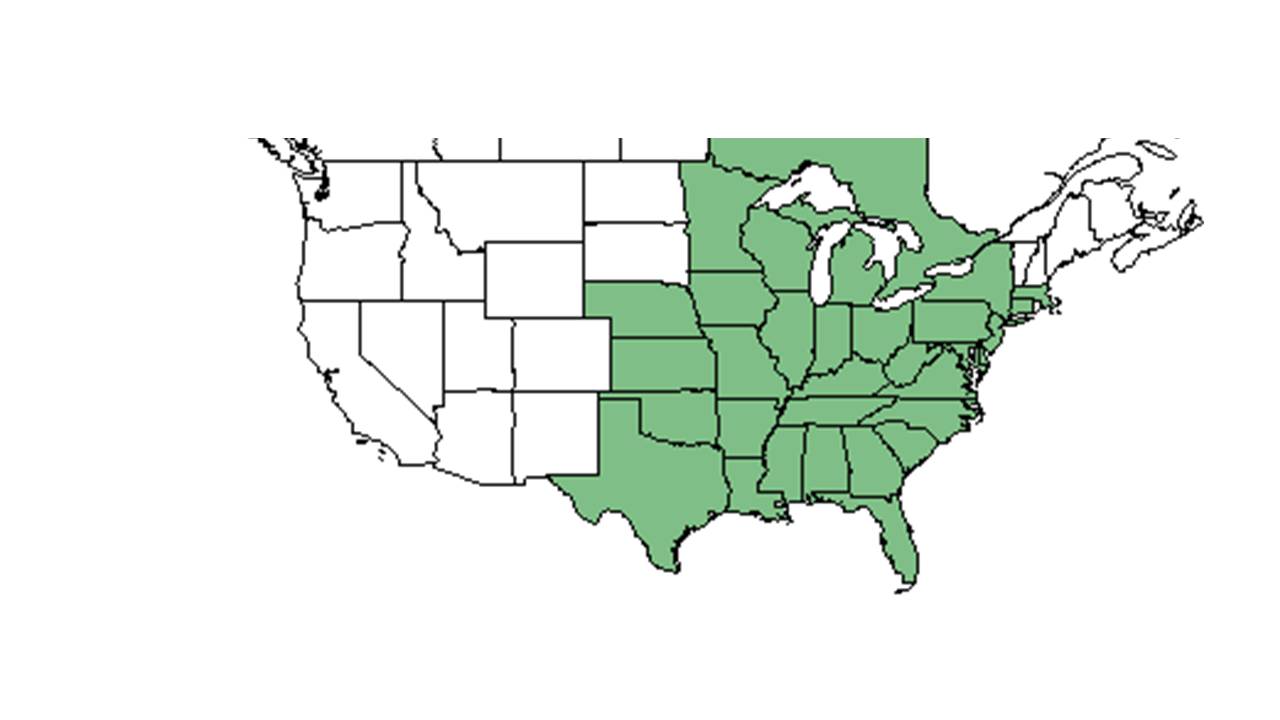
| Natural range of Eupatorium altissimum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: tall thoroughwort
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none.[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
A description of Eupatorium altissimum is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
It is seen as far noth as CT; stretches south to Florida, and to Texas.[1] It is mostly seen in the midwest on limestone substrates, but uncommon east of the mountains.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
It is found in woodlands, old fields, woodland edges, and openings over mafic rocks or calcareous rocks. [2] It is also found in roadside ditches. [3]
Phenology
E. altissimum has been observed flowering in July and September.[4][3] Flowers from August to November according to Weakley (2015).
Pollination
Eupatorium altissimum has been observed to host plasterer bees such as Hylaeus mesillae (family Colletidae).[5]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedWeakley 2015 - ↑ 3.0 3.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: R. Kral. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 9 DEC 2016
- ↑ Discoverlife.org [1]