Difference between revisions of "Carex comosa"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
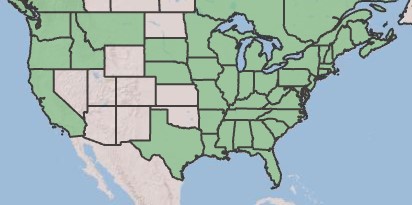
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Carex comosa'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.sc.egov.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CACO8 Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Carex comosa'' from USDA NRCS [https://plants.sc.egov.usda.gov/home/plantProfile?symbol=CACO8 Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: longhair sedge | + | Common name: longhair sedge, bottlebrush sedge, bristly sedge |
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
| − | Synonyms: | + | Synonyms: none<ref name=weakley>Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perennial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perennial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 28: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== | ===Habitat=== | ||
| − | ''C. comosa'' occurs in wet | + | ''C. comosa'' occurs in wet soil or shallow water along lake shores, river banks, swamps, and pond margins. ''C. comosa'' grows in shady conditions in loamy or sandy soil. ''C. comosa'' has been seen distributed in some disturbed areas such as roadsides and ditches.<ref name = fsu> Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2023. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, W Baker, Kurt E. Blum, David A. Breil, D. Burch, Richard Carter, Susanne Cooper, Robert K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, Wayne D. Longbottom, D. L. Martin, Sidney McDaniel, J. C. McKenzie, Gil Nelson, Roger D. Redden, G. Robinson, J. Daniel Saffer, and Richard P. Wunderlin. States and counties: Delaware: Sussex. Florida: Bay, Jefferson, Madison, Marion Leon, Levy, Pasco, Taylor, Wabash, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Tarboro. South Carolina: Claredon.</ref> |
| − | Species associated with ''C. comosa'' include ''Juncus gymnocarpus'', ''Nelumbo nucifera'', ''[[Fraxinus caroliniana]]'', ''[[Burmannia biflora]]'', ''Uticularia'' sp., ''Cephelathus occidentalis'', ''[[Acer rubrum]]'', ''Myrica cerifera'', ''Scirpus cyperinus'', ''salix'' sp., ''Taxodium ascendens'', and ''Panicum hemitomum''. | + | Species associated with ''C. comosa'' include ''Juncus gymnocarpus'', ''Nelumbo nucifera'', ''[[Fraxinus caroliniana]]'', ''[[Burmannia biflora]]'', ''Uticularia'' sp., ''Cephelathus occidentalis'', ''[[Acer rubrum]]'', ''Myrica cerifera'', ''Scirpus cyperinus'', ''salix'' sp., ''Taxodium ascendens'', and ''Panicum hemitomum''.<ref name=fsu/> |
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:08, 22 May 2023
| Carex comosa | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Carex |
| Species: | C. comosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Carex comosa Boott | |
| |
| Natural range of Carex comosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: longhair sedge, bottlebrush sedge, bristly sedge
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
C. comosa occurs in wet soil or shallow water along lake shores, river banks, swamps, and pond margins. C. comosa grows in shady conditions in loamy or sandy soil. C. comosa has been seen distributed in some disturbed areas such as roadsides and ditches.[2]
Species associated with C. comosa include Juncus gymnocarpus, Nelumbo nucifera, Fraxinus caroliniana, Burmannia biflora, Uticularia sp., Cephelathus occidentalis, Acer rubrum, Myrica cerifera, Scirpus cyperinus, salix sp., Taxodium ascendens, and Panicum hemitomum.[2]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2023. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, W Baker, Kurt E. Blum, David A. Breil, D. Burch, Richard Carter, Susanne Cooper, Robert K. Godfrey, Bruce Hansen, Wayne D. Longbottom, D. L. Martin, Sidney McDaniel, J. C. McKenzie, Gil Nelson, Roger D. Redden, G. Robinson, J. Daniel Saffer, and Richard P. Wunderlin. States and counties: Delaware: Sussex. Florida: Bay, Jefferson, Madison, Marion Leon, Levy, Pasco, Taylor, Wabash, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Tarboro. South Carolina: Claredon.