Difference between revisions of "Amphicarpum muehlenbergianum"
HaleighJoM (talk | contribs) |
ParkerRoth (talk | contribs) (→Description) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perennial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perennial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | According to Diaz-Torbio and Putz (2021), ''Amphicarpum muehlenbergianum'' has fibrous roots with a below-ground to above-ground biomass ratio of 2.31 and nonstructural carbohydrate concentration of 58.2 mg g<sup>-1</sup>.<ref>Diaz-Torbio, M. H. and F. E Putz. 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American journal of Botany 108(3):432-442.</ref> | ||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Latest revision as of 10:42, 2 July 2024
| Amphicarpum muehlenbergianum | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae / Gramineae |
| Genus: | Amphicarpum |
| Species: | A. muehlenbergianum |
| Binomial name | |
| Amphicarpum muehlenbergianum (J.A. Schultes) A.S. Hitchcock | |
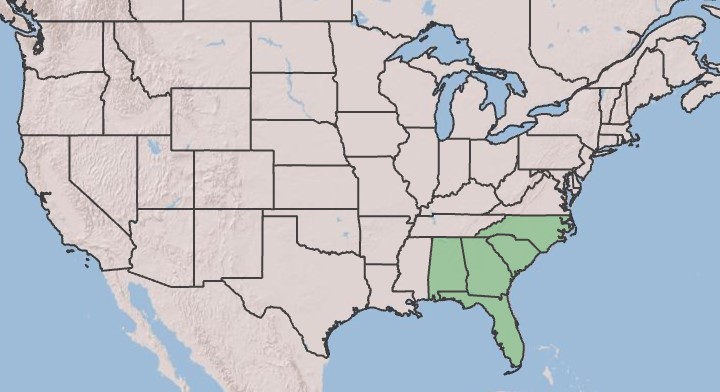
| |
| Natural range of Amphicarpum muehlenbergianum from USDA NRCS [1]. | |
Common name: Muhlenberg maidencane, Florida peanut-grass, blue maiden-cane
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms:
Description
According to Diaz-Torbio and Putz (2021), Amphicarpum muehlenbergianum has fibrous roots with a below-ground to above-ground biomass ratio of 2.31 and nonstructural carbohydrate concentration of 58.2 mg g-1.[1]
Distribution
Ecology
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Diaz-Torbio, M. H. and F. E Putz. 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American journal of Botany 108(3):432-442.